Surgeons and Robots: A Collaboration for Advanced Surgical Procedures
Introduction:
In the not-so-distant future, the world of surgery is undergoing a revolution, marked by the seamless integration of human expertise and cutting-edge robotic technology. Surgeons and robots are forming an unprecedented collaboration that promises to redefine the landscape of medical procedures, making surgeries more precise, less invasive, and ultimately improving patient outcomes. This article delves into the fascinating realm of surgical robotics, exploring the evolution of this collaboration, the current state of the field, and the potential it holds for the future.
The Evolution of Surgical Robotics:
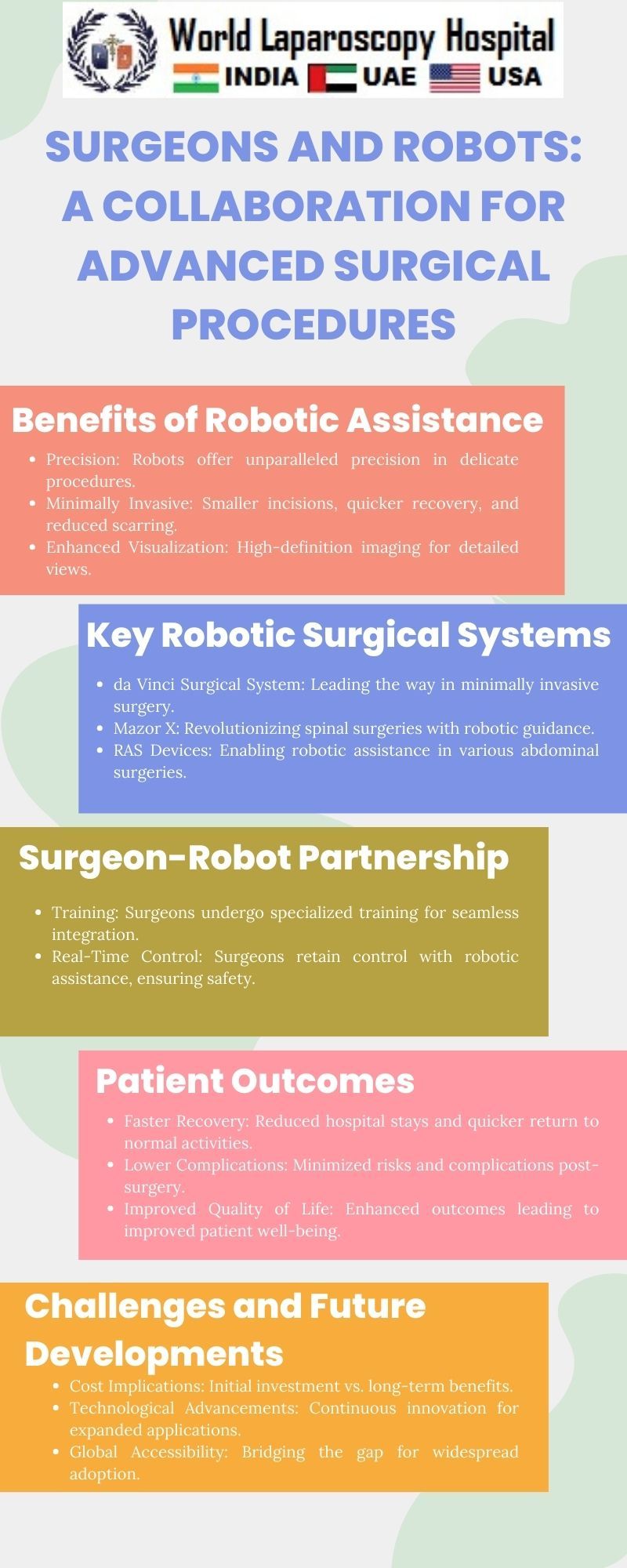
The journey towards the collaboration between surgeons and robots can be traced back to the early 20th century when the first attempts were made to introduce mechanical assistance into surgical procedures. However, it wasn't until the late 20th century that significant strides were made in the development of robotic systems for surgery. The introduction of the da Vinci Surgical System in the early 2000s marked a watershed moment, revolutionizing minimally invasive surgery.
The da Vinci System, developed by Intuitive Surgical, provided surgeons with enhanced precision, dexterity, and control through the use of robotic arms operated by a console. This breakthrough paved the way for a new era in surgical procedures, reducing the invasiveness of surgeries, minimizing scarring, and accelerating patient recovery. The success of the da Vinci System inspired further research and development in the field, leading to the creation of a diverse range of surgical robots with various capabilities.
Current State of Surgical Robotics:
As of the present day, surgical robotics has evolved far beyond its initial stages. Multiple robotic systems have been developed to cater to the specific needs of different medical specialties. For instance, the da Vinci Surgical System is widely used in urology, gynecology, and general surgery, demonstrating its versatility. Other robotic platforms, such as the Mako Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery System, have found their niche in orthopedic procedures, particularly in joint replacement surgeries.
One of the key advantages of surgical robots lies in their ability to perform minimally invasive procedures with unparalleled precision. The robotic arms, equipped with advanced instruments and guided by the surgeon's expertise, can navigate through delicate anatomical structures with a level of precision difficult to achieve through traditional methods. This precision translates into reduced trauma for patients, faster recovery times, and improved overall outcomes.
Moreover, robotic-assisted surgery allows for enhanced visualization, typically through high-definition 3D imaging systems. This provides surgeons with a detailed view of the surgical site, enabling them to make informed decisions and navigate complex anatomies with greater confidence. The incorporation of augmented reality and virtual reality technologies further augments the surgeon's spatial awareness and decision-making capabilities.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While surgical robotics has made remarkable progress, it is not without its challenges. One significant hurdle is the cost associated with acquiring and maintaining robotic systems. The initial investment and ongoing expenses can be prohibitive for many healthcare institutions, limiting the widespread adoption of this technology. Efforts are underway to address this issue, with researchers and industry stakeholders working on developing more cost-effective robotic solutions without compromising on performance.
Another challenge is the learning curve associated with mastering robotic-assisted surgery. Surgeons need to undergo specialized training to familiarize themselves with the robotic systems and refine their skills. As technology continues to advance, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms into robotic platforms holds the promise of reducing the learning curve by providing intelligent assistance and adaptive capabilities.
Despite these challenges, the opportunities presented by surgical robotics are immense. The ongoing research in the field aims to expand the applications of robotic-assisted surgery to a broader range of medical specialties. The integration of haptic feedback systems, allowing surgeons to feel the resistance and texture of tissues during robotic procedures, is a promising development that seeks to enhance the tactile experience and further blur the line between human and machine.
Future Horizons:
Looking ahead, the future of surgical robotics appears incredibly promising. One of the emerging trends is the development of collaborative robots, also known as cobots, which work alongside human surgeons. These systems leverage the strengths of both humans and robots, combining the surgeon's cognitive abilities with the robot's precision and endurance. Collaborative robots have the potential to revolutionize team-based surgical procedures, fostering a true partnership between surgeons and machines.
The integration of AI into surgical robotics is another frontier that holds great potential. AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets, identify patterns, and assist surgeons in making real-time decisions during surgery. This intelligent assistance can enhance surgical precision, reduce the risk of errors, and contribute to personalized treatment plans based on a patient's unique characteristics.
Additionally, advancements in nanotechnology are opening new possibilities for minimally invasive interventions at the molecular and cellular levels. Nanorobots, equipped with sensors and therapeutic capabilities, could navigate the human body with unprecedented precision, delivering targeted treatments and performing intricate procedures at a scale previously unimaginable.
Ethical Considerations:
As the collaboration between surgeons and robots continues to evolve, ethical considerations become paramount. Questions arise regarding the responsibility and accountability in cases of errors or malfunctions during robotic-assisted surgeries. Clear guidelines and ethical frameworks must be established to ensure the safe and responsible integration of robotic technology into medical practice.
Patient consent and transparency are crucial aspects that need careful attention. It is essential for healthcare providers to educate patients about the use of robotic systems in their procedures, addressing any concerns and ensuring informed decision-making. Striking a balance between innovation and patient safety will be a key challenge as the field of surgical robotics progresses.
Conclusion:
The collaboration between surgeons and robots represents a transformative journey in the field of surgery. From the early attempts at mechanical assistance to the sophisticated robotic systems of today, the partnership continues to redefine the possibilities of medical interventions. The current state of surgical robotics showcases the benefits of precision, minimally invasive procedures, and enhanced visualization, with ongoing research poised to unlock even greater potentials.
As we venture into the future, the evolution of surgical robotics holds the promise of expanding applications, reducing costs, and incorporating advanced technologies such as AI and nanorobotics. Ethical considerations will play a crucial role in shaping the responsible integration of robotic systems into medical practice. The symbiotic relationship between surgeons and robots is not just a technological advancement but a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of innovation in the service of healthcare and patient well-being.






