Page 59 - WJOLS - Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 59
Rajendra Shitole et al
A B
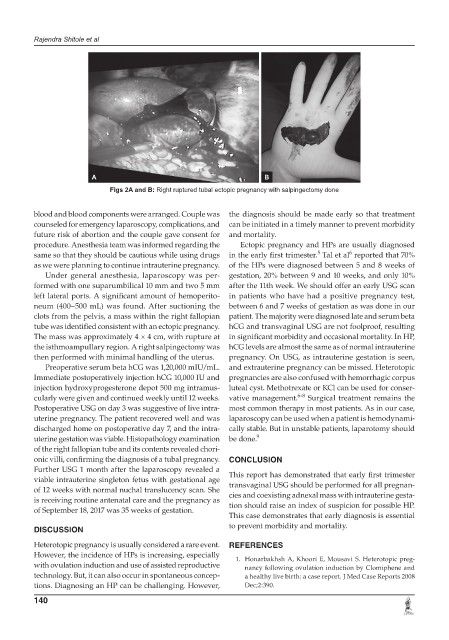
Figs 2A and B: Right ruptured tubal ectopic pregnancy with salpingectomy done
blood and blood components were arranged. Couple was the diagnosis should be made early so that treatment
counseled for emergency laparoscopy, complications, and can be initiated in a timely manner to prevent morbidity
future risk of abortion and the couple gave consent for and mortality.
procedure. Anesthesia team was informed regarding the Ectopic pregnancy and HPs are usually diagnosed
6
5
same so that they should be cautious while using drugs in the early first trimester. Tal et al reported that 70%
as we were planning to continue intrauterine pregnancy. of the HPs were diagnosed between 5 and 8 weeks of
Under general anesthesia, laparoscopy was per- gestation, 20% between 9 and 10 weeks, and only 10%
formed with one suparumbilical 10 mm and two 5 mm after the 11th week. We should offer an early USG scan
left lateral ports. A significant amount of hemoperito- in patients who have had a positive pregnancy test,
neum (400–500 mL) was found. After suctioning the between 6 and 7 weeks of gestation as was done in our
clots from the pelvis, a mass within the right fallopian patient. The majority were diagnosed late and serum beta
tube was identified consistent with an ectopic pregnancy. hCG and transvaginal USG are not foolproof, resulting
The mass was approximately 4 × 4 cm, with rupture at in significant morbidity and occasional mortality. In HP,
the isthmoampullary region. A right salpingectomy was hCG levels are almost the same as of normal intrauterine
then performed with minimal handling of the uterus. pregnancy. On USG, as intrauterine gestation is seen,
Preoperative serum beta hCG was 1,20,000 mIU/mL. and extrauterine pregnancy can be missed. Heterotopic
Immediate postoperatively injection hCG 10,000 IU and pregnancies are also confused with hemorrhagic corpus
injection hydroxyprogesterone depot 500 mg intramus- luteal cyst. Methotrexate or KCl can be used for conser-
6-8
cularly were given and continued weekly until 12 weeks. vative management. Surgical treatment remains the
Postoperative USG on day 3 was suggestive of live intra- most common therapy in most patients. As in our case,
uterine pregnancy. The patient recovered well and was laparoscopy can be used when a patient is hemodynami-
discharged home on postoperative day 7, and the intra- cally stable. But in unstable patients, laparotomy should
uterine gestation was viable. Histopathology examination be done. 9
of the right fallopian tube and its contents revealed chori-
onic villi, confirming the diagnosis of a tubal pregnancy. CONCLUSION
Further USG 1 month after the laparoscopy revealed a
viable intrauterine singleton fetus with gestational age This report has demonstrated that early first trimester
transvaginal USG should be performed for all pregnan-
of 12 weeks with normal nuchal translucency scan. She
is receiving routine antenatal care and the pregnancy as cies and coexisting adnexal mass with intrauterine gesta-
tion should raise an index of suspicion for possible HP.
of September 18, 2017 was 35 weeks of gestation.
This case demonstrates that early diagnosis is essential
to prevent morbidity and mortality.
DISCUSSION
Heterotopic pregnancy is usually considered a rare event. REFERENCES
However, the incidence of HPs is increasing, especially 1. Honarbakhsh A, Khoori E, Mousavi S. Heterotopic preg-
with ovulation induction and use of assisted reproductive nancy following ovulation induction by Clomiphene and
technology. But, it can also occur in spontaneous concep- a healthy live birth: a case report. J Med Case Reports 2008
tions. Diagnosing an HP can be challenging. However, Dec;2:390.
140