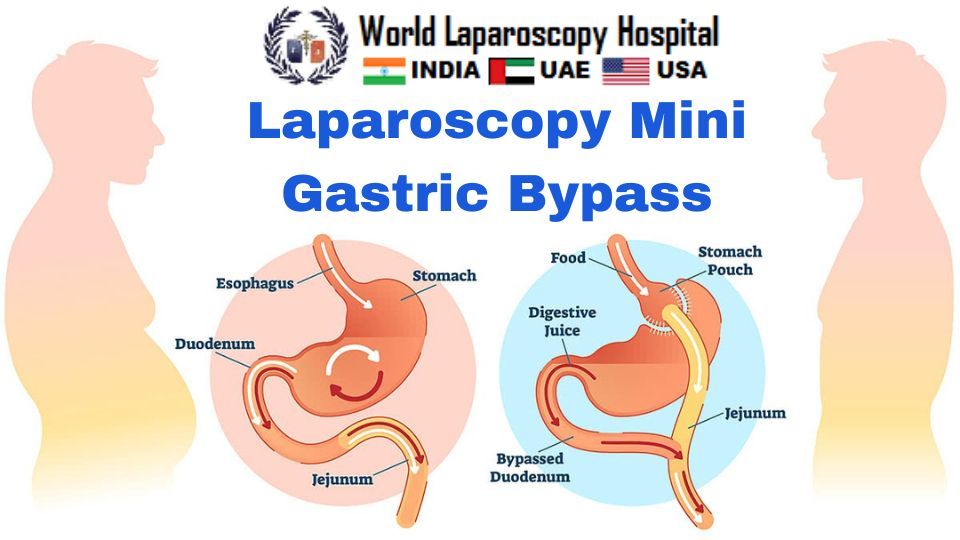
Laparoscopic Mini Gastric Bypass (LMGB) is a type of bariatric surgery that involves creating a small stomach pouch and rerouting a portion of the small intestine to this new pouch. This limits the amount of food a patient can eat and reduces the amount of calories and nutrients that are absorbed by the body. LMGB is a minimally invasive surgery that can be performed using laparoscopic techniques, which involves making small incisions in the abdomen and using a camera and specialized surgical instruments to perform the procedure. The following is a step-by-step guide to performing LMGB:
Preoperative Preparation:
Before the surgery, patients will undergo a thorough medical evaluation to ensure that they are a good candidate for LMGB. This may include blood tests, imaging studies, and a psychological evaluation. Patients will also need to follow a special diet and exercise regimen in the weeks leading up to the surgery to help reduce the size of their liver and make the surgery easier to perform.
Anesthesia:
LMGB is typically performed under general anesthesia, which means that the patient will be asleep throughout the procedure. The anesthesia team will administer medications to induce sleep and ensure that the patient is comfortable and pain-free during the surgery.
Incisions:
Once the patient is asleep, the surgeon will make several small incisions in the abdomen. These incisions are typically less than an inch in length and are used to insert a camera and surgical instruments into the abdomen.
Creating the Stomach Pouch:
Using surgical instruments, the surgeon will carefully separate the upper portion of the stomach from the rest of the stomach, creating a small pouch that can hold approximately 30 milliliters of food. The remainder of the stomach is left intact and remains connected to the lower part of the small intestine.
Rerouting the Small Intestine:
The surgeon will then reroute a portion of the small intestine to the new stomach pouch. This is done by dividing the small intestine and connecting one end to the new stomach pouch, while connecting the other end further down the small intestine. This allows food to bypass the lower portion of the stomach and a portion of the small intestine, reducing the amount of calories and nutrients that are absorbed by the body.
Closing Incisions:
Once the rerouting of the small intestine is complete, the surgeon will carefully inspect the surgical site to ensure that there are no leaks or other complications. The incisions are then closed using sutures or surgical staples.
Postoperative Care:
After the surgery, patients will be closely monitored in a recovery area until they are awake and able to drink clear liquids. Patients will then be discharged from the hospital and given specific instructions for postoperative care, including dietary guidelines and instructions for caring for the incision sites.
Patients will typically be advised to consume only liquids for the first week after surgery, followed by a gradual transition to solid foods over the next several weeks. Patients will also need to take vitamin and mineral supplements to help prevent nutritional deficiencies.
It is important for patients to attend all follow-up appointments with their surgeon to monitor their progress and make adjustments to their treatment plan as necessary. By carefully following their surgeon's instructions and making lifestyle changes to support their weight loss goals, patients can achieve excellent weight loss results with LMGB and improve their overall health and well-being. Here are some additional details about LMGB that patients should be aware of:
- The entire procedure typically takes between one and two hours to complete.
- Patients can expect to stay in the hospital for one to two days after the surgery.
- The recovery period for LMGB is typically shorter than for other types of bariatric surgery, with most patients able to return to work and other normal activities within one to two weeks.
- LMGB has been shown to be effective in helping patients achieve significant weight loss and improve their overall health. Patients can expect to lose between 60% and 80% of their excess body weight within two years after the surgery.
- LMGB is generally considered safe, with a low risk of serious complications. However, as with any surgery, there are potential risks and complications associated with the procedure. Patients should discuss the potential risks and benefits of LMGB with their surgeon before deciding to undergo the surgery.
Here are some potential benefits of LMGB:
- Significant weight loss: Patients can expect to lose a significant amount of weight within the first year after the surgery, with ongoing weight loss for up to two years after the surgery. This can improve overall health and reduce the risk of obesity-related health conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease.
- Improved quality of life: Many patients report feeling more confident and having a better quality of life after the surgery, due to improvements in their physical health and self-esteem.
- Reduced need for medication: After the surgery, patients may require fewer medications to manage obesity-related health conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure.
However, as with any surgery, there are potential risks associated with LMGB, including:
Bleeding and infection:As with any surgery, there is a risk of bleeding and infection.
Leaks:
There is a risk of developing leaks at the surgical site, which can cause serious complications and require additional surgery to correct.
Nutritional deficiencies:
After the surgery, patients may be at risk of developing nutritional deficiencies due to the reduced absorption of nutrients by the body. It is important for patients to take vitamin and mineral supplements as directed by their surgeon to prevent these deficiencies.
Here are some additional details about the potential risks and complications associated with LMGB and how they can be managed:
Bleeding and infection:
These risks can be minimized by carefully following all pre- and post-operative instructions provided by the surgeon. Patients should keep the incision sites clean and dry and avoid any activities that could put stress on the incisions while they are healing. Patients should also seek prompt medical attention if they experience any signs of bleeding or infection, such as fever, chills, or excessive pain or swelling.
Leaks:
Although rare, leaks can occur at the surgical site and can cause serious complications. Patients should be closely monitored after the surgery to ensure that there are no signs of leakage, such as fever, abdominal pain, or increased heart rate. If a leak is suspected, additional surgery may be required to repair the affected area.
Nutritional deficiencies:
Patients who undergo LMGB may be at risk of developing nutritional deficiencies due to the reduced absorption of nutrients by the body. Patients should take vitamin and mineral supplements as directed by their surgeon to prevent these deficiencies. Patients may also need to undergo regular blood tests to monitor their nutrient levels and make adjustments to their supplement regimen as necessary.
Dumping syndrome:
Dumping syndrome is a relatively common complication of LMGB and can cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Patients can minimize their risk of dumping syndrome by consuming small, frequent meals and avoiding foods that are high in sugar or fat.
Stomach stretching:
In rare cases, the stomach may stretch out over time, which can reduce the effectiveness of the surgery. Patients can minimize their risk of stomach stretching by carefully adhering to their dietary and exercise recommendations and seeking prompt medical attention if they experience any unusual symptoms or complications.
Here are some additional details about the potential risks and complications associated with LMGB and how they can be managed:
Bleeding and infection:
These risks can be minimized by carefully following all pre- and post-operative instructions provided by the surgeon. Patients should keep the incision sites clean and dry and avoid any activities that could put stress on the incisions while they are healing. Patients should also seek prompt medical attention if they experience any signs of bleeding or infection, such as fever, chills, or excessive pain or swelling.
Leaks:
Although rare, leaks can occur at the surgical site and can cause serious complications. Patients should be closely monitored after the surgery to ensure that there are no signs of leakage, such as fever, abdominal pain, or increased heart rate. If a leak is suspected, additional surgery may be required to repair the affected area.
Nutritional deficiencies:
Patients who undergo LMGB may be at risk of developing nutritional deficiencies due to the reduced absorption of nutrients by the body. Patients should take vitamin and mineral supplements as directed by their surgeon to prevent these deficiencies. Patients may also need to undergo regular blood tests to monitor their nutrient levels and make adjustments to their supplement regimen as necessary.
Dumping syndrome:
Dumping syndrome is a relatively common complication of LMGB and can cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Patients can minimize their risk of dumping syndrome by consuming small, frequent meals and avoiding foods that are high in sugar or fat.
Stomach stretching:
In rare cases, the stomach may stretch out over time, which can reduce the effectiveness of the surgery. Patients can minimize their risk of stomach stretching by carefully adhering to their dietary and exercise recommendations and seeking prompt medical attention if they experience any unusual symptoms or complications.
It is important for patients to carefully weigh the potential benefits and risks of LMGB before deciding to undergo the surgery. Patients should also be sure to choose a qualified and experienced bariatric surgeon to perform the procedure and to carefully follow their surgeon's instructions before and after the surgery. By doing so, patients can minimize their risk of complications and achieve excellent weight loss results with LMGB.
Laparoscopic Mini Gastric Bypass (LMGB) is generally considered safe, but as with any surgery, there are potential risks and complications that patients should be aware of. Here are some of the most common complications associated with LMGB:
Bleeding and infection:
As with any surgery, there is a risk of bleeding and infection. Patients may experience bleeding or infection at the incision site or in the abdominal cavity. Infection can be treated with antibiotics, but bleeding may require additional surgery to control.
Leaks:
There is a risk of developing leaks at the surgical site where the small intestine is connected to the new stomach pouch. This can cause serious complications and require additional surgery to correct. Patients may experience symptoms such as fever, abdominal pain, or increased heart rate if a leak is present.
Nutritional deficiencies:
After the surgery, patients may be at risk of developing nutritional deficiencies due to the reduced absorption of nutrients by the body. This can lead to deficiencies in vitamins and minerals such as iron, calcium, and vitamin B12. Patients may need to take vitamin and mineral supplements as directed by their surgeon to prevent these deficiencies.
Dumping syndrome:
Dumping syndrome is a common complication of LMGB and can cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. This occurs when food moves too quickly through the digestive system and causes the body to release large amounts of insulin. Patients can minimize their risk of dumping syndrome by consuming small, frequent meals and avoiding foods that are high in sugar or fat.
Stomach stretching:
In rare cases, the stomach pouch may stretch out over time, reducing the effectiveness of the surgery. This can lead to weight regain or other complications. Patients can minimize their risk of stomach stretching by carefully adhering to their dietary and exercise recommendations and seeking prompt medical attention if they experience any unusual symptoms or complications.
Gallstones:
Rapid weight loss after LMGB can increase the risk of developing gallstones. Patients may experience symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting if they develop gallstones. In some cases, surgery may be required to remove the gallbladder.
Blood clots:
Patients who undergo LMGB are at an increased risk of developing blood clots. This can be due to a combination of factors such as the surgery itself, the reduced mobility during recovery, and the changes in blood flow that occur after the surgery. Patients may need to take blood-thinning medication or wear compression stockings to prevent blood clots.
Strictures:
In some cases, the connection between the small intestine and the stomach pouch may narrow, causing a stricture. This can cause food to get stuck and may require additional surgery to correct.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD):
Some patients may develop GERD after LMGB due to changes in the anatomy of the digestive system. This can cause symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and chest pain. Patients may need to take medication to reduce the production of stomach acid or undergo additional surgery to correct the issue.
The management of complications following Laparoscopic Mini Gastric Bypass (LMGB) depends on the specific complication and its severity. Here are some management strategies for the most common complications associated with LMGB:
Bleeding and infection:
Patients who develop bleeding or infection may need to undergo additional surgery to control the bleeding or drain any infected fluid or tissue. Patients may also be given antibiotics to help fight the infection.
Leaks:
In cases of leaks, patients may need to undergo additional surgery to repair the damaged area. Patients may also need to undergo additional tests, such as CT scans or endoscopies, to monitor the healing of the surgical site.
Nutritional deficiencies:
Patients who develop nutritional deficiencies may need to take vitamin and mineral supplements to help prevent or treat these deficiencies. Patients may also be advised to consume foods that are rich in the nutrients they need, such as lean protein, fruits, and vegetables.
Dumping syndrome:
Patients who develop dumping syndrome may need to make dietary changes to reduce their risk of symptoms. This may include consuming smaller, more frequent meals, avoiding sugary or high-fat foods, and drinking fluids between meals rather than with meals.
Stomach stretching:
In rare cases of stomach stretching, patients may need to undergo additional surgery to reduce the size of the stomach pouch. Patients may also be advised to consume smaller, more frequent meals and to avoid consuming too much food or liquid at once.
Gallstones:
Patients who develop gallstones may need to undergo surgery to remove the gallbladder. In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help dissolve the gallstones.
Blood clots:
Patients who are at risk of developing blood clots may be prescribed blood-thinning medications or instructed to wear compression stockings to improve blood flow.
Strictures:
Patients who develop strictures may need to undergo additional surgery to correct the issue. In some cases, endoscopic procedures may be used to widen the narrowed area.
GERD:
Patients who develop GERD after LMGB may need to take medications to reduce the production of stomach acid. In some cases, additional surgery may be required to correct the issue.
In addition to these specific management strategies, patients who experience complications following LMGB should also be closely monitored by their surgeon and medical team. Patients may need to undergo additional tests or procedures to monitor their progress and ensure that any complications are being properly managed. By carefully following their surgeon's instructions and seeking prompt medical attention if any complications arise, patients can minimize their risk of complications and achieve excellent weight loss results with LMGB
It is important for patients to be aware of these potential risks and complications and to carefully weigh the risks and benefits of LMGB before deciding to undergo the surgery. Patients should also be sure to choose a qualified and experienced bariatric surgeon to perform the procedure and to carefully follow their surgeon's instructions before and after the surgery. By doing so, patients can minimize their risk of complications and achieve excellent weight loss results with LMGB.
| Older Post | Home | Newer Post |





