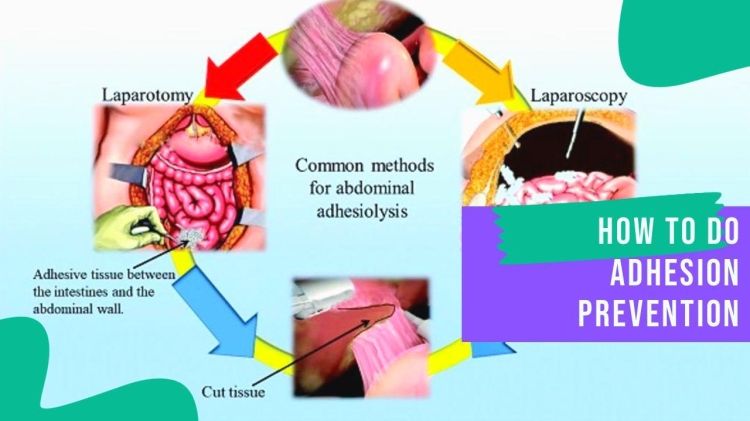
Adhesion Prevention during Laparoscopic Surgery
Reduction of adhesion formation during laparoscopic surgery is facilitated by minimal tissue handling and trauma, avoidance of exposure to foreign bodies (powder from gloves, gauze particles, and prevention of air pollution in the peritoneal cavity that leads to the reduction of tissue drying.
If performed adequately by well-trained surgeons, laparoscopy should induce less direct surgical trauma because of gentle tissue handling, meticulous hemostasis, constant irrigation, the use of microsurgical instruments, and the smaller operative field, which may reduce the risk of adhesion formation.
An adhesion barrier is a medical device that prevents adhesion during laparoscopic surgery. The adhesion barrier is used to separate internal tissues and organs to prevent the creation of scar tissue known as adhesion. The expansion of this market is being fueled by an increase in the number of surgeries and athletic injuries, as well as an increase in the aging population and the increasing awareness of adhesion-related disorders. oxidized regenerated cellulose, expanded polytetrafluoroethylene, sodium hyaluronate, and carboxymethylcellulose are used to make adhesion barriers. In surgeries and other operations, it is used widely.
The increasing aging population and the increasing awareness of the device’s benefits for various diseases can boost the demand in the market. Advancement in the sophisticated healthcare devices in developing nations, policy initiatives and financing by the government to improve necessary infrastructure, Research and Development to boost the efficiency of adhesion barriers devices. The rising prevalence of neurological illnesses, gynecological disorders, ophthalmic disorders, and cardiac disorders have also aided the market’s expansion.
Adhesion formation is one of the most significant complications of laparoscopic surgery, causing significant morbidity and mortality. Adhesion formation occurs when scar tissue develops between organs or tissues, which can lead to chronic pain, bowel obstruction, infertility, and other complications. The laparoscopic approach to surgery is becoming increasingly popular because it is minimally invasive, has a shorter recovery time, and results in fewer complications than traditional open surgery. However, laparoscopic surgery does not eliminate the risk of adhesion formation. In this essay, we will explore adhesion prevention during laparoscopic surgery and discuss some of the techniques used to minimize adhesion formation.
Factors Contributing to Adhesion Formation
There are several factors that contribute to adhesion formation during laparoscopic surgery. One of the primary factors is tissue trauma. When tissues are traumatized, such as during dissection or manipulation, it can cause inflammation, which can lead to adhesion formation. Another factor is ischemia, which occurs when tissues are deprived of oxygen and nutrients. Ischemia can occur when blood vessels are damaged or clamped during surgery, which can lead to tissue necrosis and subsequent adhesion formation. Additionally, the use of foreign materials, such as surgical meshes, can also contribute to adhesion formation.
Prevention of Adhesion Formation
There are several techniques used to prevent adhesion formation during laparoscopic surgery. These include the use of barrier materials, the use of anti-inflammatory agents, and the use of physical barriers.
Barrier Materials
Barrier materials are used to prevent the formation of adhesions by separating the tissues and preventing them from coming into contact with each other. There are several types of barrier materials used in laparoscopic surgery, including absorbable and non-absorbable materials.
Absorbable materials, such as oxidized regenerated cellulose (ORC) and hyaluronic acid-based products, are broken down and absorbed by the body over time. These materials are typically used for short-term prevention of adhesion formation.
Non-absorbable materials, such as expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) and polyethylene glycol (PEG), are not absorbed by the body and remain in place to prevent adhesion formation. These materials are typically used for long-term prevention of adhesion formation.
Anti-inflammatory Agents
Anti-inflammatory agents, such as corticosteroids, are used to reduce inflammation and prevent adhesion formation. Corticosteroids are typically administered intraoperatively or postoperatively and have been shown to reduce adhesion formation in some studies. However, there are concerns about the side effects of corticosteroids, including an increased risk of infection and delayed wound healing.
Physical Barriers
Physical barriers are used to prevent adhesion formation by separating tissues and preventing them from coming into contact with each other. There are several types of physical barriers used in laparoscopic surgery, including saline solution, non-stick coatings, and laparoscopic instruments.
Saline solution is often used to irrigate the surgical site and prevent tissues from sticking together. Non-stick coatings, such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and silicone, are applied to laparoscopic instruments to prevent tissue trauma and reduce the risk of adhesion formation. Laparoscopic instruments with a smooth surface and a reduced number of teeth also help to minimize tissue trauma and reduce the risk of adhesion formation.
There are other techniques used to prevent adhesion formation during laparoscopic surgery that are worth discussing, including the use of intraoperative fluids, laparoscopic techniques, and adhesion barriers.
Intraoperative Fluids
Intraoperative fluids, such as lactated Ringer's solution, have been shown to reduce the incidence of adhesion formation during laparoscopic surgery. The exact mechanism by which intraoperative fluids prevent adhesion formation is not well understood, but it is believed that the fluids help to reduce tissue trauma and inflammation.
Laparoscopic Techniques
Laparoscopic techniques, such as gentle tissue handling, can also help to prevent adhesion formation. Gentle tissue handling involves using a light touch when manipulating tissues, avoiding excessive tension on the tissues, and minimizing the use of electrocautery. This technique helps to reduce tissue trauma and inflammation, which can lead to a decreased risk of adhesion formation.
Adhesion Barriers
Adhesion barriers are materials that are placed at the site of surgery to prevent adhesion formation. These barriers can be absorbable or non-absorbable and can be placed in various locations, including the peritoneal cavity and the surgical incision. Adhesion barriers work by physically separating tissues and preventing them from coming into contact with each other.
One type of adhesion barrier is the hyaluronic acid-based barrier, which has been shown to reduce adhesion formation in some studies. Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring substance in the body that has anti-inflammatory and anti-adhesive properties. Another type of adhesion barrier is the Seprafilm barrier, which is a non-absorbable barrier that is placed in the peritoneal cavity to prevent adhesion formation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, adhesion formation is a significant complication of laparoscopic surgery, and several techniques can be used to prevent its occurrence. These techniques include the use of barrier materials, anti-inflammatory agents, physical barriers, intraoperative fluids, laparoscopic techniques, and adhesion barriers. It is essential to individualize the approach to adhesion prevention based on the patient's specific surgical needs and risk factors. By utilizing these techniques, surgeons can minimize the risk of adhesion formation and improve patient outcomes.
Top
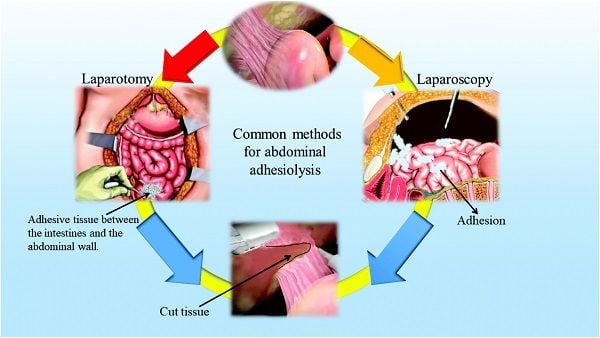
If performed adequately by well-trained surgeons, laparoscopy should induce less direct surgical trauma because of gentle tissue handling, meticulous hemostasis, constant irrigation, the use of microsurgical instruments, and the smaller operative field, which may reduce the risk of adhesion formation.

An adhesion barrier is a medical device that prevents adhesion during laparoscopic surgery. The adhesion barrier is used to separate internal tissues and organs to prevent the creation of scar tissue known as adhesion. The expansion of this market is being fueled by an increase in the number of surgeries and athletic injuries, as well as an increase in the aging population and the increasing awareness of adhesion-related disorders. oxidized regenerated cellulose, expanded polytetrafluoroethylene, sodium hyaluronate, and carboxymethylcellulose are used to make adhesion barriers. In surgeries and other operations, it is used widely.
The increasing aging population and the increasing awareness of the device’s benefits for various diseases can boost the demand in the market. Advancement in the sophisticated healthcare devices in developing nations, policy initiatives and financing by the government to improve necessary infrastructure, Research and Development to boost the efficiency of adhesion barriers devices. The rising prevalence of neurological illnesses, gynecological disorders, ophthalmic disorders, and cardiac disorders have also aided the market’s expansion.
Adhesion formation is one of the most significant complications of laparoscopic surgery, causing significant morbidity and mortality. Adhesion formation occurs when scar tissue develops between organs or tissues, which can lead to chronic pain, bowel obstruction, infertility, and other complications. The laparoscopic approach to surgery is becoming increasingly popular because it is minimally invasive, has a shorter recovery time, and results in fewer complications than traditional open surgery. However, laparoscopic surgery does not eliminate the risk of adhesion formation. In this essay, we will explore adhesion prevention during laparoscopic surgery and discuss some of the techniques used to minimize adhesion formation.
Factors Contributing to Adhesion Formation
There are several factors that contribute to adhesion formation during laparoscopic surgery. One of the primary factors is tissue trauma. When tissues are traumatized, such as during dissection or manipulation, it can cause inflammation, which can lead to adhesion formation. Another factor is ischemia, which occurs when tissues are deprived of oxygen and nutrients. Ischemia can occur when blood vessels are damaged or clamped during surgery, which can lead to tissue necrosis and subsequent adhesion formation. Additionally, the use of foreign materials, such as surgical meshes, can also contribute to adhesion formation.
Prevention of Adhesion Formation
There are several techniques used to prevent adhesion formation during laparoscopic surgery. These include the use of barrier materials, the use of anti-inflammatory agents, and the use of physical barriers.
Barrier Materials
Barrier materials are used to prevent the formation of adhesions by separating the tissues and preventing them from coming into contact with each other. There are several types of barrier materials used in laparoscopic surgery, including absorbable and non-absorbable materials.
Absorbable materials, such as oxidized regenerated cellulose (ORC) and hyaluronic acid-based products, are broken down and absorbed by the body over time. These materials are typically used for short-term prevention of adhesion formation.
Non-absorbable materials, such as expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) and polyethylene glycol (PEG), are not absorbed by the body and remain in place to prevent adhesion formation. These materials are typically used for long-term prevention of adhesion formation.
Anti-inflammatory Agents
Anti-inflammatory agents, such as corticosteroids, are used to reduce inflammation and prevent adhesion formation. Corticosteroids are typically administered intraoperatively or postoperatively and have been shown to reduce adhesion formation in some studies. However, there are concerns about the side effects of corticosteroids, including an increased risk of infection and delayed wound healing.
Physical Barriers
Physical barriers are used to prevent adhesion formation by separating tissues and preventing them from coming into contact with each other. There are several types of physical barriers used in laparoscopic surgery, including saline solution, non-stick coatings, and laparoscopic instruments.
Saline solution is often used to irrigate the surgical site and prevent tissues from sticking together. Non-stick coatings, such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and silicone, are applied to laparoscopic instruments to prevent tissue trauma and reduce the risk of adhesion formation. Laparoscopic instruments with a smooth surface and a reduced number of teeth also help to minimize tissue trauma and reduce the risk of adhesion formation.
There are other techniques used to prevent adhesion formation during laparoscopic surgery that are worth discussing, including the use of intraoperative fluids, laparoscopic techniques, and adhesion barriers.
Intraoperative Fluids
Intraoperative fluids, such as lactated Ringer's solution, have been shown to reduce the incidence of adhesion formation during laparoscopic surgery. The exact mechanism by which intraoperative fluids prevent adhesion formation is not well understood, but it is believed that the fluids help to reduce tissue trauma and inflammation.
Laparoscopic Techniques
Laparoscopic techniques, such as gentle tissue handling, can also help to prevent adhesion formation. Gentle tissue handling involves using a light touch when manipulating tissues, avoiding excessive tension on the tissues, and minimizing the use of electrocautery. This technique helps to reduce tissue trauma and inflammation, which can lead to a decreased risk of adhesion formation.
Adhesion Barriers
Adhesion barriers are materials that are placed at the site of surgery to prevent adhesion formation. These barriers can be absorbable or non-absorbable and can be placed in various locations, including the peritoneal cavity and the surgical incision. Adhesion barriers work by physically separating tissues and preventing them from coming into contact with each other.
One type of adhesion barrier is the hyaluronic acid-based barrier, which has been shown to reduce adhesion formation in some studies. Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring substance in the body that has anti-inflammatory and anti-adhesive properties. Another type of adhesion barrier is the Seprafilm barrier, which is a non-absorbable barrier that is placed in the peritoneal cavity to prevent adhesion formation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, adhesion formation is a significant complication of laparoscopic surgery, and several techniques can be used to prevent its occurrence. These techniques include the use of barrier materials, anti-inflammatory agents, physical barriers, intraoperative fluids, laparoscopic techniques, and adhesion barriers. It is essential to individualize the approach to adhesion prevention based on the patient's specific surgical needs and risk factors. By utilizing these techniques, surgeons can minimize the risk of adhesion formation and improve patient outcomes.