Robotic Assisted Microsurgery: A New Precision
Introduction:
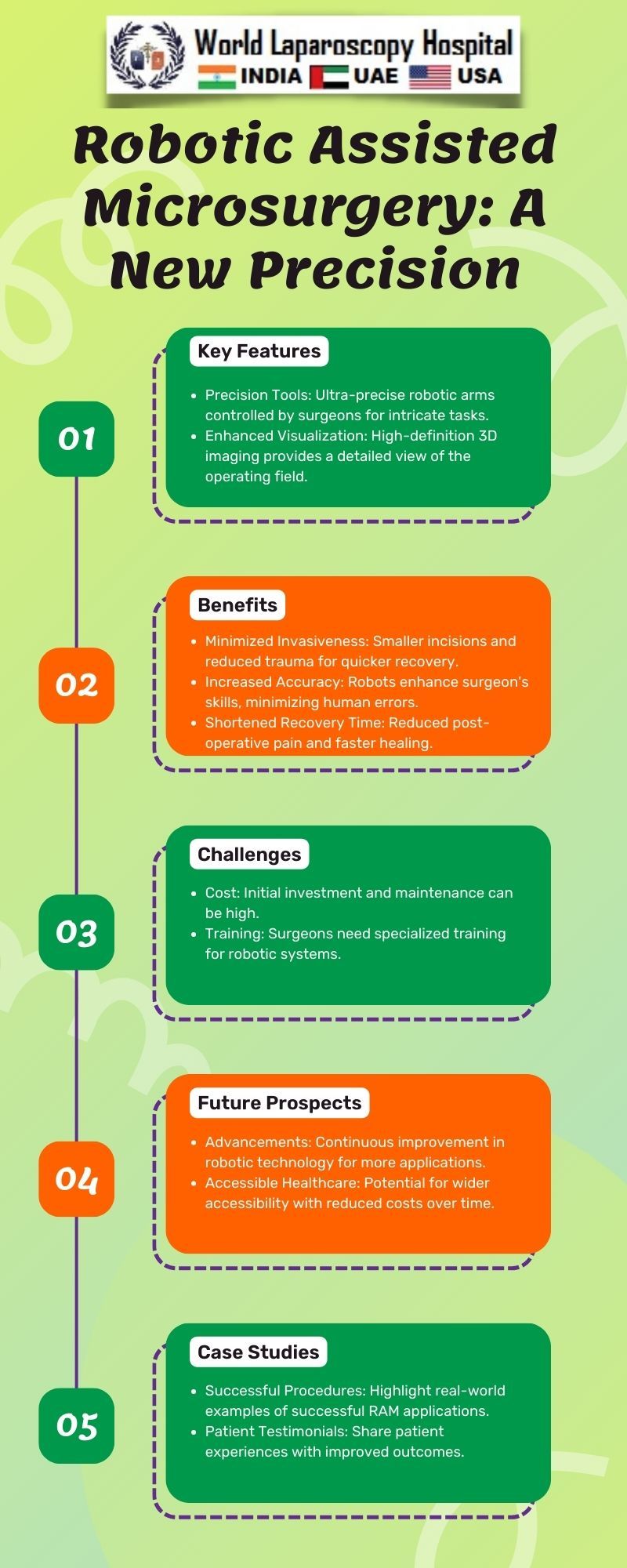
In the ever-evolving landscape of medical technology, robotic-assisted microsurgery has emerged as a groundbreaking innovation, offering unprecedented levels of precision and control. This cutting-edge approach integrates the capabilities of robotics with the finesse of microsurgery, opening new horizons for surgical procedures across various medical specialties. In this article, we will explore the evolution of robotic-assisted microsurgery, its applications, benefits, challenges, and the potential it holds for the future of healthcare.
The Evolution of Robotic-Assisted Microsurgery:
Origins of Microsurgery:
Microsurgery, with its roots dating back to the mid-20th century, marked a significant advancement in surgical techniques. The introduction of the surgical microscope enabled surgeons to perform intricate procedures with enhanced visualization. However, the limitations of human dexterity and the need for more precise tools laid the foundation for the integration of robotics.
Emergence of Surgical Robots:
The late 20th century witnessed the advent of surgical robots, with the da Vinci Surgical System leading the way. Initially designed for large-scale surgeries, the da Vinci system paved the path for miniaturization and adaptation to microsurgical procedures. The transition from traditional microsurgery to robotic-assisted microsurgery was underway.
Integration of Robotics and Microsurgery:
The convergence of robotic technology and microsurgery marked a paradigm shift. Manufacturers began developing specialized robotic platforms designed to facilitate microsurgical tasks with unparalleled precision. These systems incorporated advanced imaging, haptic feedback, and robotic arms equipped with microscale instruments, enabling surgeons to perform procedures with enhanced accuracy.
Applications of Robotic-Assisted Microsurgery:
Ophthalmology:
Robotic-assisted microsurgery has found a significant application in ophthalmology, particularly in delicate procedures such as retinal surgery. The ability of robotic systems to compensate for hand tremors and offer precise movements enhances the surgeon's capability to work on microscopic structures within the eye.
Neurosurgery:
In neurosurgery, where precision is paramount, robotic-assisted microsurgery has proven invaluable. Surgeons can navigate through intricate brain structures with enhanced control, minimizing the risk of damage to surrounding tissues. The integration of real-time imaging and robotic guidance has revolutionized procedures like tumor resections and aneurysm repairs.
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery:
Microsurgery plays a crucial role in plastic and reconstructive procedures, and the incorporation of robotic assistance has elevated the precision of tissue manipulation. Robotic systems allow for intricate suturing and grafting, facilitating complex reconstructive surgeries with improved outcomes.
Urology:
Within urology, robotic-assisted microsurgery has gained prominence in procedures such as prostatectomies and kidney reconstructions. The robotic platform provides enhanced dexterity and visualization, enabling surgeons to perform precise maneuvers in confined spaces with reduced invasiveness.
Benefits of Robotic-Assisted Microsurgery:
Enhanced Precision:
The primary advantage of robotic-assisted microsurgery is the unparalleled precision it offers. The robotic arms, controlled by a surgeon at a console, can execute movements at a microscale, minimizing the risk of errors and improving overall accuracy.
Improved Visualization:
Advanced imaging technologies integrated into robotic-assisted microsurgery systems provide surgeons with high-resolution, three-dimensional views of the surgical site. This enhanced visualization aids in navigating complex anatomical structures with greater confidence.
Minimally Invasive Approaches:
Robotic-assisted microsurgery allows for minimally invasive procedures, reducing the need for large incisions. This results in faster patient recovery, decreased postoperative pain, and a reduced risk of complications associated with open surgeries.
Tremor Elimination:
The incorporation of robotic systems helps eliminate hand tremors, a natural limitation of human dexterity. This is particularly crucial in microsurgery, where even the slightest tremor can have significant consequences.
Challenges and Limitations:
Cost:
The high cost of acquiring and maintaining robotic-assisted microsurgery systems remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption. The initial investment, coupled with ongoing expenses for training and system maintenance, poses financial challenges for healthcare institutions.
Learning Curve:
Mastery of robotic-assisted microsurgery requires surgeons to undergo specialized training to operate the robotic console effectively. The learning curve can be steep, and not all surgeons may readily adapt to this technology.
Availability and Accessibility:
The availability of robotic-assisted microsurgery is not uniform across all medical institutions. Rural and less affluent areas may face challenges in accessing this technology, leading to disparities in patient care.
Ethical and Legal Considerations:
The integration of robotics in healthcare raises ethical and legal questions, including issues related to patient consent, liability in case of system malfunctions, and the potential dehumanization of the doctor-patient relationship.
Future Perspectives:
Continued Technological Advancements:
The field of robotic-assisted microsurgery is poised for continuous advancements. Future systems may incorporate artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms for real-time decision support, further enhancing surgical precision and efficiency.
Expansion of Applications:
As technology evolves, the applications of robotic-assisted microsurgery are likely to expand into new medical specialties. Emerging fields, such as nanomedicine, may benefit from the integration of robotics at a molecular level.
Improved Affordability and Accessibility:
Efforts to reduce the cost of robotic-assisted microsurgery systems and enhance training programs are underway. Increased affordability and accessibility will contribute to broader adoption and improved patient outcomes.
Ethical Guidelines and Regulations:
As the technology advances, establishing clear ethical guidelines and regulations is crucial. Addressing concerns related to patient autonomy, data security, and the responsible use of robotic-assisted microsurgery will be paramount for its widespread acceptance.
Conclusion:
Robotic-assisted microsurgery represents a remarkable convergence of technology and medicine, offering a new level of precision that was once unimaginable. While challenges such as cost, training, and ethical considerations remain, the potential benefits for patients and the evolution of healthcare are substantial. As research and development in this field continue, robotic-assisted microsurgery is poised to redefine the boundaries of what is achievable in the realm of surgical interventions, ushering in a new era of precision medicine.



