Page 75 - tmp
P. 75
Laparoscopic Hemicolectomy vs Laparoscopic Transverse Colectomy
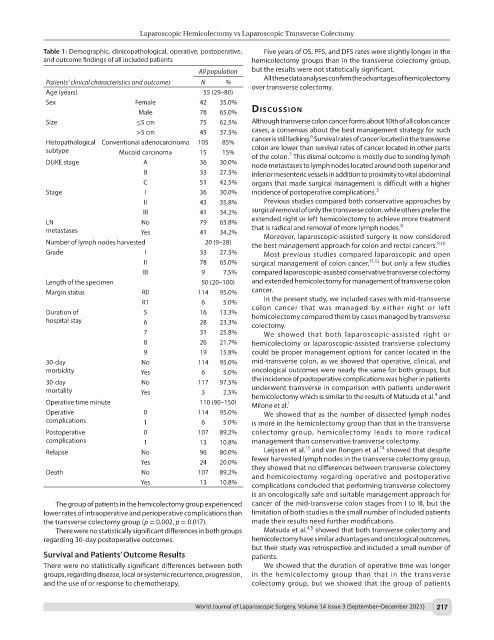
Table 1: Demographic, clinicopathological, operative, postoperative, Five years of OS, PFS, and DFS rates were slightly longer in the
and outcome findings of all included patients hemicolectomy groups than in the transverse colectomy group,
All population but the results were not statistically significant.
All these data analyses confirm the advantages of hemicolectomy
Patients’ clinical characteristics and outcomes N % over transverse colectomy.
Age (years) 55 (29–80)
Sex Female 42 35.0%
Male 78 65.0% dIscussIon
Size ≤5 cm 75 62.5% Although transverse colon cancer forms about 10th of all colon cancer
>5 cm 45 37.5% cases, a consensus about the best management strategy for such
6
Histopathological Conventional adenocarcinoma 105 85% cancer is still lacking. Survival rates of cancer located in the transverse
subtype Mucoid carcinoma 15 15% colon are lower than survival rates of cancer located in other parts
7
of the colon. This dismal outcome is mostly due to sending lymph
DUKE stage A 36 30.0% node metastases to lymph nodes located around both superior and
B 33 27.5% inferior mesenteric vessels in addition to proximity to vital abdominal
C 51 42.5% organs that made surgical management is difficult with a higher
Stage I 36 30.0% incidence of postoperative complications. 3
II 43 35.8% Previous studies compared both conservative approaches by
III 41 34.2% surgical removal of only the transverse colon, while others prefer the
LN No 79 65.8% extended right or left hemicolectomy to achieve more treatment
8
metastases Yes 41 34.2% that is radical and removal of more lymph nodes.
Moreover, laparoscopic-assisted surgery is now considered
Number of lymph nodes harvested 20 (9–28) the best management approach for colon and rectal cancers. 9,10
Grade I 33 27.5% Most previous studies compared laparoscopic and open
II 78 65.0% surgical management of colon cancer, 11,12 but only a few studies
III 9 7.5% compared laparoscopic-assisted conservative transverse colectomy
Length of the specimen 50 (20–100) and extended hemicolectomy for management of transverse colon
Margin status R0 114 95.0% cancer.
R1 6 5.0% In the present study, we included cases with mid-transverse
Duration of 5 16 13.3% colon cancer that was managed by either right or left
hemicolectomy compared them by cases managed by transverse
hospital stay 6 28 23.3% colectomy.
7 31 25.8% We showed that both laparoscopic-assisted right or
8 26 21.7% hemicolectomy or laparoscopic-assisted transverse colectomy
9 19 15.8% could be proper management options for cancer located in the
30-day No 114 95.0% mid-transverse colon, as we showed that operative, clinical, and
morbidity Yes 6 5.0% oncological outcomes were nearly the same for both groups, but
30-day No 117 97.5% the incidence of postoperative complications was higher in patients
mortality Yes 3 2.5% underwent transverse in comparison with patients underwent
4
hemicolectomy which is similar to the results of Matsuda et al. and
Operative time minute 110 (90–150) Milone et al. 1
Operative 0 114 95.0% We showed that as the number of dissected lymph nodes
complications 1 6 5.0% is more in the hemicolectomy group than that in the transverse
Postoperative 0 107 89.2% colectomy group, hemicolectomy leads to more radical
complications 1 13 10.8% management than conservative transverse colectomy.
14
13
Relapse No 96 80.0% Leijssen et al. and van Rongen et al. showed that despite
Yes 24 20.0% fewer harvested lymph nodes in the transverse colectomy group,
Death No 107 89.2% they showed that no differences between transverse colectomy
and hemicolectomy regarding operative and postoperative
Yes 13 10.8% complications concluded that performing transverse colectomy
is an oncologically safe and suitable management approach for
The group of patients in the hemicolectomy group experienced cancer of the mid-transverse colon stages from I to III, but the
lower rates of intraoperative and perioperative complications than limitation of both studies is the small number of included patients
the transverse colectomy group (p = 0.002, p = 0.017). made their results need further modifications.
4,5
There were no statistically significant differences in both groups Matsuda et al. showed that both transverse colectomy and
regarding 30-day postoperative outcomes. hemicolectomy have similar advantages and oncological outcomes,
but their study was retrospective and included a small number of
Survival and Patients’ Outcome Results patients.
There were no statistically significant differences between both We showed that the duration of operative time was longer
groups, regarding disease, local or systemic recurrence, progression, in the hemicolectomy group than that in the transverse
and the use of or response to chemotherapy. colectomy group, but we showed that the group of patients
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 14 Issue 3 (September–December 2021) 217