Introduction:
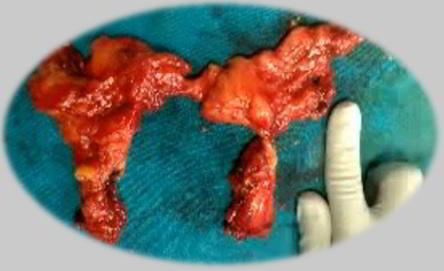
The Thymus gland is a specialized lymphatic organ from the body's defence mechanism. The thymus "educates" T-lymphocytes, that are critical cells with the adaptive disease fighting capability. Each T cell attacks a foreign substance which it identifies with its receptor. T cells have specialized receptors that are generated by randomly shuffling gene segments. Each T cell attacks an alternative antigen. T cells that attack your bodys own proteins are eliminated from the thymus. Thymic epithelial cells express major proteins from elsewhere by the body processes, and T cells that react to those proteins are eliminated through programmed cell death called apoptosis.
The thymus is largest and most active during the neonatal and pre-adolescent periods. By the early teens, the thymus begins to atrophy and thymic stroma is replaced by adipose tissue. Nevertheless, sometime residual T lymphopoiesis continues throughout adult life. Tumours originating from the thymic epithelial cells are called thymomas, and are found in about 10-15% of patients with myasthenia gravis.
A thymectomy is most frquently applied to take out a thymus gland which has been affected by cancerous cells, but it's also an entensively utilized surgical approach to assist patients dealing from the infrequent neurologic disorders such as myasthenia gravis.
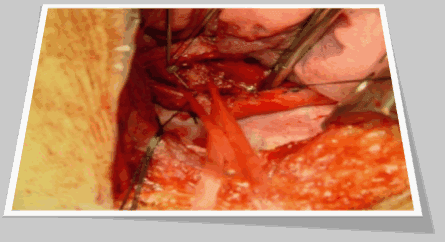
Thoracoscopic Thymectomy for Myasthenia gravis:
Myasthenia gravis may be linked with different irregularities of the thymus gland. The thymus gland located underlying the breastbone and is a significant constituent of the human defense system - immune system in nonage and early adolescence. The affiliation concerning with the thymus gland and myasthenia gravis has contributed to the medical guidance that the gland be eliminated through thymectomy. Nearly 10 percent of myasthenia gravis patients contain a tumor of the gland that is thymoma and are cured by thymectomy, as well. Since the 1940's, myasthenia gravis has been treated by thymectomy with some patients exhibiting some good results just after 6 months to 1 year subsequent to surgery.
The margin of getting success right after surgery is not estimated, but can be considerable. Myasthenia gravis patients who possibly suffer in excess of least indications should take into consideration of thymectomy for treatment. Surgical procedure of Thoracoscopic Thymectomy:
A thymectomy is most frquently applied to take out a thymus gland which has been affected by cancerous cells, but it's also a entensively utilized surgical approach to assist patients dealing from the infrequent neurologic disorders such as myasthenia gravis.
Thoracoscopic Thymectomy
This approach is far less invasive and persistent as compare to the sternotomy. With the thoracoscopic technique, the minimal access surgeon typically makes 2 to 3 small clefts of 3/4 inch in length on the side of the chest. A tiny telescope and dissecting tools are instilled by means of the opening holes. The thymus gland is visualized and eliminated. For this operation a chest tube is needed for few days and will be excluded right before you get back to home. This is due to the location and the tiny size of the clefts; this is the most cosmetic technique for thymectomy.
Expectation after Thymectomy:
No matter which technique is used open or thoracoscopy; the surgeon will eliminate the complete thymus gland and convey it for examination. The pathologist will investigate the tissue for thymoma and various other disproportionate cells. The final pathology report is normally ready in 10-14 days. The surgeon will observe the patient of the outcomes at the surgical next appointment, normally 2-4 weeks right after discharge.
The healing varies with the particular surgical technique used and the sort of work or activity the patient does daily. Resurgence from a entire sternotomy technique may need up to 3 months off from work. This duration of time is particularly reduced with less invasive surgical technique.and may be as small as 1-2 weeks with the transcervical thymectomy technique.
It is especially important that patients ensure that their myasthenia gravis indications are highly monitored in the postoperative time whereas they are healing from surgery. The neurologist will be very concerned in modifying the medication dosages for maximum management of indications.
Most patients will observe success rate in their myasthenia gravis indications right after surgery but may still have flare-ups frequently, whereas these flare-ups are probably less severe compared they would be without thymectomy. It may require to 6 to 12 months for patients to observe particular improvement in their symptoms.
Conclusion:
It may be concluded as that Thoracoscopic Thymectomyis most frquently applied to take out a thymus gland which has been affected by cancerous cells, but it's also a entensively utilized surgical approach to assist patients dealing from the infrequent neurologic disorders such as myasthenia gravis.The timing of returning to work or school and resuming driving privileges will be decided by both the neurologist and the surgeon. This usually occurs once the patient is well healed from the surgery and their myasthenia gravis is under control.
World Laparoscopy Hospital, Cyber City, DLF Phase II, Gurugram, NCR Delhi, 122 002, India
PHONES:
For Training: +919811416838
For Treatment: +919811912768
For General Enquiry: +91(0)124 - 2351555





