Common Laparoscopic Procedures: A Comprehensive Guide
Laparoscopic surgery, often referred to as minimally invasive surgery or keyhole surgery, has revolutionized the field of surgery in recent decades. This innovative technique offers numerous advantages over traditional open surgery, including smaller incisions, reduced pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the most common laparoscopic procedures, their benefits, and what patients can expect during and after surgery.
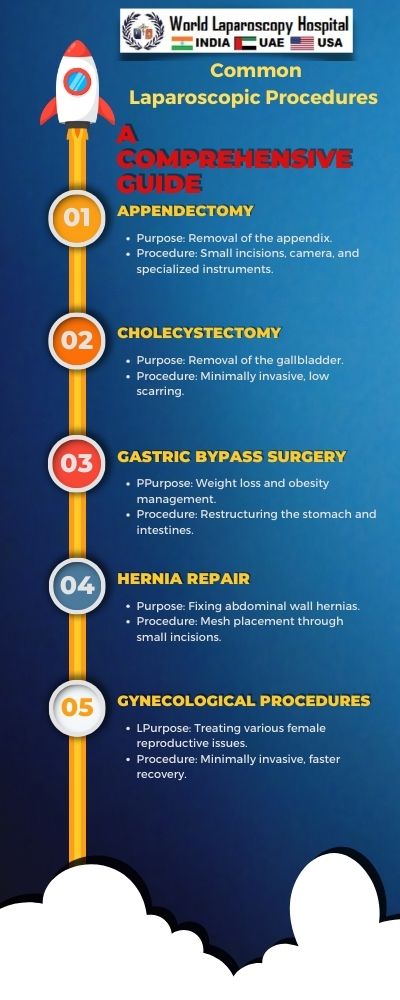
Introduction to Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery involves making small incisions (usually less than half an inch in length) through which a laparoscope and other specialized instruments are inserted. The laparoscope is equipped with a camera that provides a high-definition view of the surgical site, which is projected onto a monitor for the surgeon to see. This minimally invasive approach allows surgeons to perform a wide range of procedures with precision and minimal disruption to the patient's body.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery
Before delving into specific laparoscopic procedures, it's essential to understand the numerous benefits associated with this approach:
-
Smaller Incisions: Laparoscopic surgery typically involves tiny incisions, reducing scarring and the risk of infection.
-
Less Pain: Patients often experience less pain after laparoscopic procedures compared to open surgery.
-
Shorter Hospital Stays: Many laparoscopic surgeries are performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home the same day.
-
Faster Recovery: Patients can usually resume normal activities more quickly following laparoscopic surgery.
-
Reduced Blood Loss: Minimized bleeding is a significant advantage of laparoscopic procedures.
-
Lower Risk of Complications: Laparoscopy is associated with a lower risk of wound complications and hernias.
Common Laparoscopic Procedures
Now, let's explore some of the most common laparoscopic procedures and the conditions they address:
A. Cholecystectomy (Gallbladder Removal)
-
Indications: Gallstones, gallbladder inflammation (cholecystitis)
-
Procedure: The surgeon removes the gallbladder through small incisions, typically using four ports.
-
Benefits: Minimal scarring, reduced postoperative pain, and a shorter recovery period.
B. Appendectomy (Appendix Removal)
-
Indications: Acute appendicitis
-
Procedure: The inflamed appendix is removed using laparoscopic instruments.
-
Benefits: Faster recovery, reduced risk of wound infection.
C. Hernia Repair (Inguinal, Ventral, or Hiatal Hernia)
-
Indications: Hernias in the groin (inguinal), abdomen (ventral), or diaphragm (hiatal)
-
Procedure: The surgeon repairs the hernia by reinforcing the weakened area with mesh.
-
Benefits: Smaller incisions, less pain, and quicker return to regular activities.
D. Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
-
Indications: Removal of the uterus (often for conditions like fibroids or endometriosis)
-
Procedure: The uterus is removed through small abdominal incisions, either partially or completely.
-
Benefits: Reduced scarring and shorter hospital stay compared to traditional hysterectomy.
E. Laparoscopic Colon Resection
-
Indications: Treatment of colorectal conditions like diverticulitis or colon cancer
-
Procedure: The affected part of the colon is removed, and the healthy ends are reconnected.
-
Benefits: Faster recovery, fewer complications, and a shorter hospital stay.
F. Laparoscopic Nissen Fundoplication (Anti-Reflux Surgery)
-
Indications: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
-
Procedure: The top of the stomach is wrapped around the lower esophagus to prevent acid reflux.
-
Benefits: Relief from heartburn and GERD symptoms without the need for open surgery.
What to Expect During a Laparoscopic Procedure
Patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery can expect the following:
-
Anesthesia: General anesthesia is administered to ensure the patient remains asleep during the procedure.
-
Incisions: Small incisions are made in strategic locations to access the surgical site.
-
Carbon Dioxide Gas: Carbon dioxide gas is introduced into the abdomen to create a working space for the surgeon.
-
Insertion of Instruments: Specialized instruments and the laparoscope are inserted through the incisions.
-
Surgical Manipulation: The surgeon performs the necessary procedure while watching a live video feed from the laparoscope.
-
Closing Incisions: At the end of the procedure, the incisions are closed with sutures or surgical tape.
Recovery After Laparoscopic Surgery
Recovery after laparoscopic surgery varies depending on the specific procedure and individual factors. However, there are some general guidelines:
-
Hospital Stay: Many laparoscopic procedures are performed as outpatient surgeries, meaning you can return home the same day. For others, a short hospital stay of 1-2 days may be necessary.
-
Pain Management: Pain is typically minimal and can be managed with over-the-counter or prescription medications.
-
Diet: You may need to follow a special diet for a few days or weeks, depending on the surgery. Your surgeon will provide dietary instructions.
-
Physical Activity: Gradually increase physical activity as advised by your surgeon. You'll be encouraged to walk and do light activities to promote healing.
-
Follow-up: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your surgeon to monitor your progress and address any concerns.
Potential Risks and Complications
While laparoscopic surgery is generally safe, it's essential to be aware of potential risks and complications, which can include:
-
Infection: Although the risk is low, infections can occur at the incision sites.
-
Bleeding: Excessive bleeding during surgery may require open conversion.
-
Organ Injury: There is a slight risk of accidental injury to nearby organs.
-
Anesthesia Complications: Allergic reactions or adverse effects to anesthesia are possible.
-
Blood Clots: Prolonged immobility can increase the risk of blood clots.
Conclusion
In conclusion, laparoscopic surgery has transformed the world of surgical interventions by offering patients less invasive alternatives with shorter recovery times and reduced discomfort. Common laparoscopic procedures like cholecystectomy, appendectomy, hernia repair, hysterectomy, colon resection, and anti-reflux surgery have become routine in many hospitals.
If you're considering laparoscopic surgery, consult with your surgeon to determine if it's the right option for your condition. With careful preparation, skilled surgeons, and modern technology, laparoscopic procedures continue to improve the quality of care for patients worldwide, making surgery a less daunting experience.
| Older Post | Home | Newer Post |

