The Influence of Robotic Surgery on Medical Device Innovation
The Influence of Robotic Surgery on Medical Device Innovation
Introduction
The landscape of modern medicine is continually shaped by technological advancements, and one of the most revolutionary changes in recent years has been the integration of robotics into surgical procedures. Robotic surgery has not only transformed the way surgeries are performed but has also become a catalyst for innovation in medical devices. This article delves into the profound influence of robotic surgery on medical device innovation, exploring the evolution of technology and its impact on patient outcomes, surgical precision, and the overall landscape of healthcare.
The Emergence of Robotic Surgery
Historical Perspective
The roots of robotic surgery can be traced back to the mid-20th century when the first robotic system, Unimate, was developed for industrial applications. The concept of using robotic assistance in surgery gained momentum in the 1980s, with the introduction of the PUMA 560 robotic surgical arm. However, it wasn't until the late 1990s that the da Vinci Surgical System, a breakthrough in robotic-assisted surgery, made its debut in the medical field.
Evolution of the da Vinci Surgical System
The da Vinci Surgical System, developed by Intuitive Surgical, marked a significant leap forward in robotic surgery. Introduced in 1999, it provided a minimally invasive alternative to traditional open surgeries, allowing surgeons to perform complex procedures through small incisions. The system's robotic arms, controlled by a console, offered enhanced dexterity and precision, setting a new standard for surgical capabilities.
Robotic Surgery in Practice
Advantages of Robotic Surgery
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Robotic surgery enables minimally invasive procedures, reducing the need for large incisions. This results in shorter recovery times, decreased pain, and lower risk of complications compared to traditional open surgeries. Patients often experience less scarring and a faster return to normal activities.
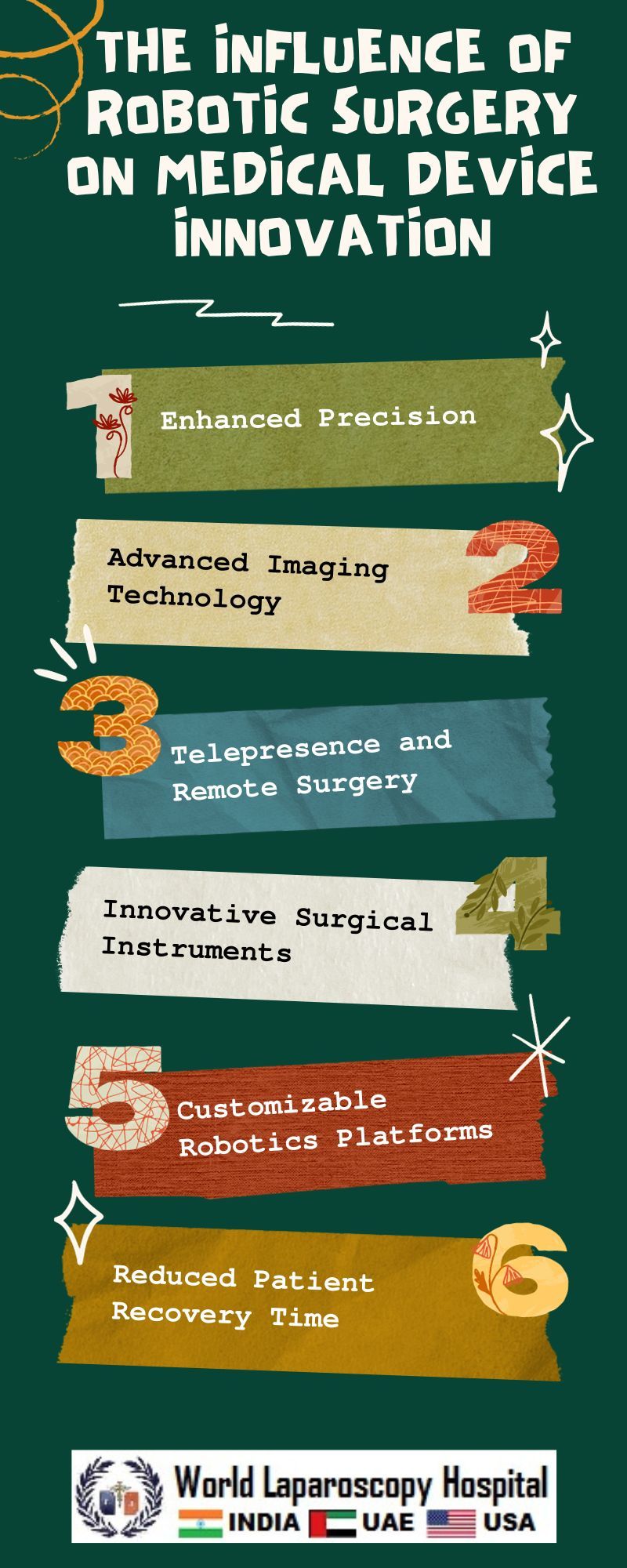
Enhanced Precision
The robotic arms of systems like the da Vinci provide surgeons with a greater range of motion and improved precision. The ability to perform intricate maneuvers with high accuracy is particularly beneficial in delicate surgeries, such as cardiac or neurosurgical procedures.
3D Visualization
Robotic surgical systems offer three-dimensional visualization, providing surgeons with a detailed and magnified view of the surgical site. This enhanced visual feedback contributes to better decision-making and more precise execution of procedures.
Applications Across Medical Specialties
Gynecology
Robotic surgery has found extensive applications in gynecological procedures, including hysterectomies and myomectomies. The minimally invasive approach of robotic-assisted surgery reduces trauma to surrounding tissues, resulting in quicker recovery times and improved patient outcomes.
Urology
In urology, robotic surgery has become a preferred option for procedures such as prostatectomies. The precision afforded by robotic systems allows for meticulous dissection and reconstruction, reducing the risk of complications and preserving surrounding structures.
General Surgery
The versatility of robotic surgical systems extends to various general surgical procedures, including colorectal surgeries and hernia repairs. Surgeons benefit from improved ergonomics and enhanced visualization, contributing to better overall surgical outcomes.
Cardiothoracic Surgery
In the realm of cardiothoracic surgery, robotic systems have been employed for procedures such as mitral valve repair and coronary artery bypass grafting. The intricate nature of cardiac surgery benefits from the precision and dexterity offered by robotic-assisted techniques.
The Impact on Medical Device Innovation
Driving Technological Advancements
Instrumentation and Tools
The introduction of robotic surgery has spurred innovation in the design and functionality of surgical instruments. Manufacturers have developed specialized robotic instruments with increased dexterity and articulation, allowing surgeons to perform complex maneuvers with greater ease.
Imaging and Visualization
Robotic surgical systems have driven improvements in imaging and visualization technologies. High-definition, three-dimensional imaging systems provide surgeons with detailed views of the surgical field, enabling more accurate and informed decision-making during procedures.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence
The convergence of robotic surgery and artificial intelligence (AI) has opened new avenues for innovation. AI algorithms can analyze real-time data from robotic systems, assisting surgeons in making informed decisions and optimizing surgical outcomes. This integration also holds promise for autonomous surgical procedures in the future.
Remote Surgery and Telemedicine
The evolution of robotic surgery has paved the way for remote surgery, allowing surgeons to perform procedures from a different location. This capability becomes crucial in scenarios where specialized expertise is needed but not physically present. Additionally, telemedicine has benefited from the integration of robotics, enabling consultations and follow-ups with patients in remote locations.
Customization and Personalization
Advancements in robotic surgery have led to a more personalized approach to patient care. The ability to tailor surgical procedures to individual patient anatomy and characteristics enhances the efficacy of treatments and reduces the risk of complications. Customizable robotic platforms cater to the unique needs of each patient, further optimizing surgical outcomes.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Cost and Accessibility
While robotic surgery offers numerous advantages, one of the primary challenges is the high cost associated with acquiring and maintaining robotic systems. This cost can limit accessibility, particularly in healthcare systems with budget constraints. Striking a balance between the benefits and costs remains a crucial consideration in the widespread adoption of robotic surgery.
Training and Learning Curve
The proficiency required to operate robotic systems adds a layer of complexity to surgical training. Surgeons must undergo specialized training to master the nuances of robotic-assisted procedures. The learning curve associated with robotic surgery raises questions about the standardization of training programs and the need for continuous education.
Ethical Considerations
As robotic surgery advances, ethical considerations come to the forefront. Questions surrounding patient consent, transparency about the use of robotic systems, and potential job displacement for non-robotic surgical staff warrant careful examination. Balancing the benefits of technological innovation with ethical concerns is essential for responsible and sustainable adoption.
Future Directions and Possibilities
Continued Advancements in Robotics
The field of robotic surgery is dynamic, with ongoing research and development aimed at further enhancing robotic systems. Continued miniaturization, increased mobility, and advancements in haptic feedback are areas of focus that promise to refine the capabilities of robotic surgical platforms.
Expansion into New Specialties
As technology evolves, robotic surgery is likely to expand into new medical specialties. Ongoing research is exploring the feasibility and efficacy of robotic-assisted procedures in areas such as orthopedics, ophthalmology, and even plastic surgery.
AI Integration and Autonomy
The integration of artificial intelligence into robotic surgery holds the potential for autonomous procedures. AI algorithms could analyze data in real time, making decisions and adjustments during surgery. While this prospect raises ethical considerations, it also opens the door to further advancements in precision and efficiency.
Conclusion
Robotic surgery has undeniably left an indelible mark on the landscape of medical device innovation. From the pioneering days of the da Vinci Surgical System to the current era of advanced robotics and artificial intelligence, the influence of robotic surgery extends far beyond the operating room. As technology continues to evolve, the synergy between robotics and medical device innovation will undoubtedly shape the future of healthcare, offering new possibilities for improved patient outcomes, personalized treatments, and a more efficient and accessible healthcare system.
Top
Introduction
The landscape of modern medicine is continually shaped by technological advancements, and one of the most revolutionary changes in recent years has been the integration of robotics into surgical procedures. Robotic surgery has not only transformed the way surgeries are performed but has also become a catalyst for innovation in medical devices. This article delves into the profound influence of robotic surgery on medical device innovation, exploring the evolution of technology and its impact on patient outcomes, surgical precision, and the overall landscape of healthcare.

The Emergence of Robotic Surgery
Historical Perspective
The roots of robotic surgery can be traced back to the mid-20th century when the first robotic system, Unimate, was developed for industrial applications. The concept of using robotic assistance in surgery gained momentum in the 1980s, with the introduction of the PUMA 560 robotic surgical arm. However, it wasn't until the late 1990s that the da Vinci Surgical System, a breakthrough in robotic-assisted surgery, made its debut in the medical field.
Evolution of the da Vinci Surgical System
The da Vinci Surgical System, developed by Intuitive Surgical, marked a significant leap forward in robotic surgery. Introduced in 1999, it provided a minimally invasive alternative to traditional open surgeries, allowing surgeons to perform complex procedures through small incisions. The system's robotic arms, controlled by a console, offered enhanced dexterity and precision, setting a new standard for surgical capabilities.
Robotic Surgery in Practice
Advantages of Robotic Surgery
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Robotic surgery enables minimally invasive procedures, reducing the need for large incisions. This results in shorter recovery times, decreased pain, and lower risk of complications compared to traditional open surgeries. Patients often experience less scarring and a faster return to normal activities.
Enhanced Precision
The robotic arms of systems like the da Vinci provide surgeons with a greater range of motion and improved precision. The ability to perform intricate maneuvers with high accuracy is particularly beneficial in delicate surgeries, such as cardiac or neurosurgical procedures.
3D Visualization
Robotic surgical systems offer three-dimensional visualization, providing surgeons with a detailed and magnified view of the surgical site. This enhanced visual feedback contributes to better decision-making and more precise execution of procedures.
Applications Across Medical Specialties
Gynecology
Robotic surgery has found extensive applications in gynecological procedures, including hysterectomies and myomectomies. The minimally invasive approach of robotic-assisted surgery reduces trauma to surrounding tissues, resulting in quicker recovery times and improved patient outcomes.
Urology
In urology, robotic surgery has become a preferred option for procedures such as prostatectomies. The precision afforded by robotic systems allows for meticulous dissection and reconstruction, reducing the risk of complications and preserving surrounding structures.
General Surgery
The versatility of robotic surgical systems extends to various general surgical procedures, including colorectal surgeries and hernia repairs. Surgeons benefit from improved ergonomics and enhanced visualization, contributing to better overall surgical outcomes.
Cardiothoracic Surgery
In the realm of cardiothoracic surgery, robotic systems have been employed for procedures such as mitral valve repair and coronary artery bypass grafting. The intricate nature of cardiac surgery benefits from the precision and dexterity offered by robotic-assisted techniques.
The Impact on Medical Device Innovation
Driving Technological Advancements
Instrumentation and Tools
The introduction of robotic surgery has spurred innovation in the design and functionality of surgical instruments. Manufacturers have developed specialized robotic instruments with increased dexterity and articulation, allowing surgeons to perform complex maneuvers with greater ease.
Imaging and Visualization
Robotic surgical systems have driven improvements in imaging and visualization technologies. High-definition, three-dimensional imaging systems provide surgeons with detailed views of the surgical field, enabling more accurate and informed decision-making during procedures.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence
The convergence of robotic surgery and artificial intelligence (AI) has opened new avenues for innovation. AI algorithms can analyze real-time data from robotic systems, assisting surgeons in making informed decisions and optimizing surgical outcomes. This integration also holds promise for autonomous surgical procedures in the future.
Remote Surgery and Telemedicine
The evolution of robotic surgery has paved the way for remote surgery, allowing surgeons to perform procedures from a different location. This capability becomes crucial in scenarios where specialized expertise is needed but not physically present. Additionally, telemedicine has benefited from the integration of robotics, enabling consultations and follow-ups with patients in remote locations.
Customization and Personalization
Advancements in robotic surgery have led to a more personalized approach to patient care. The ability to tailor surgical procedures to individual patient anatomy and characteristics enhances the efficacy of treatments and reduces the risk of complications. Customizable robotic platforms cater to the unique needs of each patient, further optimizing surgical outcomes.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Cost and Accessibility
While robotic surgery offers numerous advantages, one of the primary challenges is the high cost associated with acquiring and maintaining robotic systems. This cost can limit accessibility, particularly in healthcare systems with budget constraints. Striking a balance between the benefits and costs remains a crucial consideration in the widespread adoption of robotic surgery.
Training and Learning Curve
The proficiency required to operate robotic systems adds a layer of complexity to surgical training. Surgeons must undergo specialized training to master the nuances of robotic-assisted procedures. The learning curve associated with robotic surgery raises questions about the standardization of training programs and the need for continuous education.
Ethical Considerations
As robotic surgery advances, ethical considerations come to the forefront. Questions surrounding patient consent, transparency about the use of robotic systems, and potential job displacement for non-robotic surgical staff warrant careful examination. Balancing the benefits of technological innovation with ethical concerns is essential for responsible and sustainable adoption.
Future Directions and Possibilities
Continued Advancements in Robotics
The field of robotic surgery is dynamic, with ongoing research and development aimed at further enhancing robotic systems. Continued miniaturization, increased mobility, and advancements in haptic feedback are areas of focus that promise to refine the capabilities of robotic surgical platforms.
Expansion into New Specialties
As technology evolves, robotic surgery is likely to expand into new medical specialties. Ongoing research is exploring the feasibility and efficacy of robotic-assisted procedures in areas such as orthopedics, ophthalmology, and even plastic surgery.
AI Integration and Autonomy
The integration of artificial intelligence into robotic surgery holds the potential for autonomous procedures. AI algorithms could analyze data in real time, making decisions and adjustments during surgery. While this prospect raises ethical considerations, it also opens the door to further advancements in precision and efficiency.
Conclusion
Robotic surgery has undeniably left an indelible mark on the landscape of medical device innovation. From the pioneering days of the da Vinci Surgical System to the current era of advanced robotics and artificial intelligence, the influence of robotic surgery extends far beyond the operating room. As technology continues to evolve, the synergy between robotics and medical device innovation will undoubtedly shape the future of healthcare, offering new possibilities for improved patient outcomes, personalized treatments, and a more efficient and accessible healthcare system.



