This video demonstrates Laparoscopic Trocars. In its simplest form, a trocar is a pen-shaped instrument with a sharp triangular point at one end, typically used inside a hollow tube, known as a cannula or sleeve, to create an opening into the body through which the sleeve may be introduced, to provide an access port during surgery.
Laparoscopic trocars are medical devices used during laparoscopic surgery to create a port of entry into the abdominal cavity. These instruments consist of a long, slender, pointed shaft with a cannula, which is a hollow tube that is inserted through the skin and into the abdominal cavity.
Trocars typically have a three-part system: the shaft, the cannula, and a sleeve. The sleeve fits over the cannula and helps to stabilize it as it is inserted into the abdominal wall. Once the cannula is in place, the sleeve is removed, and instruments such as a laparoscope or surgical tools can be passed through the cannula into the abdominal cavity.
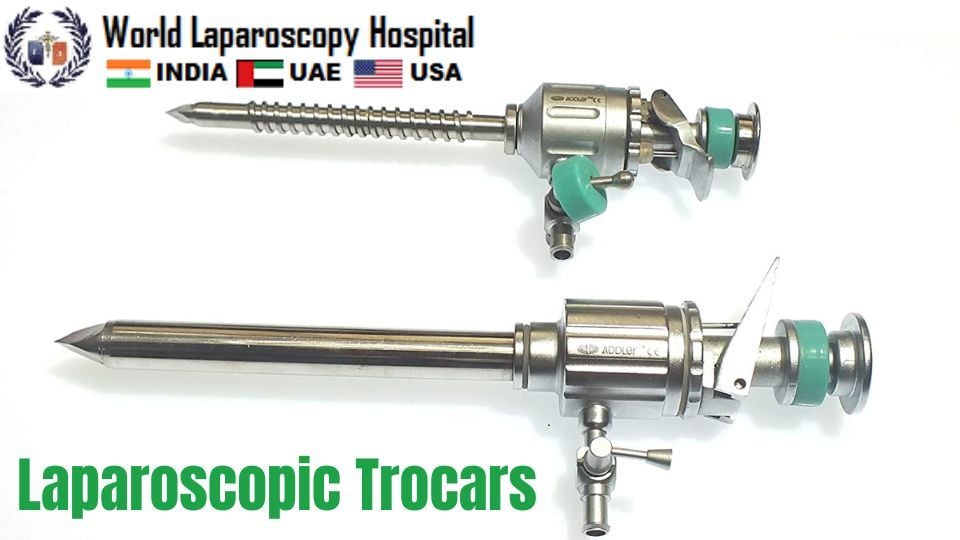
Laparoscopic trocars come in different sizes and shapes depending on the specific surgical procedure being performed. They can be reusable or disposable, and are made from materials such as stainless steel or plastic.
Proper insertion of trocars is essential to avoid damage to surrounding organs and structures. Surgeons must use caution to ensure that the trocar is inserted at the correct angle and depth to prevent injury to the patient.
During laparoscopic surgery, several trocars may be used to create multiple access ports into the abdominal cavity. The number and placement of trocars depend on the specific surgical procedure being performed and the surgeon's preference.
Laparoscopic surgery using trocars offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, including smaller incisions, less scarring, and a shorter recovery time. The use of trocars also allows for better visualization of the surgical site, which can lead to improved accuracy and precision during the procedure.
However, there are also potential risks and complications associated with the use of laparoscopic trocars, including bleeding, infection, organ damage, and gas embolism. Surgeons must be trained and experienced in the use of these devices to minimize the risk of complications.
In conclusion, laparoscopic trocars are essential instruments used in laparoscopic surgery to create access ports into the abdominal cavity. While they offer several advantages over traditional open surgery, their use requires proper training and caution to avoid potential risks and complications.
Laparoscopic trocars offer several advantages over traditional open surgery, including:
-
Smaller incisions: Laparoscopic surgery requires only small incisions, typically less than 1 cm in size, compared to the larger incisions required in open surgery. Smaller incisions mean less trauma to the surrounding tissue, less pain, and faster healing.
-
Reduced scarring: Because laparoscopic surgery requires smaller incisions, there is less scarring and a better cosmetic outcome compared to open surgery.
-
Shorter recovery time: Patients who undergo laparoscopic surgery typically have a shorter hospital stay and a faster recovery time compared to open surgery. They can return to normal activities sooner and have less time off work.
-
Better visualization: The use of laparoscopic trocars allows for better visualization of the surgical site, which can lead to improved accuracy and precision during the procedure.
-
Reduced risk of complications: Laparoscopic surgery has a lower risk of complications such as bleeding, infection, and hernia compared to open surgery.
-
Reduced pain: Laparoscopic surgery causes less pain and discomfort compared to open surgery. This is because the smaller incisions and reduced trauma to the surrounding tissue result in less tissue damage and inflammation, leading to less pain.
-
Reduced blood loss: The use of laparoscopic trocars leads to reduced blood loss during surgery compared to open surgery. This is because the smaller incisions and better visualization of the surgical site allow for more precise surgical techniques.
-
Reduced risk of infection: Laparoscopic surgery has a lower risk of infection compared to open surgery, as the smaller incisions and reduced tissue trauma result in less exposure to external contaminants.
-
Quicker return to normal activities: Patients who undergo laparoscopic surgery typically have a quicker return to normal activities compared to open surgery. This is because the smaller incisions and reduced tissue trauma result in less pain and faster healing.
In conclusion, laparoscopic trocars offer several advantages over traditional open surgery, including smaller incisions, reduced scarring, shorter recovery time, better visualization, reduced risk of complications, reduced pain, reduced blood loss, reduced risk of infection, and quicker return to normal activities. These advantages have made laparoscopic surgery the preferred choice for many surgical procedures.
While laparoscopic surgery using trocars offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, there are potential risks and complications associated with their use, including:
-
Bleeding: There is a risk of bleeding during and after laparoscopic surgery. While the risk is typically lower than in open surgery, excessive bleeding can occur and may require additional surgical intervention.
-
Infection: There is a risk of infection associated with any surgical procedure. Laparoscopic surgery has a lower risk of infection than open surgery, but infection can still occur, particularly if the surgical site is not properly cleaned or if there is a breach in the sterile field during the procedure.
-
Organ damage: The insertion of trocars carries a risk of accidental injury to surrounding organs, such as the bowel, bladder, blood vessels, or nerves. This risk is generally low, but it is important for surgeons to be trained and experienced in the use of trocars to minimize the risk of injury.
-
Gas embolism: During laparoscopic surgery, carbon dioxide gas is used to inflate the abdominal cavity to create space for the surgical instruments. There is a risk of gas embolism, which occurs when gas enters the bloodstream and can cause serious complications such as heart or lung damage.
-
Anesthesia complications: As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of complications related to anesthesia, including allergic reactions, respiratory problems, and heart problems.
-
Conversion to open surgery: In some cases, laparoscopic surgery may need to be converted to open surgery due to unforeseen complications or difficulties during the procedure.
It is important for patients to discuss the potential risks and complications of laparoscopic surgery with their surgeon before undergoing the procedure. With proper training and precautions, the risk of complications can be minimized.
super helpful video. Thanks for Demonstration of different Type of Trocar.
| Older Post | Home | Newer Post |

