Page 13 - World Association of Laparoscopic Surgeons - Journal
P. 13
Lakkanna Suggaiah et al
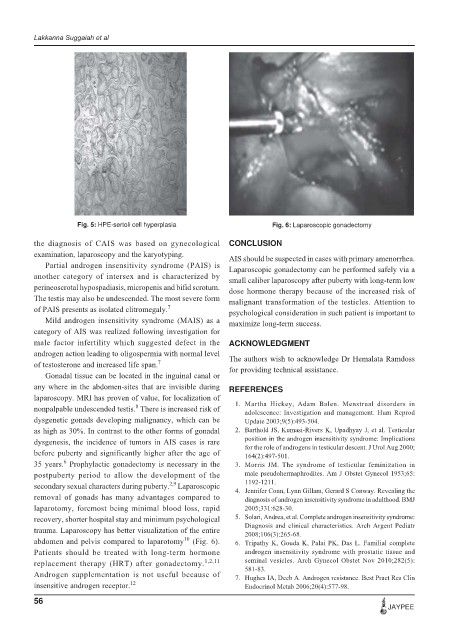
Fig. 5: HPE-sertoli cell hyperplasia Fig. 6: Laparoscopic gonadectomy
the diagnosis of CAIS was based on gynecological CONCLUSION
examination, laparoscopy and the karyotyping.
AIS should be suspected in cases with primary amenorrhea.
Partial androgen insensitivity syndrome (PAIS) is
Laparoscopic gonadectomy can be performed safely via a
another category of intersex and is characterized by
small caliber laparoscopy after puberty with long-term low
perineoscrotal hypospadiasis, micropenis and bifid scrotum.
dose hormone therapy because of the increased risk of
The testis may also be undescended. The most severe form malignant transformation of the testicles. Attention to
of PAIS presents as isolated clitromegaly. 7
psychological consideration in such patient is important to
Mild androgen insensitivity syndrome (MAIS) as a
maximize long-term success.
category of AIS was realized following investigation for
male factor infertility which suggested defect in the ACKNOWLEDGMENT
androgen action leading to oligospermia with normal level The authors wish to acknowledge Dr Hemalata Ramdoss
of testosterone and increased life span. 7
for providing technical assistance.
Gonadal tissue can be located in the inguinal canal or
any where in the abdomen-sites that are invisible during REFERENCES
laparoscopy. MRI has proven of value, for localization of
1. Martha Hickey, Adam Balen. Menstrual disorders in
8
nonpalpable undescended testis. There is increased risk of
adolescence: Investigation and management. Hum Reprod
dysgenetic gonads developing malignancy, which can be Update 2003;9(5):493-504.
as high as 30%. In contrast to the other forms of gonadal 2. Barthold JS, Kumasi-Rivers K, Upadhyay J, et al. Testicular
position in the androgen insensitivity syndrome: Implications
dysgenesis, the incidence of tumors in AIS cases is rare
for the role of androgens in testicular descent. J Urol Aug 2000;
before puberty and significantly higher after the age of
164(2):497-501.
35 years. 6 Prophylactic gonadectomy is necessary in the 3. Morris JM. The syndrome of testicular feminization in
postpuberty period to allow the development of the male pseudohermaphrodites. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1953;65:
2,9
secondary sexual characters during puberty. Laparoscopic 1192-1211.
4. Jennifer Conn, Lynn Gillam, Gerard S Conway. Revealing the
removal of gonads has many advantages compared to diagnosis of androgen insensitivity syndrome in adulthood. BMJ
laparotomy, foremost being minimal blood loss, rapid 2005;331:628-30.
recovery, shorter hospital stay and minimum psychological 5. Solari, Andrea, et al. Complete androgen insensitivity syndrome:
Diagnosis and clinical characteristics. Arch Argent Pediatr
trauma. Laparoscopy has better visualization of the entire
2008;106(3):265-68.
abdomen and pelvis compared to laparotomy 10 (Fig. 6). 6. Tripathy K, Gouda K, Palai PK, Das L. Familial complete
Patients should be treated with long-term hormone androgen insensitivity syndrome with prostatic tissue and
replacement therapy (HRT) after gonadectomy. 1,2,11 seminal vesicles. Arch Gynecol Obstet Nov 2010;282(5):
581-83.
Androgen supplementation is not useful because of
7. Hughes IA, Deeb A. Androgen resistance. Best Pract Res Clin
insensitive androgen receptor. 12 Endocrinol Metab 2006;20(4):577-98.
56
JAYPEE