Page 27 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgeons
P. 27
Maulana M Ansari
14
by Deurenberg et al. The PRS was observed in terms to short PRS as detected on conversion to TAPP (1), early
of its extent, morphology, layer, and symmetry in all the inadvertent injury to the deep inferior epigastric vessels
patients who underwent the laparoscopic TEPP hernio- (1), and early anesthetic problem secondary to excessive
plasty for the inguinal hernia. The Statistical Package CO retention (1). Three female patients with inguinal
2
for Social Sciences version 21 was used for the statistical hernia presenting in the study period were not recruited
analysis. All data were computed as mean ± SD. for the laparoscopic hernia repair due to one or more
exclusion criteria. Mean age and BMI of the 60 patients
2
RESULTS studied were 50.1 ± 17.2 years (18–80) and 22.6 ± 2.0 kg/m
(19.5–31.2) respectively. Totally, 49 out of 60 patients were
Demographic Characteristics of Patients in the ASA grade I, while 11 patients were in ASA grade
Sixty out of 63 adult male patients with primary inguinal II. By occupation, patients were manual laborers (n = 24),
hernia successfully underwent a total of 68 TEPP her- retired persons (n = 9), office workers (n = 8), students
nioplasties [unilateral 52 (left side 35; right side17), and (n = 7), farmers (n = 6), and field workers (n = 6).
bilateral 8]. Three patients were excluded due to early
forced conversion before sufficient observations were Extent of PRS
made of the PRS; and the reasons for exclusion included The PRS was found incomplete in 79.4% of cases (Figs 2 to 4)
early peritoneal injury by the first blunt trocar secondary and the PRS was complete in 20.6% of cases (Figs 5 to 8),
A B
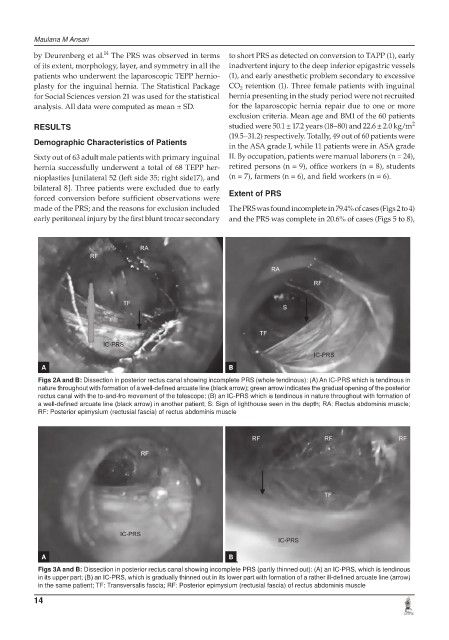
Figs 2A and B: Dissection in posterior rectus canal showing incomplete PRS (whole tendinous): (A) An IC-PRS which is tendinous in
nature throughout with formation of a well-defined arcuate line (black arrow); green arrow indicates the gradual opening of the posterior
rectus canal with the to-and-fro movement of the telescope; (B) an IC-PRS which is tendinous in nature throughout with formation of
a well-defined arcuate line (black arrow) in another patient; S: Sign of lighthouse seen in the depth; RA: Rectus abdominis muscle;
RF: Posterior epimysium (rectusial fascia) of rectus abdominis muscle
A B
Figs 3A and B: Dissection in posterior rectus canal showing incomplete PRS (partly thinned out): (A) an IC-PRS, which is tendinous
in its upper part; (B) an IC-PRS, which is gradually thinned out in its lower part with formation of a rather ill-defined arcuate line (arrow)
in the same patient; TF: Transversalis fascia; RF: Posterior epimysium (rectusial fascia) of rectus abdominis muscle
14