Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Post-Surgery or Trauma Lung Complication
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a severe lung condition that can occur as a complication following surgery or trauma. It is a life-threatening condition characterized by rapidly progressive respiratory failure, often requiring mechanical ventilation and intensive care. ARDS can significantly impact patient outcomes and is a major challenge for healthcare providers.
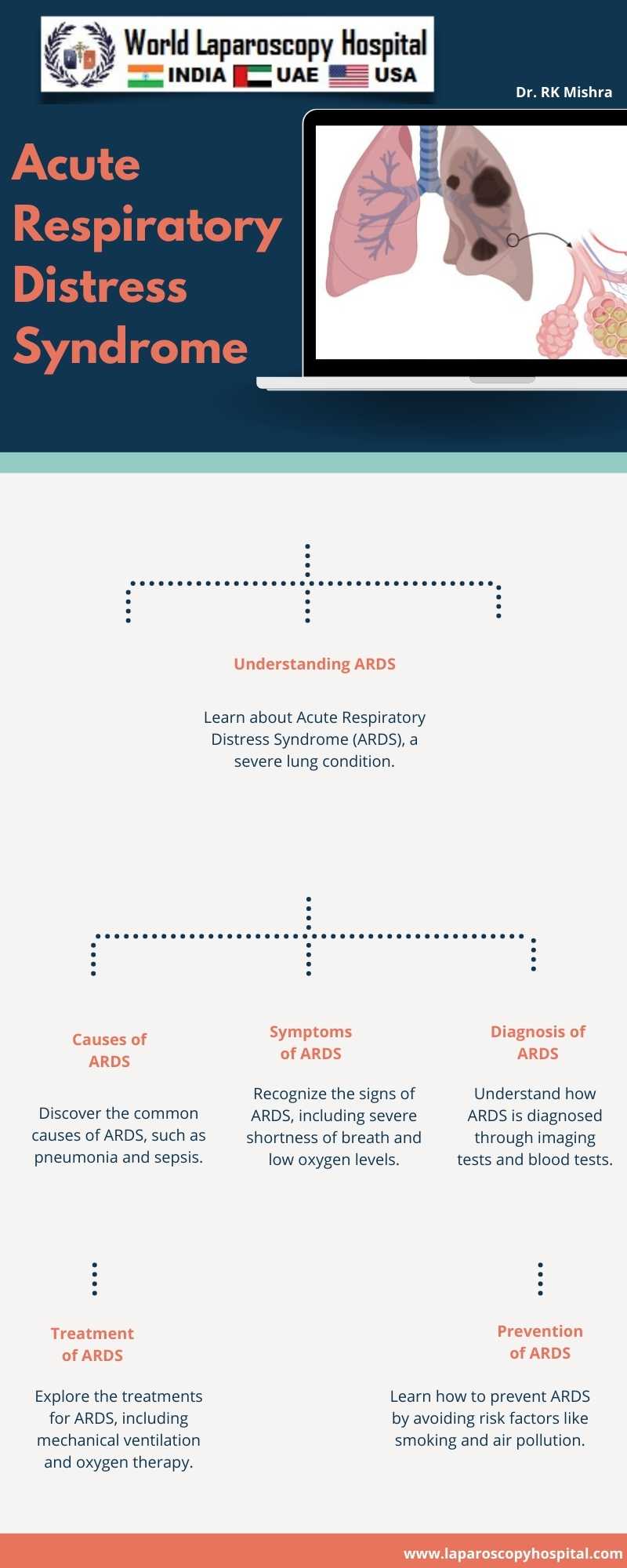
One of the most common causes of ARDS is post-surgery complications, particularly in patients undergoing major surgeries such as abdominal, thoracic, or vascular procedures. The inflammatory response triggered by surgery can lead to damage to the lungs, resulting in ARDS. Similarly, traumatic injuries, such as those sustained in accidents or falls, can also lead to ARDS due to the direct injury to the lungs or as a result of systemic inflammatory response.
The pathophysiology of ARDS involves an inflammatory cascade that leads to increased permeability of the alveolar-capillary membrane, causing protein-rich fluid to leak into the alveoli. This results in impaired gas exchange and severe hypoxemia. The hallmark symptoms of ARDS include severe shortness of breath, rapid breathing, and low oxygen levels in the blood.
Management of ARDS involves supportive care, including mechanical ventilation to support oxygenation and ventilation. Other supportive measures such as fluid management, nutrition support, and treatment of underlying infections are also important. In some cases, pharmacological interventions such as corticosteroids or neuromuscular blocking agents may be used, although their efficacy is still a matter of debate.
Prevention of ARDS is key, especially in high-risk patients undergoing surgery or trauma. Strategies to reduce the risk of ARDS include careful fluid management, minimizing the use of high tidal volumes during mechanical ventilation, and early recognition and treatment of infections.
Conclusion:
ARDS is a serious complication that can occur following surgery or trauma, with significant implications for patient outcomes. Understanding the risk factors, pathophysiology, and management strategies for ARDS is crucial for healthcare providers to improve patient outcomes and reduce the burden of this condition.

One of the most common causes of ARDS is post-surgery complications, particularly in patients undergoing major surgeries such as abdominal, thoracic, or vascular procedures. The inflammatory response triggered by surgery can lead to damage to the lungs, resulting in ARDS. Similarly, traumatic injuries, such as those sustained in accidents or falls, can also lead to ARDS due to the direct injury to the lungs or as a result of systemic inflammatory response.
The pathophysiology of ARDS involves an inflammatory cascade that leads to increased permeability of the alveolar-capillary membrane, causing protein-rich fluid to leak into the alveoli. This results in impaired gas exchange and severe hypoxemia. The hallmark symptoms of ARDS include severe shortness of breath, rapid breathing, and low oxygen levels in the blood.
Management of ARDS involves supportive care, including mechanical ventilation to support oxygenation and ventilation. Other supportive measures such as fluid management, nutrition support, and treatment of underlying infections are also important. In some cases, pharmacological interventions such as corticosteroids or neuromuscular blocking agents may be used, although their efficacy is still a matter of debate.
Prevention of ARDS is key, especially in high-risk patients undergoing surgery or trauma. Strategies to reduce the risk of ARDS include careful fluid management, minimizing the use of high tidal volumes during mechanical ventilation, and early recognition and treatment of infections.
Conclusion:
ARDS is a serious complication that can occur following surgery or trauma, with significant implications for patient outcomes. Understanding the risk factors, pathophysiology, and management strategies for ARDS is crucial for healthcare providers to improve patient outcomes and reduce the burden of this condition.
1 COMMENTS
Dr. K.D.N. Singh
#1
Feb 24th, 2024 7:13 am
ARDS, a grave post-surgery or trauma complication, profoundly affects patient outcomes. Healthcare providers must grasp its risk factors, pathophysiology, and management strategies to mitigate its impact and enhance patient welfare.
| Older Post | Home | Newer Post |








