Page 57 - tmp
P. 57
Laparoscopic TEP Using 3D Mesh to Treat Bilateral Inguinal Hernia
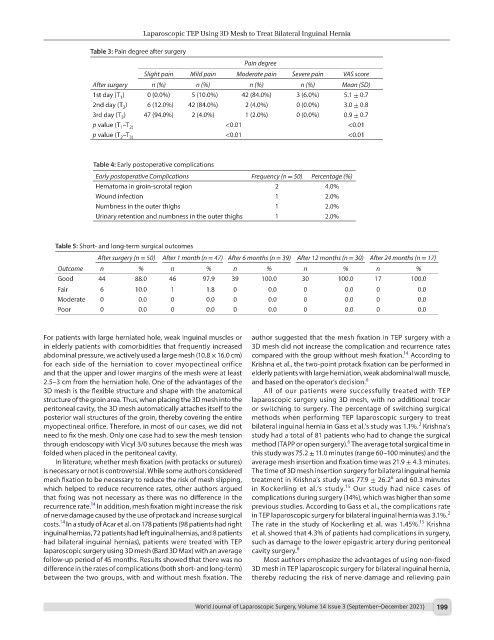
Table 3: Pain degree after surgery
Pain degree
Slight pain Mild pain Moderate pain Severe pain VAS score
After surgery n (%) n (%) n (%) n (%) Mean (SD)
1st day (T ) 0 (0.0%) 5 (10.0%) 42 (84.0%) 3 (6.0%) 5.1 ± 0.7
1
2nd day (T ) 6 (12.0%) 42 (84.0%) 2 (4.0%) 0 (0.0%) 3.0 ± 0.8
2
3rd day (T ) 47 (94.0%) 2 (4.0%) 1 (2.0%) 0 (0.0%) 0.9 ± 0.7
3
p value (T –T 2) <0.01 <0.01
1
p value (T –T 3) <0.01 <0.01
2
Table 4: Early postoperative complications
Early postoperative Complications Frequency (n = 50) Percentage (%)
Hematoma in groin-scrotal region 2 4.0%
Wound infection 1 2.0%
Numbness in the outer thighs 1 2.0%
Urinary retention and numbness in the outer thighs 1 2.0%
Table 5: Short- and long-term surgical outcomes
After surgery (n = 50) After 1 month (n = 47) After 6 months (n = 39) After 12 months (n = 30) After 24 months (n = 17)
Outcome n % n % n % n % n %
Good 44 88.0 46 97.9 39 100.0 30 100.0 17 100.0
Fair 6 10.0 1 1.8 0 0.0 0 0.0 0 0.0
Moderate 0 0.0 0 0.0 0 0.0 0 0.0 0 0.0
Poor 0 0.0 0 0.0 0 0.0 0 0.0 0 0.0
For patients with large herniated hole, weak inguinal muscles or author suggested that the mesh fixation in TEP surgery with a
in elderly patients with comorbidities that frequently increased 3D mesh did not increase the complication and recurrence rates
14
abdominal pressure, we actively used a large mesh (10.8 × 16.0 cm) compared with the group without mesh fixation. According to
for each side of the herniation to cover myopectineal orifice Krishna et al., the two-point protack fixation can be performed in
and that the upper and lower margins of the mesh were at least elderly patients with large herniation, weak abdominal wall muscle,
2.5–3 cm from the herniation hole. One of the advantages of the and based on the operator’s decision. 6
3D mesh is the flexible structure and shape with the anatomical All of our patients were successfully treated with TEP
structure of the groin area. Thus, when placing the 3D mesh into the laparoscopic surgery using 3D mesh, with no additional trocar
peritoneal cavity, the 3D mesh automatically attaches itself to the or switching to surgery. The percentage of switching surgical
posterior wall structures of the groin, thereby covering the entire methods when performing TEP laparoscopic surgery to treat
2
myopectineal orifice. Therefore, in most of our cases, we did not bilateral inguinal hernia in Gass et al.’s study was 1.1%. Krishna’s
need to fix the mesh. Only one case had to sew the mesh tension study had a total of 81 patients who had to change the surgical
6
through endoscopy with Vicyl 3/0 sutures because the mesh was method (TAPP or open surgery). The average total surgical time in
folded when placed in the peritoneal cavity. this study was 75.2 ± 11.0 minutes (range 60–100 minutes) and the
In literature, whether mesh fixation (with protacks or sutures) average mesh insertion and fixation time was 21.9 ± 4.3 minutes.
is necessary or not is controversial. While some authors considered The time of 3D mesh insertion surgery for bilateral inguinal hernia
6
mesh fixation to be necessary to reduce the risk of mesh slipping, treatment in Krishna’s study was 77.9 ± 26.2 and 60.3 minutes
15
which helped to reduce recurrence rates, other authors argued in Kockerling et al.‘s study. Our study had nice cases of
that fixing was not necessary as there was no difference in the complications during surgery (14%), which was higher than some
14
recurrence rate. In addition, mesh fixation might increase the risk previous studies. According to Gass et al., the complications rate
2
of nerve damage caused by the use of protack and increase surgical in TEP laparoscopic surgery for bilateral inguinal hernia was 3.1%.
15
14
costs. In a study of Acar et al. on 178 patients (98 patients had right The rate in the study of Kockerling et al. was 1.45%. Krishna
inguinal hernias, 72 patients had left inguinal hernias, and 8 patients et al. showed that 4.3% of patients had complications in surgery,
had bilateral inguinal hernias), patients were treated with TEP such as damage to the lower epigastric artery during peritoneal
laparoscopic surgery using 3D mesh (Bard 3D Max) with an average cavity surgery. 6
follow-up period of 45 months. Results showed that there was no Most authors emphasize the advantages of using non-fixed
difference in the rates of complications (both short- and long-term) 3D mesh in TEP laparoscopic surgery for bilateral inguinal hernia,
between the two groups, with and without mesh fixation. The thereby reducing the risk of nerve damage and relieving pain
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 14 Issue 3 (September–December 2021) 199