Page 16 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 16
Drainage of Complex Pyogenic Liver Abscess
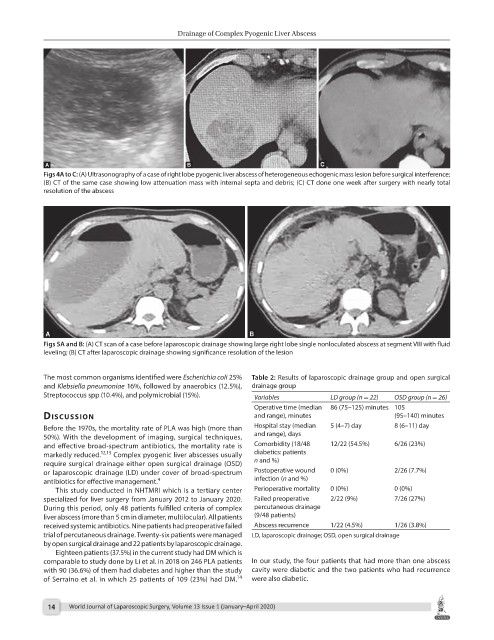
Figs 4A to C: (A) Ultrasonography of a case of right lobe pyogenic liver abscess of heterogeneous echogenic mass lesion before surgical interference;
(B) CT of the same case showing low attenuation mass with internal septa and debris; (C) CT done one week after surgery with nearly total
resolution of the abscess
Figs 5A and B: (A) CT scan of a case before laparoscopic drainage showing large right lobe single nonloculated abscess at segment VIII with fluid
leveling; (B) CT after laparoscopic drainage showing significance resolution of the lesion
The most common organisms identified were Escherichia coli 25% Table 2: Results of laparoscopic drainage group and open surgical
and Klebsiella pneumoniae 16%, followed by anaerobics (12.5%), drainage group
Streptococcus spp (10.4%), and polymicrobial (15%). Variables LD group (n = 22) OSD group (n = 26)
Operative time (median 86 (75–125) minutes 105
dIscussIon and range), minutes (95–140) minutes
Before the 1970s, the mortality rate of PLA was high (more than Hospital stay (median 5 (4–7) day 8 (6–11) day
50%). With the development of imaging, surgical techniques, and range), days
and effective broad-spectrum antibiotics, the mortality rate is Comorbidity (18/48 12/22 (54.5%) 6/26 (23%)
markedly reduced. 12,13 Complex pyogenic liver abscesses usually diabetics: patients
require surgical drainage either open surgical drainage (OSD) n and %)
or laparoscopic drainage (LD) under cover of broad-spectrum Postoperative wound 0 (0%) 2/26 (7.7%)
antibiotics for effective management. 4 infection (n and %)
This study conducted in NHTMRI which is a tertiary center Perioperative mortality 0 (0%) 0 (0%)
specialized for liver surgery from January 2012 to January 2020. Failed preoperative 2/22 (9%) 7/26 (27%)
During this period, only 48 patients fulfilled criteria of complex percutaneous drainage
liver abscess (more than 5 cm in diameter, multilocular). All patients (9/48 patients)
received systemic antibiotics. Nine patients had preoperative failed Abscess recurrence 1/22 (4.5%) 1/26 (3.8%)
trial of percutaneous drainage. Twenty-six patients were managed LD, laparoscopic drainage; OSD, open surgical drainage
by open surgical drainage and 22 patients by laparoscopic drainage.
Eighteen patients (37.5%) in the current study had DM which is
comparable to study done by Li et al. in 2018 on 246 PLA patients In our study, the four patients that had more than one abscess
with 90 (36.6%) of them had diabetes and higher than the study cavity were diabetic and the two patients who had recurrence
14
of Serraino et al. in which 25 patients of 109 (23%) had DM. were also diabetic.
14 World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 13 Issue 1 (January–April 2020)