Surgeon's Choice: Deciding Between Laparoscopic and Robotic Surgery for Common Procedures
Surgeon's Choice: Deciding Between Laparoscopic and Robotic Surgery for Common Procedures
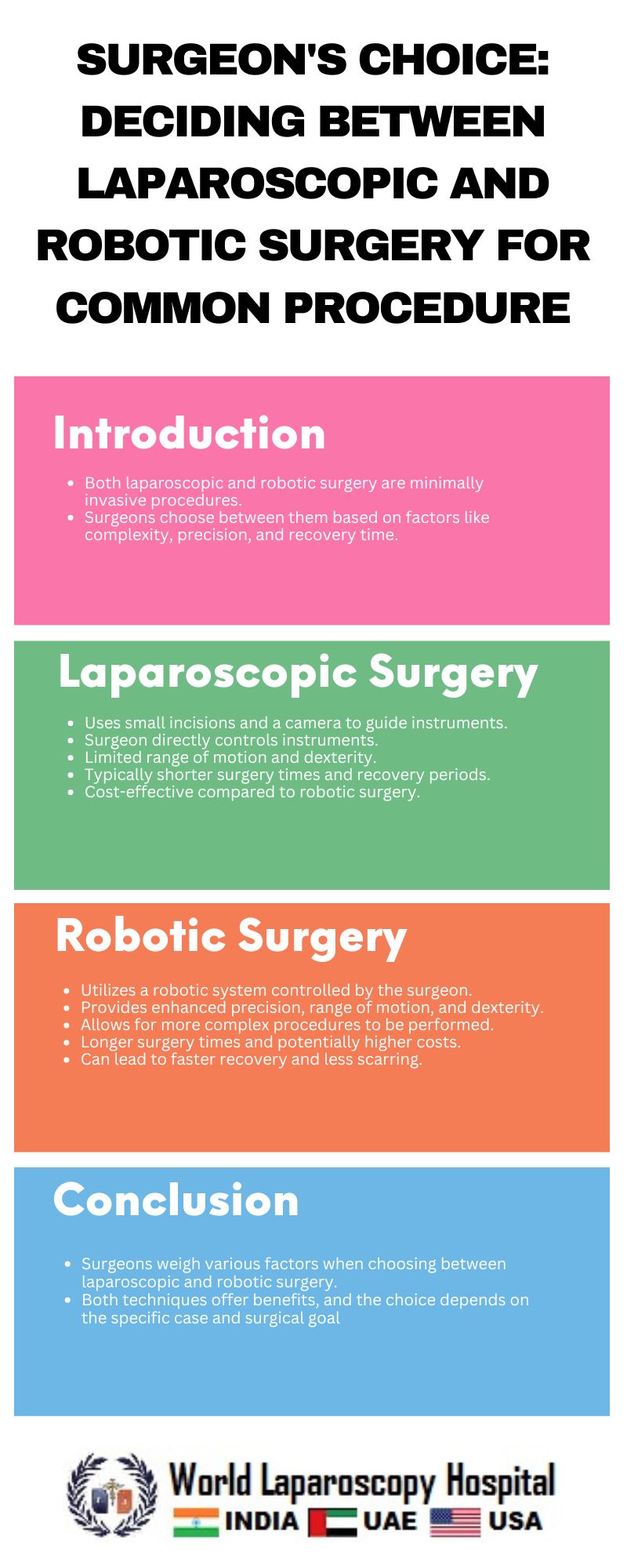
Introduction:
In the world of modern surgery, advancements in technology have revolutionized the way procedures are performed. Two key innovations, laparoscopic surgery and robotic surgery, have become increasingly popular for their minimally invasive nature and improved patient outcomes. Surgeons now face a choice between these two approaches for a variety of common procedures, each with its own set of advantages and considerations.
Laparoscopic Surgery:
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery (MIS), involves making small incisions in the abdomen through which a laparoscope and specialized surgical instruments are inserted. The laparoscope is a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light source that allows the surgeon to view the internal organs on a monitor.
One of the key benefits of laparoscopic surgery is its minimally invasive nature, which results in smaller incisions, less postoperative pain, reduced risk of infection, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times compared to traditional open surgery. Additionally, because the incisions are smaller, there is less scarring and a better cosmetic outcome for the patient.
Laparoscopic surgery is commonly used for a variety of procedures, including gallbladder removal, hernia repair, appendectomy, and certain types of bariatric surgery. Surgeons who choose laparoscopic surgery often do so because of its proven track record, widespread acceptance, and familiarity among surgical teams.
Robotic Surgery:
Robotic surgery is a more recent innovation that uses robotic arms controlled by the surgeon to perform minimally invasive procedures. The robotic system provides enhanced dexterity, precision, and control, allowing for more complex maneuvers in tight spaces.
One of the key advantages of robotic surgery is its ability to overcome the limitations of traditional laparoscopic surgery, such as limited range of motion and difficulty in manipulating instruments. The robotic system also provides a 3D, high-definition view of the surgical site, which can enhance the surgeon's visualization and decision-making.
Robotic surgery is commonly used for procedures such as prostatectomy, hysterectomy, and certain types of cardiac surgery. Surgeons who choose robotic surgery often do so for its technical advantages and potential for improved patient outcomes.
Choosing Between Laparoscopic and Robotic Surgery:
When deciding between laparoscopic and robotic surgery for a common procedure, surgeons must consider several factors, including patient anatomy, surgical complexity, surgeon experience, and cost-effectiveness.
Patient Anatomy:
The anatomy of the patient can influence the choice of surgical approach. Robotic surgery may be preferred for patients with complex anatomy or when precise maneuvers are required in tight spaces. Laparoscopic surgery may be sufficient for patients with straightforward anatomy.
Surgical Complexity:
The complexity of the procedure can also influence the choice of surgical approach. Robotic surgery may be preferred for procedures that require a high degree of precision and dexterity, such as nerve-sparing techniques in prostate surgery. Laparoscopic surgery may be sufficient for less complex procedures.
Surgeon Experience:
Surgeon experience plays a crucial role in the success of both laparoscopic and robotic surgery. Surgeons who are proficient in laparoscopic techniques may prefer to stick with what they know, while others may be eager to adopt robotic technology and expand their surgical capabilities.
Cost-Effectiveness: Cost is another important consideration. Robotic surgery is generally more expensive than laparoscopic surgery due to the cost of the robotic system and maintenance. Surgeons and hospitals must weigh the potential benefits of robotic surgery against the additional cost.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, both laparoscopic and robotic surgery offer significant advantages for common procedures, and the choice between the two depends on a variety of factors. Surgeons must carefully evaluate each case and consider patient anatomy, surgical complexity, surgeon experience, and cost-effectiveness when deciding on the most appropriate approach. Ultimately, the goal is to provide the best possible outcome for the patient while ensuring safety, efficacy, and efficiency in the surgical process.
Introduction:
In the world of modern surgery, advancements in technology have revolutionized the way procedures are performed. Two key innovations, laparoscopic surgery and robotic surgery, have become increasingly popular for their minimally invasive nature and improved patient outcomes. Surgeons now face a choice between these two approaches for a variety of common procedures, each with its own set of advantages and considerations.

Laparoscopic Surgery:
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery (MIS), involves making small incisions in the abdomen through which a laparoscope and specialized surgical instruments are inserted. The laparoscope is a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light source that allows the surgeon to view the internal organs on a monitor.
One of the key benefits of laparoscopic surgery is its minimally invasive nature, which results in smaller incisions, less postoperative pain, reduced risk of infection, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times compared to traditional open surgery. Additionally, because the incisions are smaller, there is less scarring and a better cosmetic outcome for the patient.
Laparoscopic surgery is commonly used for a variety of procedures, including gallbladder removal, hernia repair, appendectomy, and certain types of bariatric surgery. Surgeons who choose laparoscopic surgery often do so because of its proven track record, widespread acceptance, and familiarity among surgical teams.
Robotic Surgery:
Robotic surgery is a more recent innovation that uses robotic arms controlled by the surgeon to perform minimally invasive procedures. The robotic system provides enhanced dexterity, precision, and control, allowing for more complex maneuvers in tight spaces.
One of the key advantages of robotic surgery is its ability to overcome the limitations of traditional laparoscopic surgery, such as limited range of motion and difficulty in manipulating instruments. The robotic system also provides a 3D, high-definition view of the surgical site, which can enhance the surgeon's visualization and decision-making.
Robotic surgery is commonly used for procedures such as prostatectomy, hysterectomy, and certain types of cardiac surgery. Surgeons who choose robotic surgery often do so for its technical advantages and potential for improved patient outcomes.
Choosing Between Laparoscopic and Robotic Surgery:
When deciding between laparoscopic and robotic surgery for a common procedure, surgeons must consider several factors, including patient anatomy, surgical complexity, surgeon experience, and cost-effectiveness.
Patient Anatomy:
The anatomy of the patient can influence the choice of surgical approach. Robotic surgery may be preferred for patients with complex anatomy or when precise maneuvers are required in tight spaces. Laparoscopic surgery may be sufficient for patients with straightforward anatomy.
Surgical Complexity:
The complexity of the procedure can also influence the choice of surgical approach. Robotic surgery may be preferred for procedures that require a high degree of precision and dexterity, such as nerve-sparing techniques in prostate surgery. Laparoscopic surgery may be sufficient for less complex procedures.
Surgeon Experience:
Surgeon experience plays a crucial role in the success of both laparoscopic and robotic surgery. Surgeons who are proficient in laparoscopic techniques may prefer to stick with what they know, while others may be eager to adopt robotic technology and expand their surgical capabilities.
Cost-Effectiveness: Cost is another important consideration. Robotic surgery is generally more expensive than laparoscopic surgery due to the cost of the robotic system and maintenance. Surgeons and hospitals must weigh the potential benefits of robotic surgery against the additional cost.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, both laparoscopic and robotic surgery offer significant advantages for common procedures, and the choice between the two depends on a variety of factors. Surgeons must carefully evaluate each case and consider patient anatomy, surgical complexity, surgeon experience, and cost-effectiveness when deciding on the most appropriate approach. Ultimately, the goal is to provide the best possible outcome for the patient while ensuring safety, efficacy, and efficiency in the surgical process.
3 COMMENTS
DR. AADITYA RAWAT
#1
May 10th, 2024 10:44 am
Absolutely! The choice between laparoscopic and robotic surgery hinges on various factors, including patient anatomy, surgical complexity, and cost-effectiveness. Surgeons prioritize safety, efficacy, and efficiency to ensure optimal outcomes for patients.
Dr. Ahil Khan
#2
May 19th, 2024 11:04 am
This article offers a comprehensive exploration of the surgeon's dilemma when choosing between laparoscopic and robotic surgery for common procedures. By highlighting the advantages and considerations of each approach, it provides valuable insights for surgeons navigating the complexities of modern surgical techniques. With clear explanations of the benefits of laparoscopic surgery, such as its minimally invasive nature and proven track record, and the advantages of robotic surgery, such as enhanced precision and visualization, this article equips surgeons with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions for optimal patient outcomes. Whether considering patient anatomy, surgical complexity, surgeon experience, or cost-effectiveness, this article serves as an invaluable resource for surgeons seeking to deliver the highest quality of care in the evolving landscape of modern surgery.
Dr. Manish Malhotra
#3
May 24th, 2024 10:59 am
In the dynamic landscape of modern surgery, the advent of laparoscopic and robotic techniques stands as a testament to innovation, reshaping the paradigm of patient care. Surgeons today confront a pivotal decision when selecting between these two cutting-edge approaches for common procedures, each presenting a unique array of benefits and deliberations.
Laparoscopic surgery, revered for its minimally invasive nature, embodies a cornerstone of surgical evolution. Its smaller incisions herald reduced postoperative pain, diminished infection risks, and expedited recoveries, epitomizing patient-centric care. Widely adopted and esteemed for its proven efficacy, laparoscopic surgery boasts a rich legacy and familiarity among surgical cohorts.
In contrast, robotic surgery emerges as a beacon of precision and technological prowess, surmounting the constraints of traditional techniques. Empowering surgeons with enhanced dexterity and a panoramic view of the surgical landscape, robotic surgery navigates complexities with finesse. Its allure lies in the promise of improved patient outcomes and the transformative potential for surgical excellence.
Laparoscopic surgery, revered for its minimally invasive nature, embodies a cornerstone of surgical evolution. Its smaller incisions herald reduced postoperative pain, diminished infection risks, and expedited recoveries, epitomizing patient-centric care. Widely adopted and esteemed for its proven efficacy, laparoscopic surgery boasts a rich legacy and familiarity among surgical cohorts.
In contrast, robotic surgery emerges as a beacon of precision and technological prowess, surmounting the constraints of traditional techniques. Empowering surgeons with enhanced dexterity and a panoramic view of the surgical landscape, robotic surgery navigates complexities with finesse. Its allure lies in the promise of improved patient outcomes and the transformative potential for surgical excellence.
| Older Post | Home | Newer Post |






