Page 39 - World's Most Popular Laparoscopic Journal
P. 39
Bharathi Rajanna
CURRENT METHODS intramural part of fallopian tube under hysteroscope guidance
Essure Micro-insert (Fig. 2). It attracts macrophages, mononuclear cells, fibro-
blasts, foreign body giant cells, and plasma cells immediately
It is the first transvaginal approach approved by FDA in (Figs 3A to C). The inflammatory response peaks between
2002 for intertubal sterilization technique (Fig. 1). The 2 and 3 weeks and lasts approximately 10 weeks. Induced
Essure micro-insert is wound-down configuration in 4 cm fibrous reaction blocks the tube, which is irreversible. Hence,
long nickel-titanium(nitinol) alloy outer coil in which alternative contraception is advisable for three months. It is
the polyethylene terephthate (pet fibers) is inserted to preferably advised in proliferative period or 6 weeks postnatal
or post-termination allows enhanced visualization of tubal
ostia and optimizes the success rate.
It is recommended to women who have completed
Fig. 1: Expanded essure device. The essure micro-insert expands to their families and desire permanent sterilization. It is also
a diameter of 1.5 to 2 mm depending on the diameter and shape of the excellent choice for women with high risk of general
surrounding fallopian tube
anesthesia, intraoperative complication, adhesions and
bleeding. Women with an intracavity lesion, congenital
anomaly, fibroids, infection, uterine synechiae, cervical
cancer, cervical stenosis and scarring of uterus or cervix
may not be eligible for essure as visualization of tubal ostia
is compromised. Pregnancy test is essential on the day of
surgery to exclude luteal phase of pregnancy if contra-
ception not practised.
Patient Counseling
Patient’s consent is taken which briefs the name of the
surgery, procedure, benefits, risks of both sterilization and
hysteroscopy, and alternative methods. The implications of
anesthesia are also discussed and supported with information
leaflet. Although the procedure is simple, nurse or assistant
can reiterate in lay terms the procedure on the day of surgery.
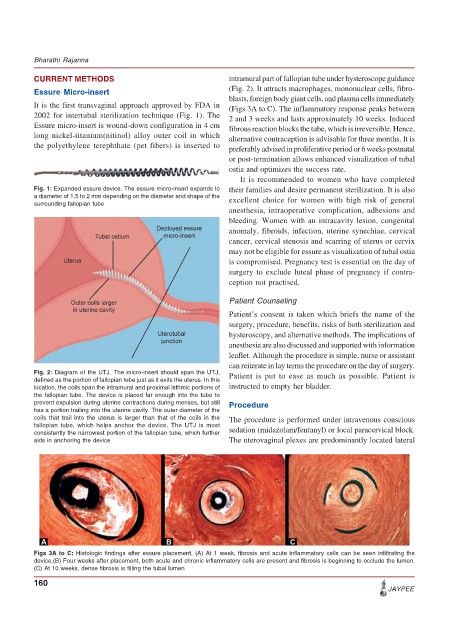
Fig. 2: Diagram of the UTJ. The micro-insert should span the UTJ, Patient is put to ease as much as possible. Patient is
defined as the portion of fallopian tube just as it exits the uterus. In this
location, the coils span the intramural and proximal isthmic portions of instructed to empty her bladder.
the fallopian tube. The device is placed far enough into the tube to
prevent expulsion during uterine contractions during menses, but still Procedure
has a portion trailing into the uterine cavity. The outer diameter of the
coils that trail into the uterus is larger than that of the coils in the The procedure is performed under intravenous conscious
fallopian tube, which helps anchor the device. The UTJ is most
consistently the narrowest portion of the fallopian tube, which further sedation (midazolam/fentanyl) or local paracervical block.
aids in anchoring the device The uterovaginal plexes are predominantly located lateral
Figs 3A to C: Histologic findings after essure placement. (A) At 1 week, fibrosis and acute inflammatory cells can be seen infiltrating the
device.(B) Four weeks after placement, both acute and chronic inflammatory cells are present and fibrosis is beginning to occlude the lumen.
(C) At 10 weeks, dense fibrosis is filling the tubal lumen
160
JAYPEE