This video demonstrate vesicovaginal fistula (VVF) repair are transabdominal repair for supratrigonal VVF and transvaginal approach for low lying fistulae. Laparoscopic surgery was introduced to duplicate the surgical steps of the transabdominal approach with reduction in morbidity.
Laparoscopic Vesicovaginal Fistula Repair is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to repair a vesicovaginal fistula. A vesicovaginal fistula is an abnormal connection between the bladder and the vagina, which can lead to the leakage of urine into the vagina. This can be a distressing condition for women, and can cause discomfort, embarrassment, and social isolation.
The laparoscopic approach to repairing a vesicovaginal fistula involves the use of small incisions in the abdomen, through which a laparoscope (a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light at the end) and other surgical instruments are inserted. This allows the surgeon to visualize the area and perform the repair without making a large incision.
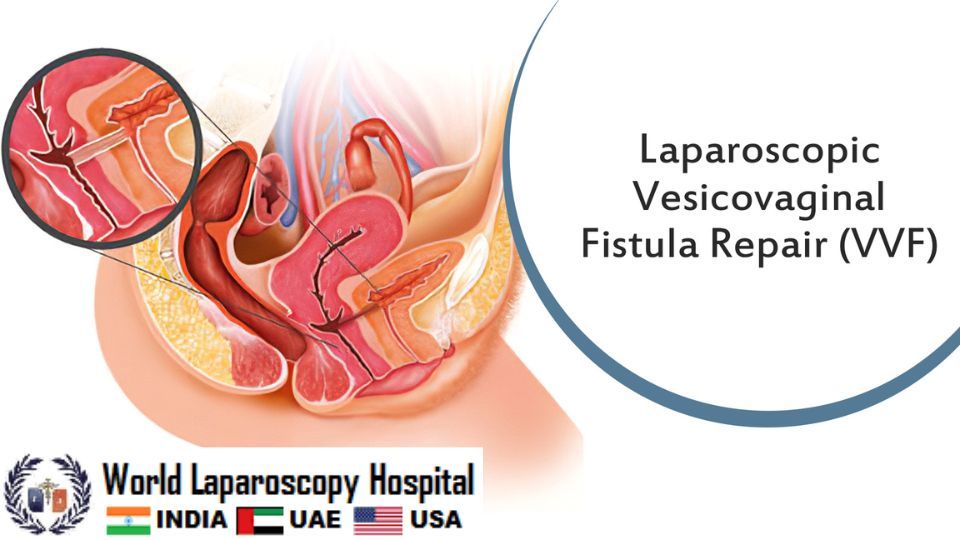
During the procedure, the surgeon will carefully separate the bladder from the surrounding tissue and identify the fistula. The fistula is then closed using sutures or other techniques, depending on the size and location of the defect. The bladder is then repositioned and secured, and the incisions are closed.
The advantages of laparoscopic vesicovaginal fistula repair include a shorter hospital stay, reduced pain and scarring, and a quicker recovery time compared to traditional open surgery. However, not all vesicovaginal fistulas are amenable to laparoscopic repair, and the decision to use this approach will depend on the specific characteristics of the fistula and the experience of the surgeon.
After the surgery, patients may experience some discomfort, swelling, and mild bleeding. Pain medication may be prescribed to manage any discomfort. Patients are typically able to return home the same day or within a few days, depending on their individual recovery progress.
It is important for patients to follow their surgeon's post-operative instructions, which may include avoiding strenuous activity and sexual intercourse for several weeks, as well as maintaining good hygiene to prevent infection.
Complications from laparoscopic vesicovaginal fistula repair are rare, but can include bleeding, infection, damage to surrounding organs, and recurrence of the fistula. Patients should report any unusual symptoms or signs of infection, such as fever, redness, or drainage, to their surgeon immediately.
Overall, laparoscopic vesicovaginal fistula repair is a safe and effective option for treating this condition. Patients should discuss the risks and benefits of this procedure with their surgeon to determine if it is the right choice for them.
There are several advantages to laparoscopic vesicovaginal fistula repair compared to traditional open surgery:
-
Minimally invasive: Laparoscopic surgery is minimally invasive, meaning that it requires smaller incisions than traditional open surgery. This can result in less pain, less scarring, and a faster recovery time.
-
Shorter hospital stay: Because laparoscopic surgery is less invasive, patients typically spend less time in the hospital than they would with open surgery.
-
Reduced risk of infection: With smaller incisions, there is a reduced risk of infection compared to traditional open surgery.
-
Quicker recovery: Because laparoscopic surgery is less invasive, patients may experience a quicker recovery time and be able to return to their normal activities sooner than with open surgery.
-
Improved cosmetic outcomes: With smaller incisions and less scarring, patients may experience better cosmetic outcomes with laparoscopic surgery.
-
Better visualization: The laparoscope used during the procedure provides the surgeon with a magnified view of the surgical site, allowing for more precise and accurate repair of the fistula.
-
Less blood loss: Laparoscopic surgery can result in less blood loss during the procedure, which can reduce the need for blood transfusions.
-
Reduced postoperative pain: With smaller incisions and less tissue trauma, patients may experience less postoperative pain with laparoscopic surgery.
-
Faster return to normal activities: Because laparoscopic surgery is less invasive and typically results in a quicker recovery time, patients may be able to return to their normal activities sooner than with open surgery.
-
Improved patient outcomes: Several studies have shown that laparoscopic vesicovaginal fistula repair can result in excellent patient outcomes, with high rates of fistula closure and low rates of complications.
It is important to note that not all vesicovaginal fistulas are amenable to laparoscopic repair, and the decision to use this approach will depend on the specific characteristics of the fistula and the experience of the surgeon. Patients should discuss the risks and benefits of laparoscopic vesicovaginal fistula repair with their surgeon to determine if it is the right treatment option for them.
Like with any surgical procedure, laparoscopic vesicovaginal fistula repair can have potential complications. Some of the possible complications include:
-
Bleeding: Bleeding during or after the procedure is a potential complication. However, bleeding is less common with laparoscopic surgery than with open surgery.
-
Infection: As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection. However, the risk of infection is lower with laparoscopic surgery than with open surgery.
-
Damage to surrounding organs: During the procedure, there is a risk of damaging surrounding organs, such as the bladder or intestines.
-
Fistula recurrence: Although laparoscopic surgery has high success rates for fistula closure, there is a risk of recurrence of the fistula.
-
Anesthesia risks: Any surgery that requires anesthesia carries a risk of complications related to the anesthesia.
-
Blood clots: Blood clots can occur after any surgery, and there is a risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE).
-
Urinary tract injury: The ureter or bladder can be injured during surgery, which can lead to further complications.
-
Nerve damage: Nerves in the surrounding area may be damaged during the procedure, which can lead to chronic pain or other neurological complications.
-
Adverse reaction to anesthesia: Some patients may have an adverse reaction to anesthesia, which can lead to complications such as respiratory distress or cardiac arrest.
-
Bowel obstruction: There is a risk of bowel obstruction or bowel perforation during laparoscopic vesicovaginal fistula repair, particularly if there are adhesions or scar tissue in the abdominal cavity.
-
Conversion to open surgery: In some cases, it may be necessary to convert to open surgery during the procedure if unexpected complications arise or if the surgeon determines that it is necessary for the safety of the patient.
Patients should also be aware that there is a learning curve associated with laparoscopic vesicovaginal fistula repair, and the success of the procedure may depend on the experience and skill of the surgeon. It is important to choose a surgeon who is experienced in performing this procedure to minimize the risk of complications.
| Older Post | Home | Newer Post |


