Laparoscopic Appendicovesicostomy: Mastering the Mitrofanoff Procedure
Laparoscopic Appendicovesicostomy, commonly known as the Mitrofanoff Procedure, has emerged as a pivotal technique in urological surgery. This innovative approach has revolutionized the way surgeons address complex bladder issues, particularly in patients who require an alternative means for urinary catheterization.
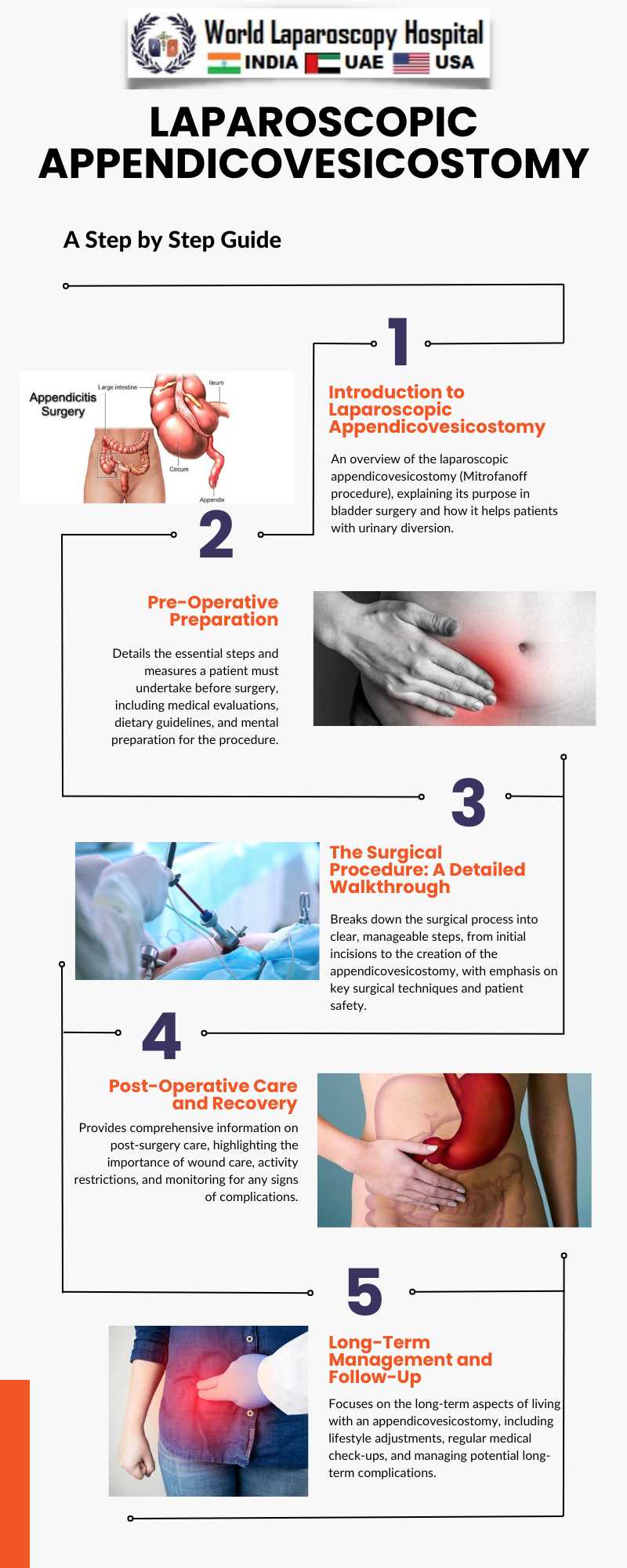
Origins and Evolution
Named after Paul Mitrofanoff, the procedure was first conceptualized in 1980. The technique originally involved creating a conduit between the bladder and the skin using the appendix. The evolution of this procedure has been significant, particularly with the advent of laparoscopic techniques. Laparoscopic Appendicovesicostomy has made this procedure less invasive, reducing recovery time and improving cosmetic outcomes.
Indications and Benefits
This procedure is primarily indicated for patients who cannot perform normal catheterization due to various conditions like spinal cord injuries, congenital anomalies, or severe urethral trauma. The benefits of the laparoscopic approach include smaller incisions, less postoperative pain, and a lower risk of infection. Furthermore, it offers patients a more discreet and convenient way to perform self-catheterization.
The Laparoscopic Technique
The laparoscopic Mitrofanoff procedure involves the isolation of the appendix, which is then detubularized and reconfigured to create a channel. This channel is then connected to the bladder and an opening on the abdominal wall. The laparoscopic approach demands high precision and skill, requiring surgeons to have advanced training in minimally invasive techniques.
Preoperative and Postoperative Care
Preoperative care includes thorough patient evaluation and counseling. Postoperative care is crucial for the success of the procedure. Patients are taught how to perform clean intermittent catheterization and are closely monitored for complications such as stenosis of the stoma or issues with continence.
Challenges and Considerations
One of the challenges of this procedure is ensuring the viability of the appendix and the adequacy of the bladder for a successful outcome. Patient selection is crucial, and the procedure might not be suitable for all patients. Also, surgeons must be prepared to manage complications, which, although rare, can include problems with the stoma or the conduit.
Future Perspectives
With advancements in laparoscopic technologies and techniques, the future of Laparoscopic Appendicovesicostomy looks promising. Innovations like robotic assistance could further refine the procedure, offering even greater precision and better outcomes. Research into alternative conduits for patients without a suitable appendix is also ongoing, expanding the potential applicability of this technique.
Conclusion:
Laparoscopic Appendicovesicostomy represents a significant advancement in urological surgery. Its minimally invasive nature, combined with the autonomy it provides to patients, makes it a valuable technique. As technology and surgical skills continue to advance, this procedure will likely become more prevalent, offering hope and improved quality of life to many patients facing complex urinary challenges.
Origins and Evolution
Named after Paul Mitrofanoff, the procedure was first conceptualized in 1980. The technique originally involved creating a conduit between the bladder and the skin using the appendix. The evolution of this procedure has been significant, particularly with the advent of laparoscopic techniques. Laparoscopic Appendicovesicostomy has made this procedure less invasive, reducing recovery time and improving cosmetic outcomes.
Indications and Benefits
This procedure is primarily indicated for patients who cannot perform normal catheterization due to various conditions like spinal cord injuries, congenital anomalies, or severe urethral trauma. The benefits of the laparoscopic approach include smaller incisions, less postoperative pain, and a lower risk of infection. Furthermore, it offers patients a more discreet and convenient way to perform self-catheterization.
The Laparoscopic Technique
The laparoscopic Mitrofanoff procedure involves the isolation of the appendix, which is then detubularized and reconfigured to create a channel. This channel is then connected to the bladder and an opening on the abdominal wall. The laparoscopic approach demands high precision and skill, requiring surgeons to have advanced training in minimally invasive techniques.
Preoperative and Postoperative Care
Preoperative care includes thorough patient evaluation and counseling. Postoperative care is crucial for the success of the procedure. Patients are taught how to perform clean intermittent catheterization and are closely monitored for complications such as stenosis of the stoma or issues with continence.
Challenges and Considerations
One of the challenges of this procedure is ensuring the viability of the appendix and the adequacy of the bladder for a successful outcome. Patient selection is crucial, and the procedure might not be suitable for all patients. Also, surgeons must be prepared to manage complications, which, although rare, can include problems with the stoma or the conduit.
Future Perspectives
With advancements in laparoscopic technologies and techniques, the future of Laparoscopic Appendicovesicostomy looks promising. Innovations like robotic assistance could further refine the procedure, offering even greater precision and better outcomes. Research into alternative conduits for patients without a suitable appendix is also ongoing, expanding the potential applicability of this technique.
Conclusion:
Laparoscopic Appendicovesicostomy represents a significant advancement in urological surgery. Its minimally invasive nature, combined with the autonomy it provides to patients, makes it a valuable technique. As technology and surgical skills continue to advance, this procedure will likely become more prevalent, offering hope and improved quality of life to many patients facing complex urinary challenges.
No comments posted...
| Older Post | Home | Newer Post |

