Cutting-edge Technology: How Robotic Surgery is Changing Healthcare
Introduction
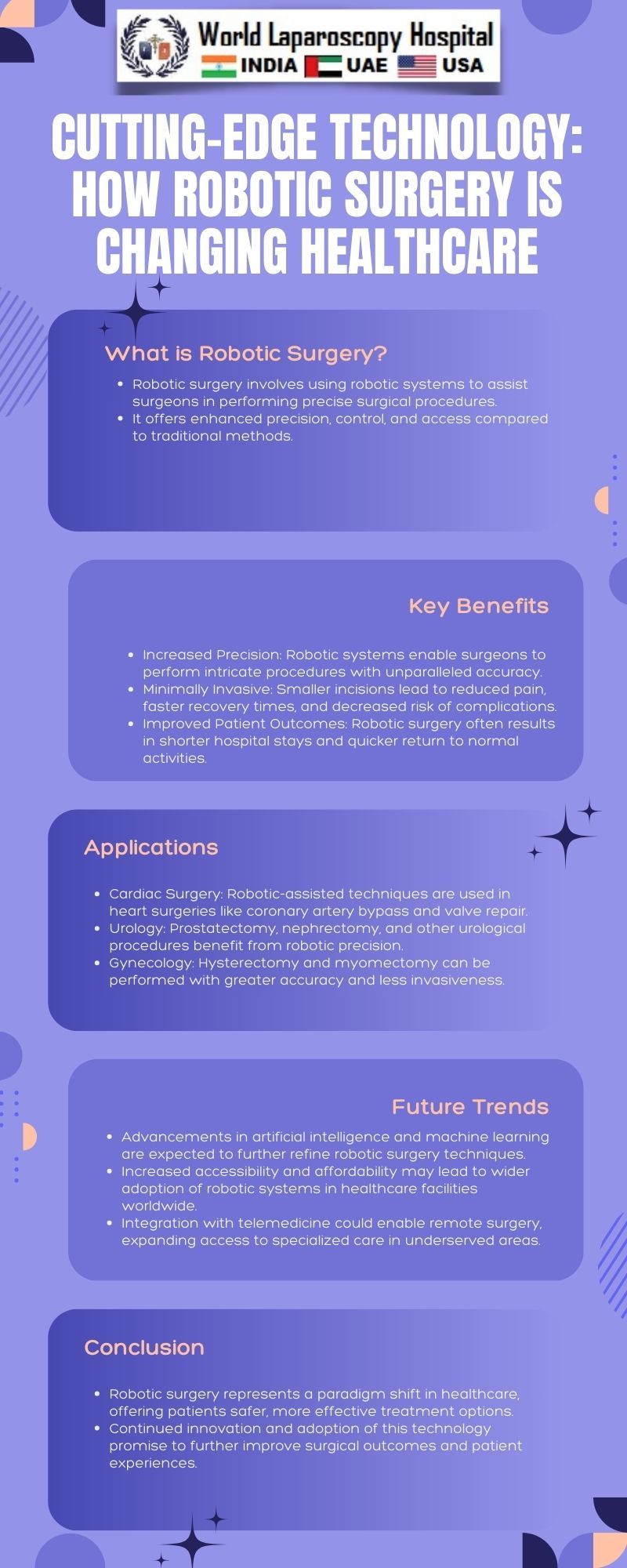
In the realm of modern medicine, few advancements have captured the imagination and transformed surgical practice quite like robotic surgery. With its precision, dexterity, and minimally invasive approach, robotic surgery has emerged as a game-changer in healthcare. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the intricate workings of robotic surgery, its evolution, current applications, benefits, challenges, and the future trajectory of this cutting-edge technology.
Evolution of Robotic Surgery
The genesis of robotic surgery can be traced back to the late 20th century, with the development of the first robotic surgical system, the PUMA 560, in the early 1980s. However, it was not until the late 1990s that the da Vinci Surgical System, developed by Intuitive Surgical, entered the scene, marking a significant milestone in the field. The da Vinci System introduced enhanced capabilities, including improved visualization, greater maneuverability, and ergonomic enhancements for surgeons.
Since its introduction, robotic surgery has witnessed rapid evolution, with subsequent iterations of the da Vinci System incorporating advancements such as high-definition imaging, improved instrumentation, and intuitive user interfaces. Today, robotic surgery platforms have diversified beyond the da Vinci System, with companies worldwide developing their own robotic-assisted surgical systems tailored to specific medical specialties and procedures.
Current Applications
Robotic surgery has found applications across various surgical specialties, ranging from urology and gynecology to cardiothoracic and colorectal surgery. In urology, robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy has become the gold standard for the treatment of prostate cancer, offering superior outcomes in terms of oncologic control and functional preservation. Similarly, in gynecology, robotic-assisted hysterectomy has gained popularity for its reduced blood loss, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times compared to traditional open surgery.
The versatility of robotic surgery extends to cardiothoracic procedures, where it is utilized for coronary artery bypass grafting, mitral valve repair, and lung resections. In colorectal surgery, robotic-assisted techniques have demonstrated benefits in terms of improved visualization of the surgical field, precise tissue dissection, and reduced complications, particularly in cases of rectal cancer resection.
Benefits of Robotic Surgery
The adoption of robotic surgery offers numerous benefits for patients, surgeons, and healthcare institutions alike. One of the primary advantages is the minimally invasive nature of robotic procedures, which typically involve smaller incisions, reduced trauma to surrounding tissues, and decreased postoperative pain. As a result, patients experience shorter hospital stays, faster recovery times, and improved cosmetic outcomes compared to traditional open surgery.
Furthermore, robotic surgery enables surgeons to overcome the limitations of conventional laparoscopic techniques by providing enhanced visualization and instrument maneuverability within the confined space of the surgical field. This translates to greater precision, accuracy, and control during procedures, ultimately leading to improved surgical outcomes and reduced risk of complications.
For surgeons, robotic surgery offers ergonomic benefits, allowing for comfortable positioning and natural hand movements while operating the robotic console. The intuitive interface and three-dimensional visualization provided by robotic systems enhance surgical performance and facilitate complex maneuvers with ease. Moreover, robotic-assisted procedures often require less physical exertion from surgeons, reducing fatigue and mitigating the risk of musculoskeletal injuries associated with prolonged operating times.
From a healthcare economics standpoint, robotic surgery can result in cost savings for hospitals and payers despite the initial investment required for purchasing and maintaining robotic systems. By reducing the length of hospital stays, minimizing postoperative complications, and enabling faster return to normal activities, robotic procedures contribute to overall healthcare efficiency and resource utilization.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its remarkable capabilities, robotic surgery is not without challenges and limitations. One of the primary concerns is the high initial cost associated with acquiring and maintaining robotic systems, which can pose financial barriers for healthcare institutions, particularly in resource-limited settings. Additionally, the learning curve for mastering robotic-assisted techniques may be steep for some surgeons, requiring dedicated training and proctoring to achieve proficiency.
Another challenge is the lack of tactile feedback inherent in robotic surgery, which can potentially compromise the surgeon's ability to assess tissue texture, tension, and adherence during procedures. Although advancements in haptic feedback technology aim to address this limitation, achieving a true sense of touch remains an ongoing area of research and development in robotic surgery.
Furthermore, while robotic surgery offers advantages in terms of precision and dexterity, it may not be suitable for every surgical indication or patient population. Certain complex procedures may still require the expertise and judgment of highly skilled open or laparoscopic surgeons, particularly in cases involving extensive tissue dissection, anatomical variability, or intraoperative complications.
Future Directions
Looking ahead, the future of robotic surgery promises continued innovation and expansion into new frontiers of medical practice. Advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning hold the potential to enhance the capabilities of robotic systems, enabling autonomous decision-making, adaptive assistance, and personalized surgical workflows. Integration with imaging modalities such as augmented reality (AR) and intraoperative imaging could further augment surgical navigation and visualization, enhancing precision and safety.
Moreover, ongoing research in miniaturization and remote-controlled robotics may pave the way for the development of miniature surgical robots capable of accessing and operating within confined spaces within the body, opening up new possibilities for minimally invasive interventions in areas such as neurosurgery and interventional radiology.
As robotic surgery continues to evolve, it is essential to prioritize patient safety, efficacy, and equitable access to ensure that the benefits of this transformative technology are realized across diverse populations and healthcare settings. Collaboration between industry, academia, regulatory agencies, and healthcare stakeholders will be key to driving innovation, optimizing outcomes, and shaping the future landscape of robotic surgery.
Conclusion
Robotic surgery has emerged as a paradigm-shifting technology with the potential to revolutionize healthcare delivery and surgical practice. With its precision, dexterity, and minimally invasive approach, robotic systems offer numerous advantages over traditional surgical techniques, including improved patient outcomes, enhanced surgeon ergonomics, and cost-effective healthcare delivery.
While challenges and limitations remain, ongoing advancements in technology, training, and clinical integration hold promise for overcoming these hurdles and unlocking the full potential of robotic surgery. As we navigate the evolving landscape of healthcare, embracing innovation and harnessing the transformative power of robotic surgery will be critical to advancing the frontiers of medicine and improving the lives of patients worldwide.