Page 61 - tmp
P. 61
Umbilical Port Site in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
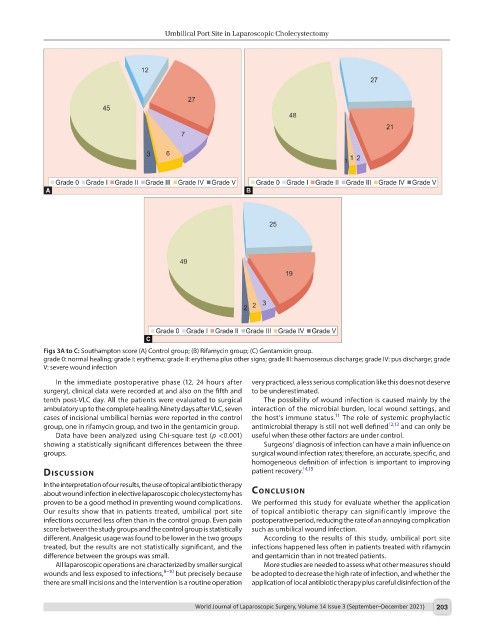
Figs 3A to C: Southampton score (A) Control group; (B) Rifamycin group; (C) Gentamicin group.
grade 0: normal healing; grade I: erythema; grade II: erythema plus other signs; grade III: haemoserous discharge; grade IV: pus discharge; grade
V: severe wound infection
In the immediate postoperative phase (12, 24 hours after very practiced, a less serious complication like this does not deserve
surgery), clinical data were recorded at and also on the fifth and to be underestimated.
tenth post-VLC day. All the patients were evaluated to surgical The possibility of wound infection is caused mainly by the
ambulatory up to the complete healing. Ninety days after VLC, seven interaction of the microbial burden, local wound settings, and
11
cases of incisional umbilical hernias were reported in the control the host’s immune status. The role of systemic prophylactic
group, one in rifamycin group, and two in the gentamicin group. antimicrobial therapy is still not well defined 12,13 and can only be
Data have been analyzed using Chi-square test (p <0.001) useful when these other factors are under control.
showing a statistically significant differences between the three Surgeons’ diagnosis of infection can have a main influence on
groups. surgical wound infection rates; therefore, an accurate, specific, and
homogeneous definition of infection is important to improving
dIscussIon patient recovery. 14,15
In the interpretation of our results, the use of topical antibiotic therapy
about wound infection in elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy has conclusIon
proven to be a good method in preventing wound complications. We performed this study for evaluate whether the application
Our results show that in patients treated, umbilical port site of topical antibiotic therapy can significantly improve the
infections occurred less often than in the control group. Even pain postoperative period, reducing the rate of an annoying complication
score between the study groups and the control group is statistically such as umbilical wound infection.
different. Analgesic usage was found to be lower in the two groups According to the results of this study, umbilical port site
treated, but the results are not statistically significant, and the infections happened less often in patients treated with rifamycin
difference between the groups was small. and gentamicin than in not treated patients.
All laparoscopic operations are characterized by smaller surgical More studies are needed to assess what other measures should
wounds and less exposed to infections, 8–10 but precisely because be adopted to decrease the high rate of infection, and whether the
there are small incisions and the intervention is a routine operation application of local antibiotic therapy plus careful disinfection of the
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 14 Issue 3 (September–December 2021) 203