Page 33 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 33
Perioperative Outcome of Laparoscopy in the Management of Periappendiceal Abscess
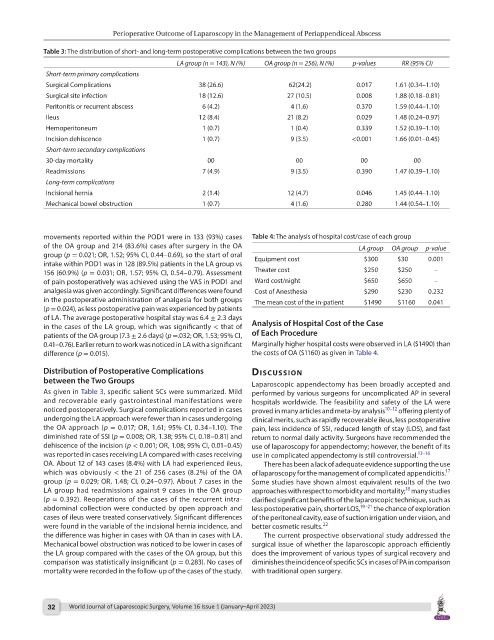
Table 3: The distribution of short- and long-term postoperative complications between the two groups
LA group (n = 143), N (%) OA group (n = 256), N (%) p-values RR (95% CI)
Short-term primary complications
Surgical Complications 38 (26.6) 62(24.2) 0.017 1.61 (0.34–1.10)
Surgical site infection 18 (12.6) 27 (10.5) 0.008 1.88 (0.18–0.81)
Peritonitis or recurrent abscess 6 (4.2) 4 (1.6) 0.370 1.59 (0.44–1.10)
Ileus 12 (8.4) 21 (8.2) 0.029 1.48 (0.24–0.97)
Hemoperitoneum 1 (0.7) 1 (0.4) 0.339 1.52 (0.39–1.10)
Incision dehiscence 1 (0.7) 9 (3.5) <0.001 1.66 (0.01–0.45)
Short-term secondary complications
30-day mortality 00 00 00 00
Readmissions 7 (4.9) 9 (3.5) 0.390 1.47 (0.39–1.10)
Long-term complications
Incisional hernia 2 (1.4) 12 (4.7) 0.046 1.45 (0.44–1.10)
Mechanical bowel obstruction 1 (0.7) 4 (1.6) 0.280 1.44 (0.54–1.10)
movements reported within the POD1 were in 133 (93%) cases Table 4: The analysis of hospital cost/case of each group
of the OA group and 214 (83.6%) cases after surgery in the OA LA group OA group p-value
group (p = 0.021; OR, 1.52; 95% CI, 0.44–0.69), so the start of oral Equipment cost $300 $30 0.001
intake within POD1 was in 128 (89.5%) patients in the LA group vs
156 (60.9%) (p = 0.031; OR, 1.57; 95% CI, 0.54–0.79). Assessment Theater cost $250 $250 –
of pain postoperatively was achieved using the VAS in POD1 and Ward cost/night $650 $650 –
analgesia was given accordingly. Significant differences were found Cost of Anesthesia $290 $230 0.232
in the postoperative administration of analgesia for both groups The mean cost of the in-patient $1490 $1160 0.041
(p = 0.024), as less postoperative pain was experienced by patients
of LA. The average postoperative hospital stay was 6.4 ± 2.3 days
in the cases of the LA group, which was significantly < that of Analysis of Hospital Cost of the Case
patients of the OA group (7.3 ± 2.6 days) (p =.032; OR, 1.53; 95% CI, of Each Procedure
0.41–0.76). Earlier return to work was noticed in LA with a significant Marginally higher hospital costs were observed in LA ($1490) than
difference (p = 0.015). the costs of OA ($1160) as given in Table 4.
Distribution of Postoperative Complications dIscussIon
between the Two Groups Laparoscopic appendectomy has been broadly accepted and
As given in Table 3, specific salient SCs were summarized. Mild performed by various surgeons for uncomplicated AP in several
and recoverable early gastrointestinal manifestations were hospitals worldwide. The feasibility and safety of the LA were
noticed postoperatively. Surgical complications reported in cases proved in many articles and meta-by analysis 10–12 offering plenty of
undergoing the LA approach were fewer than in cases undergoing clinical merits, such as rapidly recoverable ileus, less postoperative
the OA approach (p = 0.017; OR, 1.61; 95% CI, 0.34–1.10). The pain, less incidence of SSI, reduced length of stay (LOS), and fast
diminished rate of SSI (p = 0.008; OR, 1.38; 95% CI, 0.18–0.81) and return to normal daily activity. Surgeons have recommended the
dehiscence of the incision (p < 0.001; OR, 1.08; 95% CI, 0.01–0.45) use of laparoscopy for appendectomy; however, the benefit of its
was reported in cases receiving LA compared with cases receiving use in complicated appendectomy is still controversial. 13–16
OA. About 12 of 143 cases (8.4%) with LA had experienced ileus, There has been a lack of adequate evidence supporting the use
17
which was obviously < the 21 of 256 cases (8.2%) of the OA of laparoscopy for the management of complicated appendicitis.
group (p = 0.029; OR, 1.48; CI, 0.24–0.97). About 7 cases in the Some studies have shown almost equivalent results of the two
LA group had readmissions against 9 cases in the OA group approaches with respect to morbidity and mortality; many studies
18
(p = 0.392). Reoperations of the cases of the recurrent intra- clarified significant benefits of the laparoscopic technique, such as
abdominal collection were conducted by open approach and less postoperative pain, shorter LOS, 19–21 the chance of exploration
cases of ileus were treated conservatively. Significant differences of the peritoneal cavity, ease of suction irrigation under vision, and
were found in the variable of the incisional hernia incidence, and better cosmetic results. 22
the difference was higher in cases with OA than in cases with LA. The current prospective observational study addressed the
Mechanical bowel obstruction was noticed to be lower in cases of surgical issue of whether the laparoscopic approach efficiently
the LA group compared with the cases of the OA group, but this does the improvement of various types of surgical recovery and
comparison was statistically insignificant (p = 0.283). No cases of diminishes the incidence of specific SCs in cases of PA in comparison
mortality were recorded in the follow-up of the cases of the study. with traditional open surgery.
32 World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 16 Issue 1 (January–April 2023)