Surgical Efficiency: Operation Times in Laparoscopic vs. Robotic Procedures
Introduction
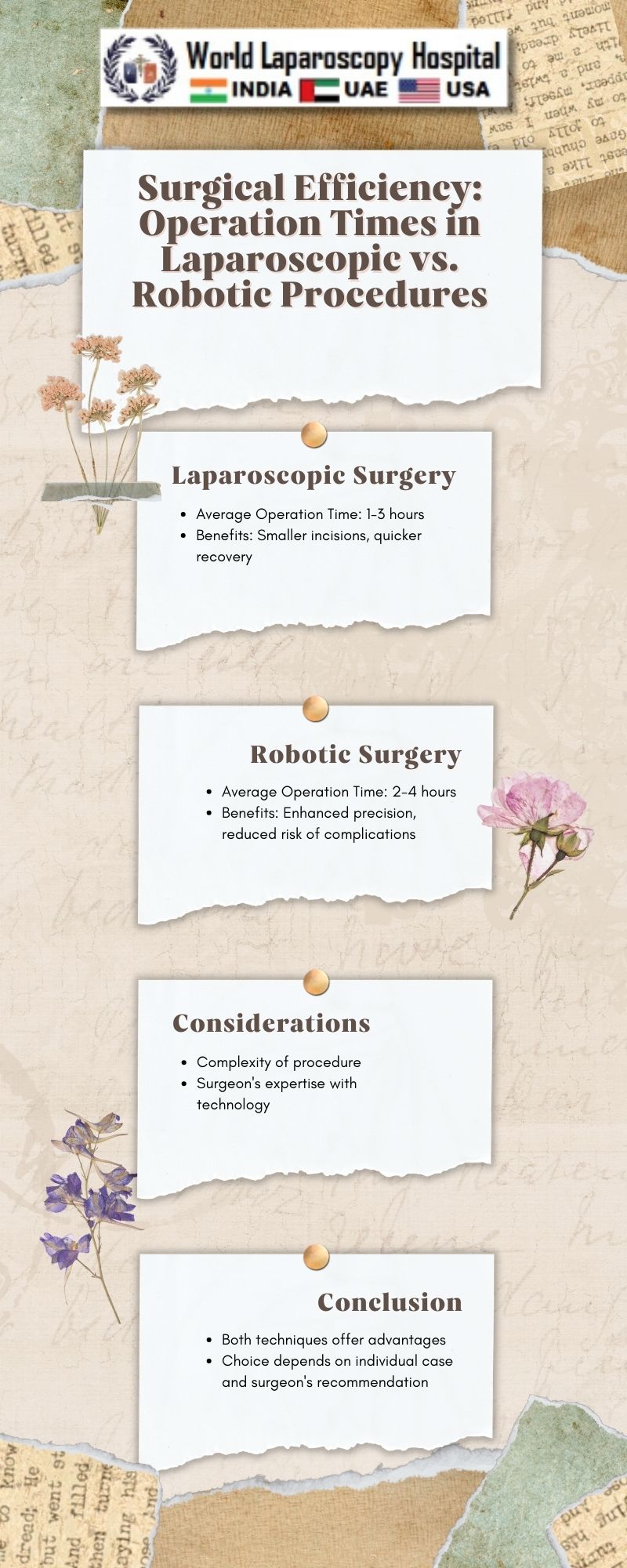
Surgical procedures have evolved significantly over the years, with advancements in technology playing a crucial role in enhancing patient outcomes and surgical efficiency. Laparoscopic and robotic-assisted surgeries are two such advancements that have revolutionized the field of surgery. These minimally invasive techniques offer several advantages over traditional open surgeries, including reduced blood loss, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times. One key aspect of surgical efficiency is the operation time, which refers to the duration of the surgical procedure from incision to closure. This article aims to explore and compare operation times in laparoscopic and robotic procedures, highlighting the factors that influence these times and their implications for patient care.
Laparoscopic Surgery: A Brief Overview
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery, involves making small incisions in the abdomen through which a laparoscope and other surgical instruments are inserted. The laparoscope is a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light source that allows the surgeon to see inside the abdomen and perform the surgery. Laparoscopic procedures have become increasingly common for a variety of surgeries, including cholecystectomy, appendectomy, and hysterectomy, among others.
Robotic Surgery: An Introduction
Robotic surgery is a form of minimally invasive surgery that utilizes robotic systems to assist surgeons in performing complex surgical procedures with enhanced precision and control. The da Vinci Surgical System is one of the most widely used robotic systems in surgery. It consists of robotic arms controlled by the surgeon, which hold surgical instruments and a camera. The surgeon sits at a console, where they view a 3D image of the surgical site and manipulate the instruments using hand and foot controls.
Comparing Operation Times: Laparoscopic vs. Robotic Procedures
Operation times in laparoscopic and robotic procedures can vary depending on several factors, including the complexity of the surgery, the surgeon's experience, and the patient's condition. Generally, robotic procedures tend to have longer operation times compared to laparoscopic procedures. This is partly due to the setup time required for the robotic system and the learning curve associated with using the system.
Factors Influencing Operation Times
Several factors can influence operation times in both laparoscopic and robotic procedures. These include:
-
Surgical Complexity: Complex surgeries are likely to take longer to perform, regardless of the surgical approach used. Robotic surgery may offer advantages in complex cases due to its enhanced precision and dexterity.
-
Surgeon Experience: Surgeons who are more experienced with a particular technique are likely to perform the procedure more efficiently, leading to shorter operation times.
-
Patient Factors: The patient's anatomy, overall health, and any complications that arise during surgery can also impact operation times.
-
Equipment Setup: Robotic surgery requires the setup of the robotic system, which can add to the overall operation time compared to laparoscopic surgery.
-
Learning Curve: Surgeons who are new to robotic surgery may take longer to perform procedures initially as they familiarize themselves with the system.
Implications for Patient Care
Operation times play a crucial role in patient care, as shorter operation times are generally associated with reduced risk of complications, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times. However, it is important to note that the focus should not solely be on reducing operation times, but also on ensuring that the procedure is performed safely and effectively.
Future Directions
As technology continues to advance, the field of minimally invasive surgery is likely to see further improvements in operation times and patient outcomes. Future research may focus on optimizing surgical techniques, enhancing robotic systems, and further reducing the learning curve associated with robotic surgery.
Conclusion
In conclusion, operation times in laparoscopic and robotic procedures are influenced by various factors, including surgical complexity, surgeon experience, and patient factors. While robotic procedures tend to have longer operation times compared to laparoscopic procedures, they offer several advantages in terms of precision and control. As technology continues to advance, further improvements in operation times and patient outcomes can be expected in the field of minimally invasive surgery.
The comparison between laparoscopic and robotic procedures underscores the nuanced interplay of surgical complexity, surgeon experience, and technological advancements. While robotic procedures may entail longer operation times initially due to setup and learning curve, they offer unparalleled precision and control, particularly in complex surgeries.
The article's emphasis on patient factors and implications for patient care resonates deeply within the medical community, highlighting the paramount importance of optimizing surgical techniques to ensure safe and effective outcomes.
As the field continues to evolve, this insightful exploration serves as a guiding beacon, illuminating the path toward enhanced surgical efficiency and improved patient care.
Laparoscopic surgery, characterized by its minimally invasive approach, offers swift operation times facilitated by streamlined procedures and precise instrumentation. Surgeons adept in laparoscopic techniques navigate intricate surgeries with efficiency, ensuring optimal outcomes and swift patient recovery.
Conversely, robotic surgery, while heralding unparalleled precision and control, often entails longer operation times attributed to setup requirements and the learning curve associated with robotic systems. Despite this, the benefits of enhanced precision and reduced tissue trauma afforded by robotic assistance underscore its invaluable contribution to modern surgical practice.
| Older Post | Home | Newer Post |


