Page 49 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 49
An Early Presentation of Stump Appendicitis Following Laparoscopic Appendectomy
stumpitis is the re-inflammation of the residual appendix in the
initial procedure. It has been found following open appendectomy
2
with ligation of stump, inversion of stump, and laparoscopic
5
appendectomy. The prevalence is more with laparoscopic
6
procedure due to small field of vision, absence of tactile, and
three-dimensional perception.
The other factors for stump appendicitis include inflammation
causing inadequate exposure of base, a subserosal or retrocecal
appendix, lighting the appendix without stump invagination, long
stump left in the fear of injuring the cecum, and local ulceration
4
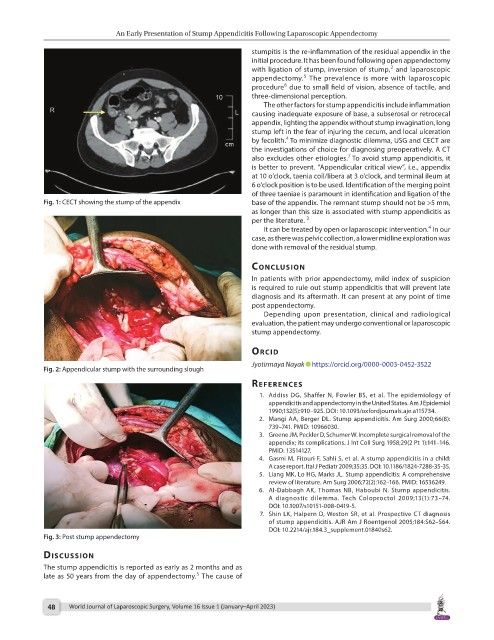
by fecolith. To minimize diagnostic dilemma, USG and CECT are
the investigations of choice for diagnosing preoperatively. A CT
7
also excludes other etiologies. To avoid stump appendicitis, it
is better to prevent. “Appendicular critical view”, i.e., appendix
at 10 o’clock, taenia coil/libera at 3 o’clock, and terminal ileum at
6 o’clock position is to be used. Identification of the merging point
of three taeniae is paramount in identification and ligation of the
Fig. 1: CECT showing the stump of the appendix base of the appendix. The remnant stump should not be >5 mm,
as longer than this size is associated with stump appendicitis as
per the literature. 3
4
It can be treated by open or laparoscopic intervention. In our
case, as there was pelvic collection, a lower midline exploration was
done with removal of the residual stump.
conclusIon
In patients with prior appendectomy, mild index of suspicion
is required to rule out stump appendicitis that will prevent late
diagnosis and its aftermath. It can present at any point of time
post appendectomy.
Depending upon presentation, clinical and radiological
evaluation, the patient may undergo conventional or laparoscopic
stump appendectomy.
orcId
Jyotirmaya Nayak https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0452-3522
Fig. 2: Appendicular stump with the surrounding slough
references
1. Addiss DG, Shaffer N, Fowler BS, et al. The epidemiology of
appendicitis and appendectomy in the United States. Am J Epidemiol
1990;132(5):910–925. DOI: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115734.
2. Mangi AA, Berger DL. Stump appendicitis. Am Surg 2000;66(8):
739–741. PMID: 10966030.
3. Greene JM, Peckler D, Schumer W. Incomplete surgical removal of the
appendix; its complications. J Int Coll Surg 1958;29(2 Pt 1):141–146.
PMID: 13514127.
4. Gasmi M, Fitouri F, Sahli S, et al. A stump appendicitis in a child:
A case report. Ital J Pediatr 2009;35:35. DOI: 10.1186/1824-7288-35-35.
5. Liang MK, Lo HG, Marks JL. Stump appendicitis: A comprehensive
review of literature. Am Surg 2006;72(2):162–166. PMID: 16536249.
6. Al-Dabbagh AK, Thomas NB, Haboubi N. Stump appendicitis.
A diagnostic dilemma. Tech Coloproctol 2009;13(1):73–74.
DOI: 10.1007/s10151-008-0419-5.
7. Shin LK, Halpern D, Weston SR, et al. Prospective CT diagnosis
of stump appendicitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2005;184:S62–S64.
DOI: 10.2214/ajr.184.3_supplement.01840s62.
Fig. 3: Post stump appendectomy
dIscussIon
The stump appendicitis is reported as early as 2 months and as
5
late as 50 years from the day of appendectomy. The cause of
48 World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 16 Issue 1 (January–April 2023)