This video demonstrate by Dr R K Mishra delivering lecture on Laparoscopic Repair of Large Hiatus Hernia at World Laparoscopy Hospital. Any time an internal body part pushes into an area where it doesn't belong, it's called a hernia.
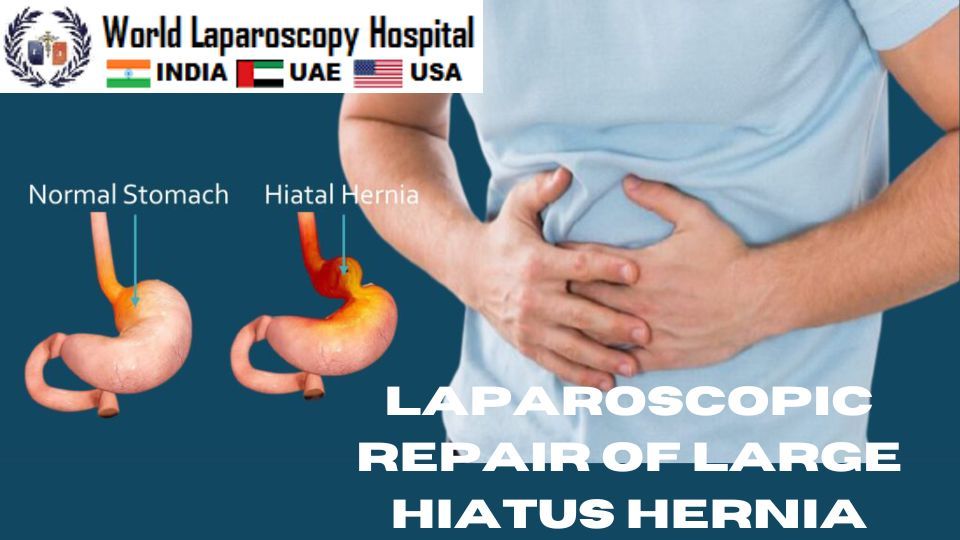
Laparoscopic repair of large hiatus hernia is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that is used to treat a condition in which a portion of the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm and into the chest cavity. This can lead to symptoms such as heartburn, chest pain, difficulty swallowing, and reflux of stomach acid into the esophagus.
During the laparoscopic repair procedure, small incisions are made in the abdomen, and a laparoscope (a thin, flexible tube with a camera attached) is inserted through one of the incisions. The surgeon uses the laparoscope to view the area of the hernia and guide the surgical instruments used to repair the hernia.
The procedure typically involves reducing the herniated portion of the stomach back into the abdominal cavity and reinforcing the weakened diaphragm muscle with mesh. This helps to prevent the hernia from recurring.
Laparoscopic repair of large hiatus hernias has several advantages over traditional open surgery, including smaller incisions, less pain, reduced scarring, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times. However, not all patients are suitable candidates for this procedure, and it is important to discuss the risks and benefits of laparoscopic repair with a qualified surgeon.
After the laparoscopic repair of a large hiatus hernia, patients may experience some discomfort, including abdominal pain, bloating, and difficulty swallowing. These symptoms usually subside within a few days to a week after the surgery. Most patients are able to return to their normal activities within two to four weeks.
Some potential risks associated with laparoscopic repair of large hiatus hernias include bleeding, infection, damage to nearby organs or tissues, and recurrence of the hernia. However, these risks are relatively low when the procedure is performed by an experienced surgeon.
Patients should follow their surgeon's instructions for post-operative care, which may include taking pain medications, following a special diet, avoiding strenuous activity, and attending follow-up appointments to monitor their progress.
In summary, laparoscopic repair of a large hiatus hernia is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that can effectively treat this condition with fewer complications and a faster recovery time compared to traditional open surgery. However, it is important to discuss the risks and benefits of the procedure with a qualified surgeon to determine if it is the best option for each patient.
There are several advantages to laparoscopic repair of large hiatus hernias over traditional open surgery:
-
Smaller incisions: Laparoscopic surgery involves making a few small incisions, each only about 1 cm in length, compared to a large incision made in traditional open surgery.
-
Less pain: Laparoscopic surgery results in less postoperative pain and discomfort than traditional open surgery.
-
Reduced scarring: Because the incisions made during laparoscopic surgery are much smaller than those made during open surgery, scarring is greatly reduced.
-
Shorter hospital stay: Patients who undergo laparoscopic surgery typically spend less time in the hospital than those who undergo traditional open surgery.
-
Faster recovery time: Patients can often return to their normal activities faster after laparoscopic surgery compared to open surgery.
-
Reduced risk of complications: Laparoscopic surgery is associated with fewer complications than traditional open surgery.
-
Better cosmetic results: Laparoscopic surgery results in better cosmetic outcomes, as the smaller incisions and reduced scarring are less visible than a large incision.
Overall, laparoscopic repair of large hiatus hernias is a safe and effective minimally invasive procedure with several advantages over traditional open surgery. However, as with any surgical procedure, there are some risks, and patients should discuss the benefits and risks of laparoscopic surgery with their surgeon.
Although laparoscopic repair of large hiatus hernias is generally a safe procedure, as with any surgery, there are potential complications. Some possible complications that can occur with laparoscopic repair of large hiatus hernias include:
-
Bleeding: This can occur during the surgery or postoperatively, and in rare cases, may require additional surgery.
-
Infection: This can occur in the incision sites or in the chest or abdominal cavity.
-
Damage to nearby organs: During the surgery, nearby organs such as the esophagus, stomach, spleen, or liver can be accidentally injured.
-
Difficulty swallowing: Some patients may experience difficulty swallowing after the surgery, which usually resolves within a few weeks.
-
Recurrence of the hernia: Although rare, the hernia can recur after the surgery.
-
Chronic pain: Some patients may experience chronic pain in the area of the surgery.
-
Anesthesia-related complications: Although rare, there is a risk of complications related to the anesthesia used during the surgery.
-
Pneumothorax: This is a rare complication in which air leaks into the chest cavity, causing the lung to collapse.
It is important to discuss the potential complications with a qualified surgeon before undergoing laparoscopic repair of a large hiatus hernia. Your surgeon will also provide post-operative instructions on how to minimize the risk of complications and what to do if you experience any symptoms or complications after the surgery.
| Older Post | Home | Newer Post |



