Page 27 - Laparoscopic Surgery Online Journal
P. 27
WJOLS
Retrospective Review of Laparoscopic Adrenalectomy: An Experience at King Fahad Medical City, Riyadh
metal clips and divided. The dissection proceeds superiorly, incision to completion of skin closure, estimated blood loss
with the fatty tissue containing small vessels between the was obtained from the anesthesia record, and length of stay
adrenal gland and the lateral aspect of the inferior vena cava was defined by the number of days in the hospital after the
being divided carefully. The posterior and inferior operative procedure.
musculature of the diaphragm can be seen at this point. The
dissection proceeds inferiorly until the inferior medial aspect RESULTS
of the gland is well identified and freed from Gerota’s fascia.
Laparoscopic adrenalectomy was performed in 10 patients
This is facilitated by the liberal use of clips to divide
over a period of 4 years. The youngest patients in our study
numerous small vessels in the retroperitoneal tissue. The
was 23 years old, while the eldest was 64 years.
posterior, medial, and superior aspects of the adrenal are
There was a female preponderance, with 8 females as
dissected more easily from the undersurface of the
compared to 2 males. Out of the 10 tumors, 6 were found to
diaphragm and retroperitoneal tissues. The adrenal gland is
be functional. Tumors were located on the left side in
removed in a endoscopic bag through the lateral most port
6 patients and on the right side in 4 patients.
site. The retroperitoneal space is examined for any evidence
The size of the tumor ranged from 1.5 × 1.5 × 1.2 cm to
of bleeding. This dissection is facilitated by using a
the largest being 10.5 × 8 × 5 cm. In our study the histo-
30-degree viewing laparoscope. The left adrenal gland is
pathological examination of the specimen’s revealed 5 cases
approached by a similar transperitoneal procedure in the
of adrenal adenomas. Two patients had pheochromocytomas
lateral decubitus position, but here additionally only two
and 1 patient had an adrenal teratoma. 2 patients were
more ports are placed. After the splenic flexure has been
diagnosed to have adrenal lipomas as listed in the Table 1.
incised and the colon reflected inferiorly, the spleen is
The mean operative time for laparoscopic adrenalec-
mobilized by dividing the peritoneum posterior to the spleen
tomies was 3 hours and 45 minutes. Blood loss ranged from
completely and by dividing the phrenolienal ligament. The
50 to 500 ml. None of the patients required blood
weight of the spleen causes it to fall forward, facilitating
transfusion. Complications were seen in 3 patients, 2 patients
the exposure so that the spleen does not need to be retracted
developed chest infection and 1 developed a port site hernia.
by instruments. Dissection of the tissue surrounding the
No other complications were encountered.
posterior surface of the tail of the pancreas helps define the
The hospital stay ranged from 1 to 5 days with a mean
anterior border of the left adrenal gland. The dissection
of 2.5 days. Postoperative narcotic requirement was
continues in the posterior and inferior fibrofatty tissue
significantly low in our study.
between the adrenal and kidney and proceeds anteriorly in
an attempt to locate the left adrenal vein. When this is
DISCUSSION
identified, it is doubly clipped and divided. The fibrofatty
tissue on the superior, posterior, and medial aspects of the Classically, adrenalectomy for a benign disease has been
adrenal gland is divided using electrocautery and metal clips performed by a retroperitoneal posterior or transperitoneal
and the adrenal is removed. anterior approach. Gagner et al in 1992 described a
Data were collected in a retrospective fashion in all method for removal of benign adrenal tumors through a
patients by review of the medical records, including the laparoscopic approach. 10
anesthesia record, pathology report, and operative note. The The age, gender distribution, functional status, of the
operative time was defined as the time of the initial skin tumor, tumor characteristics like site and size were consistent
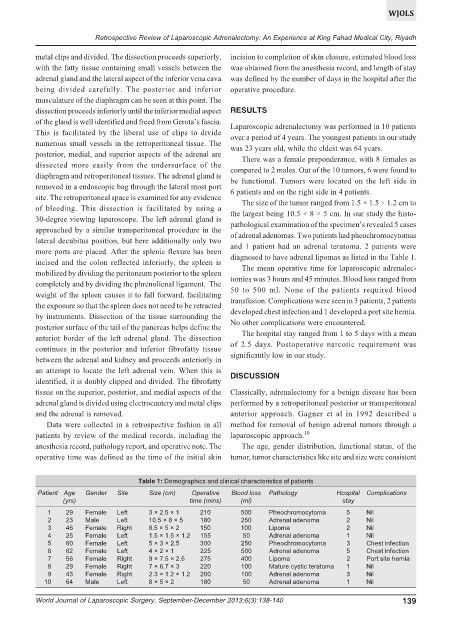
Table 1: Demographics and clinical characteristics of patients
Patient Age Gender Site Size (cm) Operative Blood loss Pathology Hospital Complications
(yrs) time (mins) (ml) stay
1 29 Female Left 3 × 2.5 × 1 210 500 Pheochromocytoma 5 Nil
2 23 Male Left 10.5 × 8 × 5 180 250 Adrenal adenoma 2 Nil
3 46 Female Right 8.5 × 5 × 2 150 100 Lipoma 2 Nil
4 25 Female Left 1.5 × 1.5 × 1.2 155 50 Adrenal adenoma 1 Nil
5 60 Female Left 5 × 3 × 2.5 300 250 Pheochromocytoma 3 Chest infection
6 62 Female Left 4 × 2 × 1 225 500 Adrenal adenoma 5 Chest infection
7 56 Female Right 9 × 7.5 × 2.5 275 400 Lipoma 2 Port site hernia
8 29 Female Right 7 × 6.7 × 3 220 100 Mature cystic teratoma 1 Nil
9 43 Female Right 2.3 × 1.2 × 1.2 200 100 Adrenal adenoma 3 Nil
10 64 Male Left 8 × 5 × 2 180 50 Adrenal adenoma 1 Nil
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, September-December 2013;6(3):138-140 139