Pediatric Laparoscopy: Special Considerations and Techniques
"Pediatric Laparoscopy: Special Considerations and Techniques" is a comprehensive topic that encompasses various aspects of minimally invasive surgery in children. This article aims to discuss the unique considerations, techniques, and advancements in pediatric laparoscopy, providing insights into its application, benefits, and challenges.
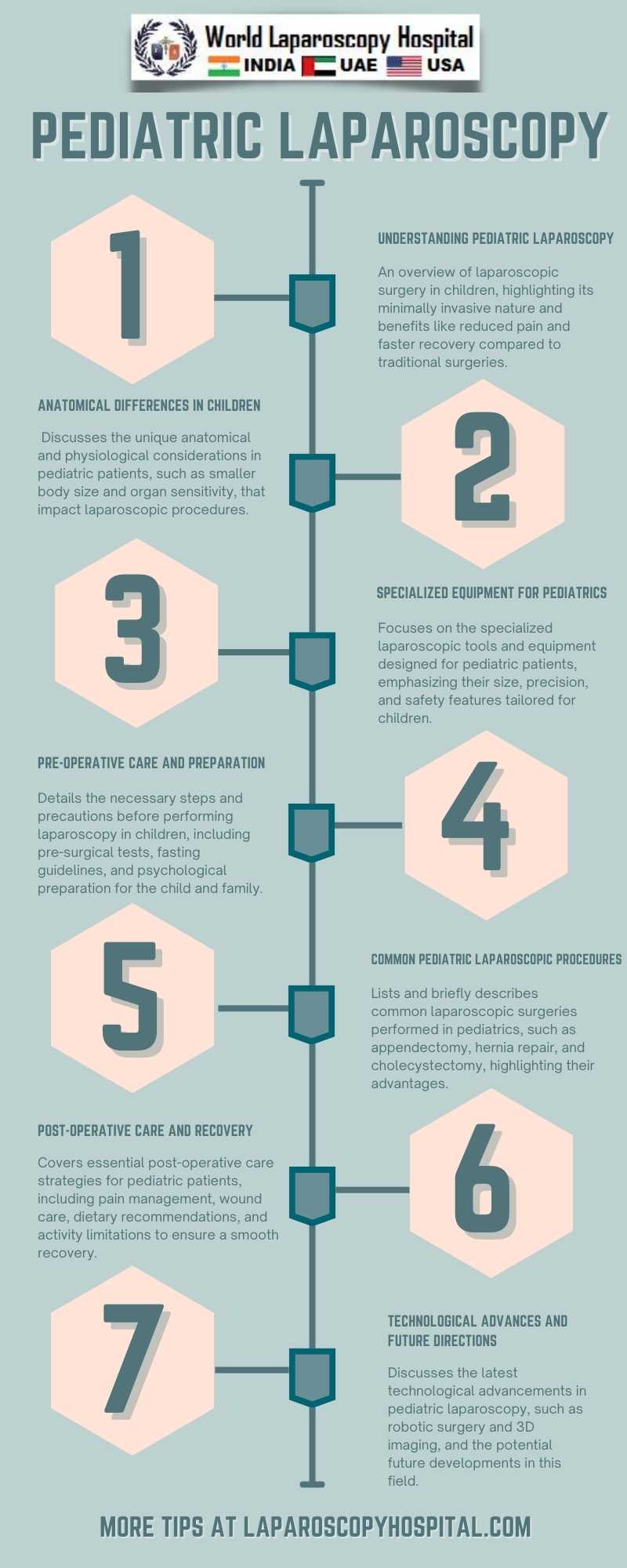
Introduction to Pediatric Laparoscopy
Pediatric laparoscopy refers to a minimally invasive surgical technique used to perform operations within the abdomen or pelvis of children. It involves making small incisions and using specialized instruments, including a laparoscope – a thin tube with a camera and light at the end. This approach offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, such as reduced pain, faster recovery, minimal scarring, and shorter hospital stays.
Anatomical and Physiological Considerations
Children, especially infants and neonates, present unique anatomical and physiological challenges that impact laparoscopic procedures. Their small body size, limited abdominal space, and sensitive organs require precise and delicate handling. Additionally, children have different metabolic and physiological responses to surgery, necessitating tailored anesthetic and postoperative care.
Instrumentation and Equipment
Pediatric laparoscopy demands specialized instruments due to the smaller size and delicate nature of pediatric patients. These instruments are typically smaller in diameter and length. The choice of equipment, including trocars, scissors, graspers, and energy devices, must be appropriate for the child's size and the specific procedure.
Surgical Techniques and Procedures
Common pediatric laparoscopic procedures include appendectomy, cholecystectomy, fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux, and hernia repairs. Advanced procedures like splenectomy, nephrectomy, and thoracoscopy are also increasingly being performed laparoscopically in children. Each procedure requires specific techniques adapted to pediatric anatomy.
Anesthetic Considerations
Anesthesia in pediatric laparoscopy must consider the patient's age, weight, and medical condition. Special attention is given to ventilation and the management of pneumoperitoneum – the insufflation of gas into the abdominal cavity, which can affect cardiovascular and pulmonary function in children.
Training and Skill Development
Surgeons performing pediatric laparoscopy require specialized training and skills. This includes proficiency in handling delicate tissues, understanding pediatric surgical anatomy, and mastering advanced laparoscopic techniques. Simulation-based training and continued education are critical for maintaining these skills.
Challenges and Complications
While pediatric laparoscopy is generally safe, it does pose specific challenges and potential complications, such as intraoperative injuries, postoperative infections, and anesthesia-related risks. Surgeons must be adept at recognizing and managing these complications promptly.
Technological Advancements
Recent advancements in technology, such as robotic-assisted laparoscopy, have further revolutionized pediatric minimally invasive surgery. These technologies offer enhanced precision, dexterity, and visualization, potentially reducing operative times and improving outcomes.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
Pediatric surgery, including laparoscopy, often involves ethical and legal considerations. Informed consent, respecting the autonomy of older children, and considering the best interests of the patient are paramount in pediatric surgical care.
Conclusion
Pediatric laparoscopy has significantly evolved, offering effective, safe, and minimally invasive alternatives to traditional open surgeries in children. As technology advances and surgeons’ expertise grows, the scope of pediatric laparoscopy continues to expand, promising better outcomes for young patients. However, the unique challenges of operating on children necessitate ongoing research, training, and adherence to high standards of surgical care.

Introduction to Pediatric Laparoscopy
Pediatric laparoscopy refers to a minimally invasive surgical technique used to perform operations within the abdomen or pelvis of children. It involves making small incisions and using specialized instruments, including a laparoscope – a thin tube with a camera and light at the end. This approach offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, such as reduced pain, faster recovery, minimal scarring, and shorter hospital stays.
Anatomical and Physiological Considerations
Children, especially infants and neonates, present unique anatomical and physiological challenges that impact laparoscopic procedures. Their small body size, limited abdominal space, and sensitive organs require precise and delicate handling. Additionally, children have different metabolic and physiological responses to surgery, necessitating tailored anesthetic and postoperative care.
Instrumentation and Equipment
Pediatric laparoscopy demands specialized instruments due to the smaller size and delicate nature of pediatric patients. These instruments are typically smaller in diameter and length. The choice of equipment, including trocars, scissors, graspers, and energy devices, must be appropriate for the child's size and the specific procedure.
Surgical Techniques and Procedures
Common pediatric laparoscopic procedures include appendectomy, cholecystectomy, fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux, and hernia repairs. Advanced procedures like splenectomy, nephrectomy, and thoracoscopy are also increasingly being performed laparoscopically in children. Each procedure requires specific techniques adapted to pediatric anatomy.
Anesthetic Considerations
Anesthesia in pediatric laparoscopy must consider the patient's age, weight, and medical condition. Special attention is given to ventilation and the management of pneumoperitoneum – the insufflation of gas into the abdominal cavity, which can affect cardiovascular and pulmonary function in children.
Training and Skill Development
Surgeons performing pediatric laparoscopy require specialized training and skills. This includes proficiency in handling delicate tissues, understanding pediatric surgical anatomy, and mastering advanced laparoscopic techniques. Simulation-based training and continued education are critical for maintaining these skills.
Challenges and Complications
While pediatric laparoscopy is generally safe, it does pose specific challenges and potential complications, such as intraoperative injuries, postoperative infections, and anesthesia-related risks. Surgeons must be adept at recognizing and managing these complications promptly.
Technological Advancements
Recent advancements in technology, such as robotic-assisted laparoscopy, have further revolutionized pediatric minimally invasive surgery. These technologies offer enhanced precision, dexterity, and visualization, potentially reducing operative times and improving outcomes.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
Pediatric surgery, including laparoscopy, often involves ethical and legal considerations. Informed consent, respecting the autonomy of older children, and considering the best interests of the patient are paramount in pediatric surgical care.
Conclusion
Pediatric laparoscopy has significantly evolved, offering effective, safe, and minimally invasive alternatives to traditional open surgeries in children. As technology advances and surgeons’ expertise grows, the scope of pediatric laparoscopy continues to expand, promising better outcomes for young patients. However, the unique challenges of operating on children necessitate ongoing research, training, and adherence to high standards of surgical care.
1 COMMENTS
Dr. Raj Bansal
#1
Jan 4th, 2024 7:20 am
Pediatric laparoscopy has evolved, providing safe, effective, and minimally invasive alternatives for children. Technological advancements and surgeon expertise expand its scope, promising better outcomes. Addressing unique challenges requires ongoing research, training, and adherence to high surgical standards.
| Older Post | Home | Newer Post |

