Page 66 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 66
Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: How We Do It
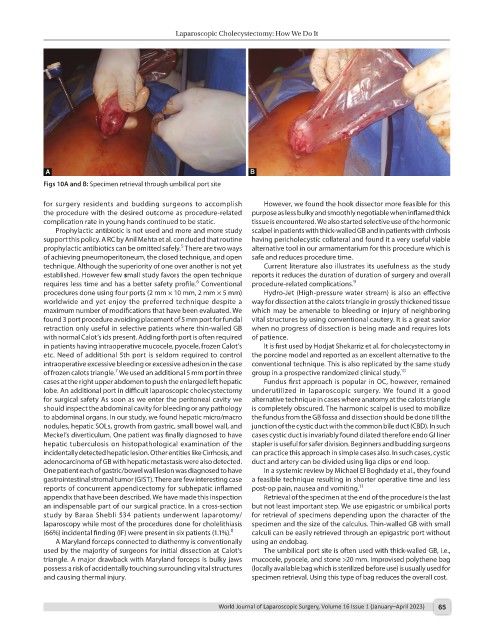
Figs 10A and B: Specimen retrieval through umbilical port site
for surgery residents and budding surgeons to accomplish However, we found the hook dissector more feasible for this
the procedure with the desired outcome as procedure-related purpose as less bulky and smoothly negotiable when inflamed thick
complication rate in young hands continued to be static. tissue is encountered. We also started selective use of the hormonic
Prophylactic antibiotic is not used and more and more study scalpel in patients with thick-walled GB and in patients with cirrhosis
support this policy. A RC by Anil Mehta et al. concluded that routine having pericholecystic collateral and found it a very useful viable
5
prophylactic antibiotics can be omitted safely. There are two ways alternative tool in our armamentarium for this procedure which is
of achieving pneumoperitoneum, the closed technique, and open safe and reduces procedure time.
technique. Although the superiority of one over another is not yet Current literature also illustrates its usefulness as the study
established. However few small study favors the open technique reports it reduces the duration of duration of surgery and overall
6
requires less time and has a better safety profile. Conventional procedure-related complications. 9
procedures done using four ports (2 mm × 10 mm, 2 mm × 5 mm) Hydro-Jet (High-pressure water stream) is also an effective
worldwide and yet enjoy the preferred technique despite a way for dissection at the calots triangle in grossly thickened tissue
maximum number of modifications that have been evaluated. We which may be amenable to bleeding or injury of neighboring
found 3 port procedure avoiding placement of 5 mm port for fundal vital structures by using conventional cautery. It is a great savior
retraction only useful in selective patients where thin-walled GB when no progress of dissection is being made and requires lots
with normal Calot’s ids present. Adding forth port is often required of patience.
in patients having intraoperative mucocele, pyocele, frozen Calot’s It is first used by Hodjat Shekarriz et al. for cholecystectomy in
etc. Need of additional 5th port is seldom required to control the porcine model and reported as an excellent alternative to the
intraoperative excessive bleeding or excessive adhesion in the case conventional technique. This is also replicated by the same study
7
of frozen calots triangle. We used an additional 5 mm port in three group in a prospective randomized clinical study. 10
cases at the right upper abdomen to push the enlarged left hepatic Fundus first approach is popular in OC, however, remained
lobe. An additional port in difficult laparoscopic cholecystectomy underutilized in laparoscopic surgery. We found it a good
for surgical safety As soon as we enter the peritoneal cavity we alternative technique in cases where anatomy at the calots triangle
should inspect the abdominal cavity for bleeding or any pathology is completely obscured. The harmonic scalpel is used to mobilize
to abdominal organs. In our study, we found hepatic micro/macro the fundus from the GB fossa and dissection should be done till the
nodules, hepatic SOLs, growth from gastric, small bowel wall, and junction of the cystic duct with the common bile duct (CBD). In such
Meckel’s diverticulum. One patient was finally diagnosed to have cases cystic duct is invariably found dilated therefore endo GI liner
hepatic tuberculosis on histopathological examination of the stapler is useful for safer division. Beginners and budding surgeons
incidentally detected hepatic lesion. Other entities like Cirrhosis, and can practice this approach in simple cases also. In such cases, cystic
adenocarcinoma of GB with hepatic metastasis were also detected. duct and artery can be divided using liga clips or end loop.
One patient each of gastric/bowel wall lesion was diagnosed to have In a systemic review by Michael El Boghdady et al., they found
gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST). There are few interesting case a feasible technique resulting in shorter operative time and less
reports of concurrent appendicectomy for subhepatic inflamed post-op pain, nausea and vomiting. 11
appendix that have been described. We have made this inspection Retrieval of the specimen at the end of the procedure is the last
an indispensable part of our surgical practice. In a cross-section but not least important step. We use epigastric or umbilical ports
study by Baraa Shebli 534 patients underwent laparotomy/ for retrieval of specimens depending upon the character of the
laparoscopy while most of the procedures done for cholelithiasis specimen and the size of the calculus. Thin-walled GB with small
(66%) incidental finding (IF) were present in six patients (1.1%). 8 calculi can be easily retrieved through an epigastric port without
A Maryland forceps connected to diathermy is conventionally using an endobag.
used by the majority of surgeons for initial dissection at Calot’s The umbilical port site is often used with thick-walled GB, i.e.,
triangle. A major drawback with Maryland forceps is bulky jaws mucocele, pyocele, and stone >20 mm. Improvised polythene bag
possess a risk of accidentally touching surrounding vital structures (locally available bag which is sterilized before use) is usually used for
and causing thermal injury. specimen retrieval. Using this type of bag reduces the overall cost.
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 16 Issue 1 (January–April 2023) 65