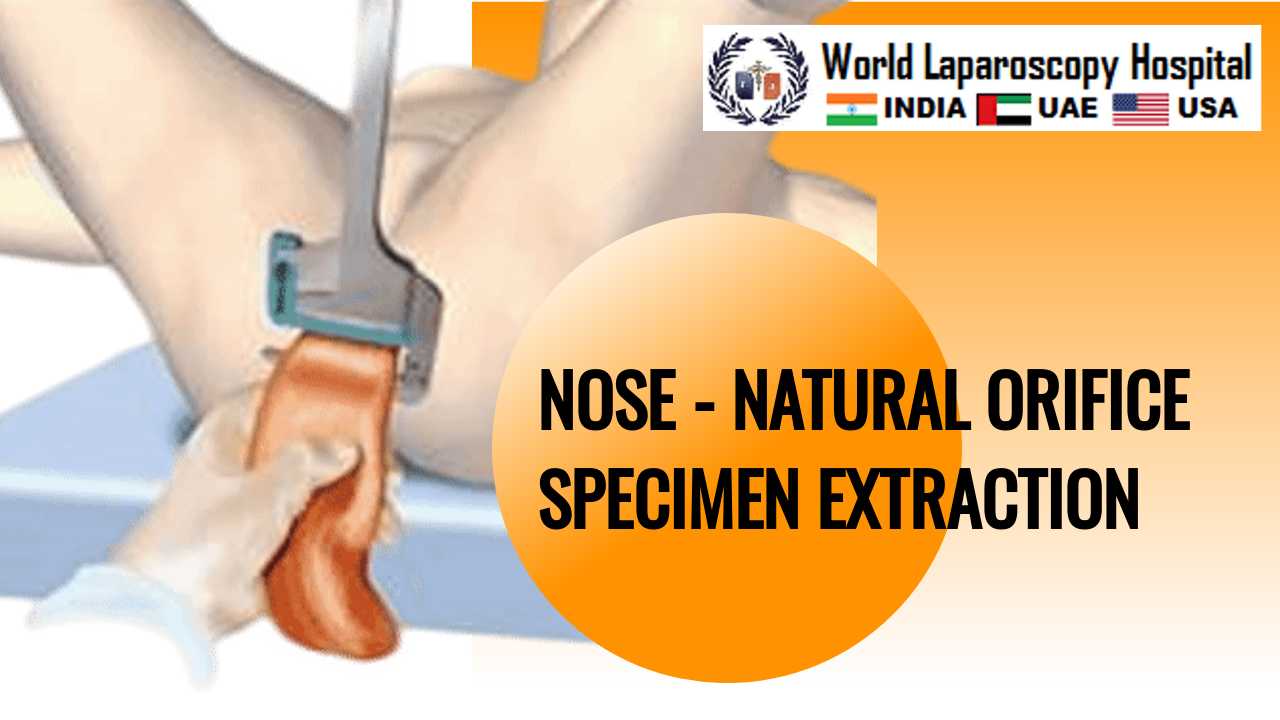
The premise of this method is to decrease the injury needed to get rid of the specimen with the expectation that this may enhance end results. Reduction in postoperative analgesic usage, quicker return of bowel function, and shorter size of medical facility stay have been observed in colorectal operations with NOSE compared to standard specimen extraction. While the feasibility of NOSE has been shown in colon surgical treatment, failings of this method have actually additionally been described. The choice of people that can successfully undergo NOSE needs additional examination. Natural orifice sampling extraction (NOSE) eliminates removal website injury, which is or else always required. NOSE is defined as the elimination of a medical specimen by opening a hollow viscus that already connects with the outdoors, such as the anus or the vaginal area. As opposed to obtaining the specimen through an abdominal laceration, a viscerotomy is utilized for specimen extraction, which permits people to completely avoid the morbidity associated with larger abdominal cuts. The feasibility of NOSE in colon surgical treatment is well documented.
The option of NOSE by means of the vaginal area appears to be the most considerable element adding to greater NOSE success in ladies compared to men. It has been well developed that the flexible residential or commercial properties of the vagina allow the removal of even more bulky specimens when compared to proctotomies.
A barrier to wider adoption of NOSE is technological trouble. The mini-laparotomy, in some cases, is utilized to execute a majority of the operation, as in hand-assisted laparoscopy. Adoption of NOSE by cosmetic surgeons that usually perform colectomies in this fashion would certainly be faced with a steeper knowing curve than surgeons that make use of the mini-laparotomy solely as a specimen extraction site. On that note, intracorporeal anastomosis is a prerequisite ability for those adopting NOSE. Removal of more proximal specimens, as in an appropriate colectomy, needs the existence of a competent endoscopist that can arrest and also pull the sampling endoluminal through the size of the distal intestinal tract. Sampling extraction via the vaginal area needs a posterior colpotomy, an operative maneuver that is not generally performed by basic or intestines doctors. Additionally, these technical challenges are amplified by an absence of standardization of the technique.
The demands for these technological abilities are more vital in getting rid of right-sided colon pathology as contrasted to left-sided pathology. There are fundamental structural elements that make NOSE for right-sided colon pathology harder. Right colectomy specimens removed via the reduced stomach tract via distal colotomy must travel the length of the continuing to be transverse, descending, as well as sigmoid colon, with the anus and out of the anus utilizing an endoscope. While this was shown to be viable in 2010 by Eshuis, it is inherently tough due to the anatomically slim and torturous sigmoid colon. Because the collection, extraction through colotomy stopped working in 2 of 10 patients because of the mass of the sampling. This strategy is still performed in some centers, though restrictions associated with the dimension of the sampling are stricter than for left-sided colon sores. This approach has little practicality because of its substantial technical challenges, therefore its restricted use.
The vaginectomy, additionally called a colpotomy, is a secure technique typically employed by gynecologists and has been applied in NOSE for both gynecologic and also intestines pathologies. The first videotaped genital specimen removals in colon surgical treatment were in the 1990s. This strategy remains to be executed, particularly for right-sided colon pathology, offered the problem of using the distal colon for specimen removal.
Several research studies recommend some benefit to NOSE over laparoscopy with traditional stomach wall surface specimen extraction. Superior results in terms of postoperative discomfort control, time to very first digestive tract function, hospital length of keep, lowered incisional issues, as well as improved cosmesis, have actually been shown. It must be noted that research studies showing these remarkable results had stringent addition requirements. Mindful exam of patient characteristics in these research studies can be used to extrapolate themes that can help in picking individuals that can most gain from NOSE in intestines surgery.
Natural Orifice Specimen Extraction (NOSE) is a surgical technique that involves the removal of specimens through natural orifices, such as the mouth, anus, or vagina, rather than through a traditional surgical incision. The NOSE technique has several potential benefits over traditional surgical techniques, including reduced scarring, reduced pain, and faster recovery times. In this essay, we will discuss the NOSE technique, its benefits and challenges, and its potential impact on the field of surgery.
The NOSE Technique:
The NOSE technique involves the removal of specimens through natural orifices, such as the mouth, anus, or vagina, rather than through a traditional surgical incision. The technique is typically used in laparoscopic surgery, where small incisions are made in the abdomen to allow the insertion of surgical instruments and a camera. After the surgical procedure is complete, the specimen is removed through a natural orifice using a special retrieval bag.
Benefits of the NOSE Technique:
The NOSE technique offers several potential benefits over traditional surgical techniques, including:
-
Reduced Scarring: The NOSE technique involves the removal of specimens through natural orifices, which can reduce scarring and improve cosmetic outcomes for patients.
-
Reduced Pain: The NOSE technique is associated with reduced pain compared to traditional surgical techniques. The technique does not require a large surgical incision, which can reduce pain and discomfort for patients.
-
Faster Recovery: The NOSE technique can lead to faster recovery times compared to traditional surgical techniques. The technique is less invasive, which can lead to shorter hospital stays and faster return to normal activities.
-
Reduced Healthcare Costs: The NOSE technique may lead to reduced healthcare costs. Shorter hospital stays and faster recovery times can reduce healthcare costs for both patients and healthcare providers.
Challenges of the NOSE Technique:
The NOSE technique also presents several challenges that must be considered, including:
-
Technical Difficulty: The NOSE technique can be technically challenging, and surgeons must undergo specialized training to become proficient in the technique.
-
Risk of Infection: The NOSE technique carries a risk of infection, as specimens are removed through natural orifices that are not typically sterile.
-
Limited Access: The NOSE technique may be limited in its ability to access certain areas of the body, as natural orifices may not provide adequate access to the surgical site.
-
Retrieval Bag Complications: The use of a retrieval bag to remove specimens through a natural orifice may present its own set of complications, including rupture of the bag and spillage of the specimen.
Potential Impact on the Field of Surgery:
The NOSE technique has the potential to revolutionize the field of surgery. The technique offers several benefits over traditional surgical techniques, including reduced scarring, reduced pain, and faster recovery times. These benefits can improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs, which is essential in an era of rising healthcare costs and increased demand for high-quality care.
The NOSE technique may also lead to further advancements in minimally invasive surgery. As surgeons become more comfortable with the technique, they may be able to perform even more complex surgical procedures with improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
In addition to its potential impact on patient outcomes and healthcare costs, the NOSE technique may also have a significant impact on surgical education and training. Surgeons will need to undergo specialized training to become proficient in the technique, and surgical education programs may need to update their curricula to incorporate this new technique.
The NOSE technique requires specialized training for surgeons, and surgical education programs may need to update their curricula to incorporate this new technique. Surgeons who become proficient in the technique may be able to perform even more complex surgical procedures with improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
In addition to its potential impact on surgical education and training, the NOSE technique may also have implications for patient education and acceptance. Patients may be hesitant to undergo surgery through natural orifices, and it will be important for healthcare providers to educate patients on the benefits and risks of the technique.
The NOSE technique is still a relatively new and evolving technique, and further research is needed to fully understand its safety, efficacy, and cost-effectiveness. Long-term studies are needed to assess the technique's impact on patient outcomes and healthcare costs.
Overall, the NOSE technique represents an exciting development in the field of surgery. The technique offers several potential benefits over traditional surgical techniques, and its adoption may lead to improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs. As surgeons become more comfortable with the technique and more patients undergo surgery through natural orifices, the true potential of the NOSE technique may be realized.
Conclusion:
The NOSE technique is a surgical technique that involves the removal of specimens through natural orifices rather than through a traditional surgical incision. The technique offers several potential benefits over traditional surgical techniques, including reduced scarring, reduced pain, and faster recovery times. However, the technique is not without its challenges, including technical difficulty, risk of infection, limited access, and retrieval bag complications. Despite these challenges, the NOSE technique has the potential to revolutionize the field of surgery and improve patient outcomes while reducing healthcare costs.


