Postoperative glaucoma: Increased intraocular pressure that can occur after ocular surgery.
Introduction
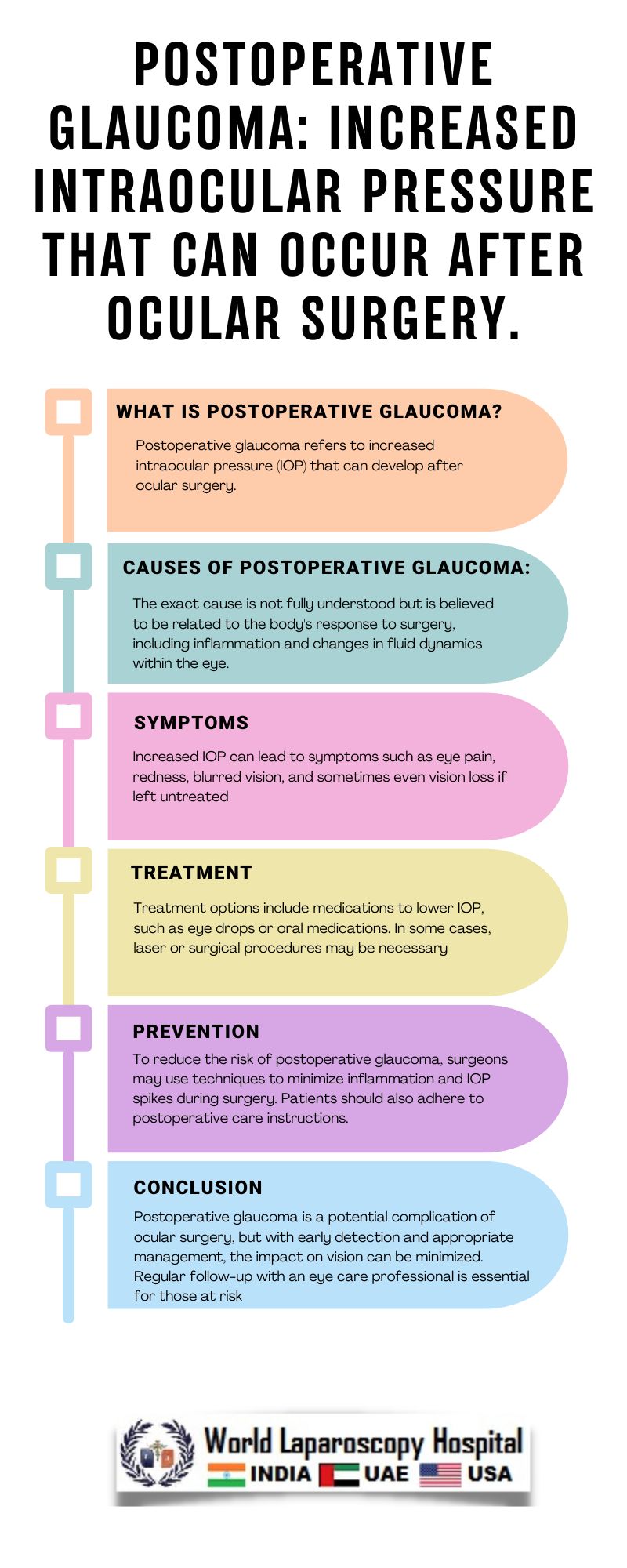
Glaucoma is a complex, progressive eye disease characterized by damage to the optic nerve, often leading to irreversible vision loss. While glaucoma can develop due to various factors, including genetics and aging, one lesser-known aspect is postoperative glaucoma. This condition can occur after ocular surgery, presenting a unique set of challenges for both patients and healthcare providers.
Understanding Postoperative Glaucoma
Postoperative glaucoma refers to a transient or persistent increase in intraocular pressure (IOP) following ocular surgery. This condition can manifest in various forms, including acute angle-closure glaucoma, open-angle glaucoma, or secondary glaucoma. The exact mechanisms underlying postoperative glaucoma are not fully understood but are believed to involve several factors, including:
Inflammation:
Ocular surgery can trigger an inflammatory response, leading to the release of cytokines and other inflammatory mediators. This can disrupt the normal aqueous humor outflow pathways, leading to an increase in IOP.
Steroid Response:
The use of topical or systemic steroids postoperatively is common to reduce inflammation. However, some individuals may be steroid responders, experiencing an increase in IOP in response to steroids.
Pupillary Block:
In certain cases, especially after cataract surgery, the intraocular lens (IOL) may cause pupillary block, leading to an increase in IOP.
Trabecular Meshwork Dysfunction:
Ocular surgery can damage the trabecular meshwork, the primary site of aqueous humor outflow, leading to impaired drainage and increased IOP.
Risk Factors for Postoperative Glaucoma
Several factors can increase the risk of developing postoperative glaucoma, including:
Preexisting Glaucoma:
Patients with preexisting glaucoma are at a higher risk of developing postoperative glaucoma, especially if their IOP is not well-controlled preoperatively.
Age:
Older individuals may be more susceptible to postoperative IOP spikes due to age-related changes in the eye's anatomy and physiology.
Race:
Certain racial groups, such as African Americans, may have a higher predisposition to developing postoperative glaucoma.
Type of Surgery:
Some types of ocular surgery, such as trabeculectomy or cataract surgery, carry a higher risk of postoperative IOP elevation.
Steroid Response:
Individuals who are steroid responders may experience a more significant increase in IOP postoperatively.
Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis
The clinical presentation of postoperative glaucoma can vary depending on the underlying mechanism and severity of the condition. Patients may experience symptoms such as eye pain, redness, blurred vision, halos around lights, and headaches. However, in many cases, postoperative glaucoma is asymptomatic and detected during routine follow-up visits.
Diagnosis of postoperative glaucoma typically involves measuring IOP using tonometry and assessing the optic nerve and visual field for signs of damage. Gonioscopy may also be performed to evaluate the angle structures and rule out angle-closure mechanisms.
Management of Postoperative Glaucoma
The management of postoperative glaucoma involves a multi-faceted approach aimed at lowering IOP and preserving vision. Treatment options may include:
Topical Medications:
Eye drops such as beta-blockers, prostaglandin analogs, and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors may be prescribed to lower IOP.
Oral Medications:
In some cases, oral medications may be used to control IOP, especially in patients who are unable to use or tolerate topical medications.
Laser Therapy:
Laser trabeculoplasty or iridotomy may be performed to improve aqueous humor outflow and reduce IOP.
Surgical Interventions:
In cases of refractory postoperative glaucoma, surgical procedures such as trabeculectomy, tube shunt implantation, or minimally invasive glaucoma surgeries (MIGS) may be considered to lower IOP.
Close Monitoring:
Regular follow-up visits with an ophthalmologist are essential to monitor IOP, optic nerve health, and visual function.
Prevention Strategies
While not all cases of postoperative glaucoma can be prevented, certain strategies may help reduce the risk, including:
Preoperative Assessment:
Thorough preoperative evaluation, including IOP measurement and assessment of optic nerve health, can help identify high-risk patients.
Intraoperative Care:
Gentle surgical techniques and minimizing trauma to ocular tissues during surgery can help reduce postoperative inflammation and IOP spikes.
Postoperative Monitoring:
Close postoperative monitoring of IOP and optic nerve health is crucial to detect and manage postoperative glaucoma early.
Individualized Treatment:
Tailoring treatment to each patient's specific needs and risk factors can help optimize outcomes and minimize complications.
Conclusion
Postoperative glaucoma is a challenging complication that can occur following ocular surgery. While the exact mechanisms are not fully understood, several factors, including inflammation, steroid response, and trabecular meshwork dysfunction, are believed to contribute to its development. Early detection and management are crucial to prevent vision loss and preserve ocular health. By understanding the risk factors, mechanisms, and management strategies associated with postoperative glaucoma, ophthalmologists can provide optimal care for their patients undergoing ocular surgery.
| Older Post | Home | Newer Post |





