Page 38 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 38
Oluwole E Ayegbusi
with cerclage placed via laparoscopy both in pregnant For the nonpregnant uterus, a solution with vasopres-
and nonpregnant phases. 5, 11-13 sin (VasopressineR 20 Units/1 mL, American Regent Inc.,
The objectives of this review are to: Shirly, New York, diluted in 50 cc 0.9% NaCl) is injected
• Ascertain the advantages of laparoscopic cerclage over under the peritoneum of the uterovesical reflection and
conventional laparotomy cerclage; lateral of the lower uterus. This facilitates the bloodless
• Review the safety of laparoscopic cerclage over con- separation of the bladder from the cervix.
ventional laparotomy cerclage; Step 2: Creation of windows in the broad ligament
• Briefly describe the procedure of laparoscopic trans- Subsequently, branches of the uterine artery and
abdominal cerclage. vein are identified, so that the cardinal ligament can
be perforated from anterior to posterior by a straight
MATERIALS AND METHODS atraumatic clamp in an avascular area on the median
side of the uterine vessels on both sites. The instru-
Searches in the literature on laparoscopic cervical cerclage
were conducted via PubMed, Google Scholar, EMBASE, ment is guided in such a way that the perforation at the
Medline, and Cochrane library database. No language posterior side is medially located from the uterosacral
restriction was applied to the searches. ligament.
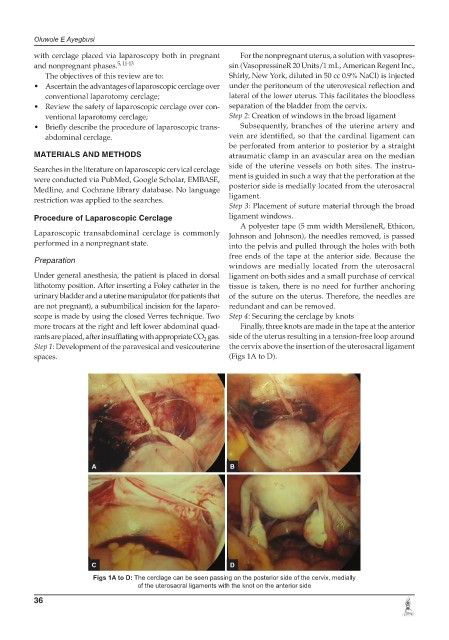
Step 3: Placement of suture material through the broad
Procedure of Laparoscopic Cerclage ligament windows.
A polyester tape (5 mm width MersileneR, Ethicon,
Laparoscopic transabdominal cerclage is commonly Johnson and Johnson), the needles removed, is passed
performed in a nonpregnant state. into the pelvis and pulled through the holes with both
free ends of the tape at the anterior side. Because the
Preparation
windows are medially located from the uterosacral
Under general anesthesia, the patient is placed in dorsal ligament on both sides and a small purchase of cervical
lithotomy position. After inserting a Foley catheter in the tissue is taken, there is no need for further anchoring
urinary bladder and a uterine manipulator (for patients that of the suture on the uterus. Therefore, the needles are
are not pregnant), a subumbilical incision for the laparo- redundant and can be removed.
scope is made by using the closed Verres technique. Two Step 4: Securing the cerclage by knots
more trocars at the right and left lower abdominal quad- Finally, three knots are made in the tape at the anterior
rants are placed, after insufflating with appropriate CO gas. side of the uterus resulting in a tension-free loop around
2
Step 1: Development of the paravesical and vesicouterine the cervix above the insertion of the uterosacral ligament
spaces. (Figs 1A to D).
A B
C D
Figs 1A to D: The cerclage can be seen passing on the posterior side of the cervix, medially
of the uterosacral ligaments with the knot on the anterior side
36