Introduction
In the realm of medical advancements, robotic surgery has emerged as a transformative force, offering precision and efficacy in treating a myriad of conditions. While initially developed for adults, the application of robotic surgery has expanded into pediatric medicine, ushering in a new era of possibilities for young patients. This article delves into the realm of pediatric robotic surgery, exploring its evolution, current applications, and the promising future it holds for improving outcomes in young individuals.
The Evolution of Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery, also known as robot-assisted surgery, first gained prominence in the 1980s with the development of the PUMA 560, a robotic system used for neurosurgical biopsies. However, it was the da Vinci Surgical System, introduced in the early 2000s, that marked a significant milestone in the field. Initially designed for adult procedures, the da Vinci system quickly demonstrated its potential for pediatric applications.
Challenges in Pediatric Surgery
Pediatric surgery poses unique challenges compared to adult procedures. The smaller size of pediatric patients, delicate tissues, and the need for utmost precision make traditional open surgeries or even laparoscopic procedures challenging. The limitations of conventional methods prompted the exploration of robotic surgery as a viable alternative.
Advantages of Pediatric Robotic Surgery
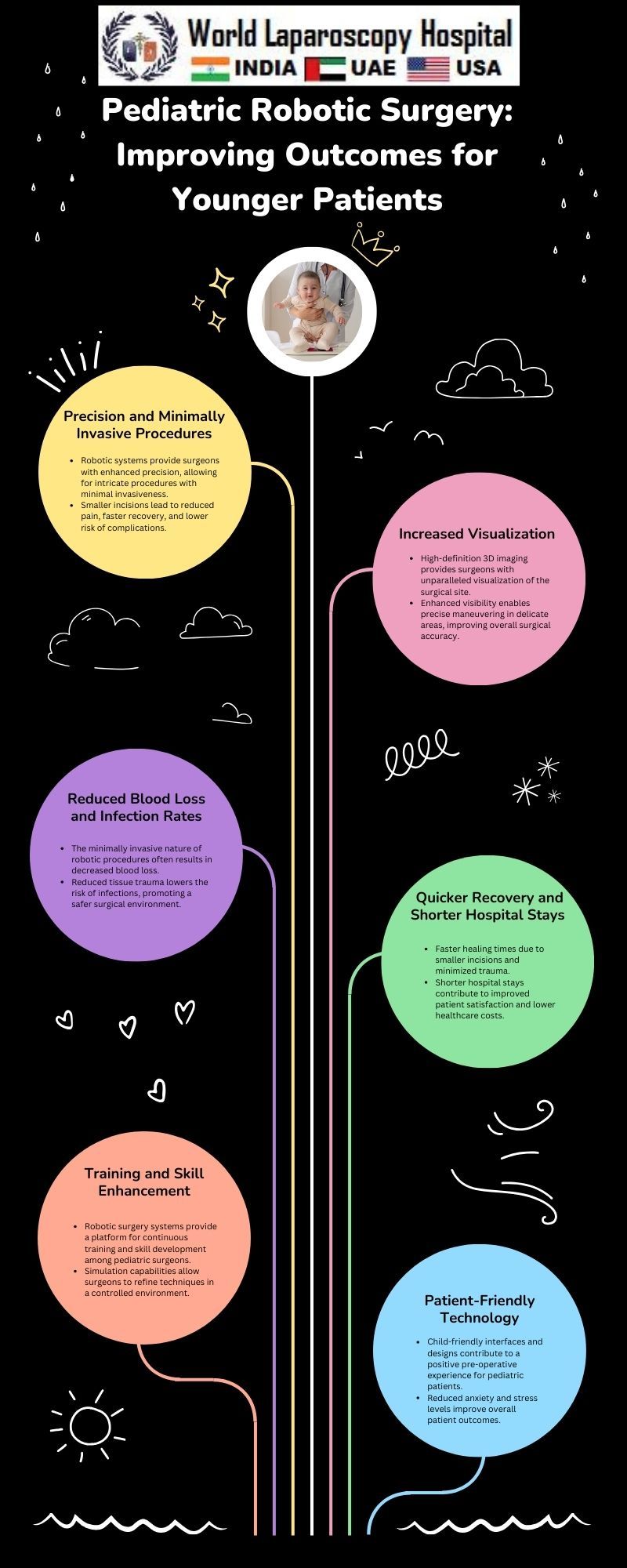
Precision and Dexterity:
One of the primary advantages of robotic surgery lies in its precision and dexterity. The robotic arms, controlled by a surgeon from a console, offer a greater range of motion and finer control than human hands alone. This is particularly advantageous in delicate pediatric surgeries where precision is paramount.
Minimally Invasive Approach:
Pediatric robotic surgery allows for a minimally invasive approach, with smaller incisions compared to traditional open surgeries. This is crucial in minimizing trauma to the young patient's body, reducing pain, and expediting recovery.
3D Visualization:
The incorporation of three-dimensional visualization in robotic surgery provides surgeons with enhanced depth perception, allowing for better navigation within the confined spaces of a child's body. This improved visualization is invaluable in intricate procedures, such as neurosurgery or cardiac surgery in pediatric patients.
Reduced Blood Loss and Scarring:
The precision of robotic surgery often results in reduced blood loss during procedures. Additionally, the smaller incisions contribute to minimal scarring, a significant aesthetic and psychological benefit for pediatric patients and their families.
Applications of Pediatric Robotic Surgery
Cardiovascular Surgery:
Pediatric robotic surgery has found success in complex cardiovascular procedures. The precision offered by robotic instruments is particularly beneficial in intricate surgeries such as repairing congenital heart defects. The ability to work in tight spaces and perform precise suturing contributes to improved outcomes in these cases.
Urological Procedures:
Robotic surgery has become a preferred option for various pediatric urological conditions, including pyeloplasty and reconstructive surgeries. The enhanced precision of robotic instruments is particularly advantageous when dealing with small and delicate structures in the urinary system.
Gastrointestinal Surgery:
In gastrointestinal surgery, pediatric patients benefit from the minimally invasive nature of robotic procedures. Conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or inflammatory bowel disease can be addressed with reduced trauma and faster recovery.
Neurosurgery:
The application of robotic surgery in pediatric neurosurgery is a groundbreaking development. Surgeons can navigate intricate structures in the brain with unprecedented precision, making it a valuable tool in the treatment of conditions such as brain tumors or epilepsy.
Orthopedic Procedures:
Robotic-assisted orthopedic surgeries are becoming increasingly common in pediatric patients. From spine surgeries to joint reconstructions, the enhanced precision of robotic instruments contributes to better long-term outcomes.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Pediatric Robotic Surgery
Robotic-Assisted Congenital Heart Surgery:
In a pioneering case, a team of surgeons successfully performed a robotic-assisted repair of a complex congenital heart defect in a newborn. The precision afforded by the robotic instruments played a crucial role in the success of the procedure, and the patient experienced a faster recovery compared to traditional open-heart surgery.
Minimally Invasive Neurosurgery:
A case study involving a pediatric patient with a brain tumor showcased the advantages of robotic-assisted neurosurgery. The surgeon, operating the robotic console, was able to precisely navigate and remove the tumor with minimal damage to surrounding healthy tissue. The patient experienced a shorter hospital stay and quicker recovery.
Pediatric Urological Robotic Surgery:
Robotic-assisted surgery has become the standard of care for certain pediatric urological conditions. A case series highlighted successful outcomes in children undergoing robotic pyeloplasty for the correction of obstructive lesions in the urinary tract. The minimally invasive approach resulted in less postoperative pain and a faster return to normal activities.
Challenges and Considerations
While pediatric robotic surgery offers numerous advantages, it is not without its challenges. The cost of robotic systems, the need for specialized training for surgeons, and concerns about long-term effects on young patients are among the considerations that the medical community must address. Additionally, ongoing research is essential to refine techniques and expand the repertoire of pediatric robotic procedures.
The Future of Pediatric Robotic Surgery
The future of pediatric robotic surgery is promising, with ongoing research and technological advancements continually expanding its applications. Some areas of development and exploration include:
Integration of Artificial Intelligence:
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into robotic surgery systems holds the potential to enhance decision-making during procedures. AI algorithms can analyze real-time data, offering insights and suggestions to the surgeon, further improving precision and outcomes.
Remote Surgery and Telemedicine:
Advancements in telemedicine and robotic technology may enable surgeons to perform procedures remotely. This has the potential to bring specialized pediatric surgical care to regions with limited access to healthcare resources, ultimately benefiting a larger population of young patients.
Customized Robotic Instruments:
As technology advances, the development of specialized robotic instruments for pediatric surgery may become more prevalent. Instruments designed specifically for the unique anatomy and requirements of pediatric patients could further improve the safety and efficacy of robotic procedures.
Ethical Considerations and Patient Safety
As with any technological advancement in medicine, ethical considerations and patient safety are paramount. The medical community must address concerns regarding the long-term effects of robotic surgery on pediatric patients, ensuring that the benefits outweigh any potential risks. Ongoing monitoring and research into the outcomes of pediatric robotic procedures will contribute to the establishment of best practices and guidelines.
Conclusion
Pediatric robotic surgery represents a groundbreaking frontier in healthcare, offering a range of benefits for young patients with complex medical conditions. From cardiovascular procedures to neurosurgery, the precision and minimally invasive nature of robotic surgery contribute to improved outcomes and faster recovery times. As technology continues to advance, the future holds even more promise, with the integration of artificial intelligence and the potential for remote surgery expanding the reach of specialized pediatric care.


