Innovative Approaches to Gastrointestinal Robotic Surgery
Introduction
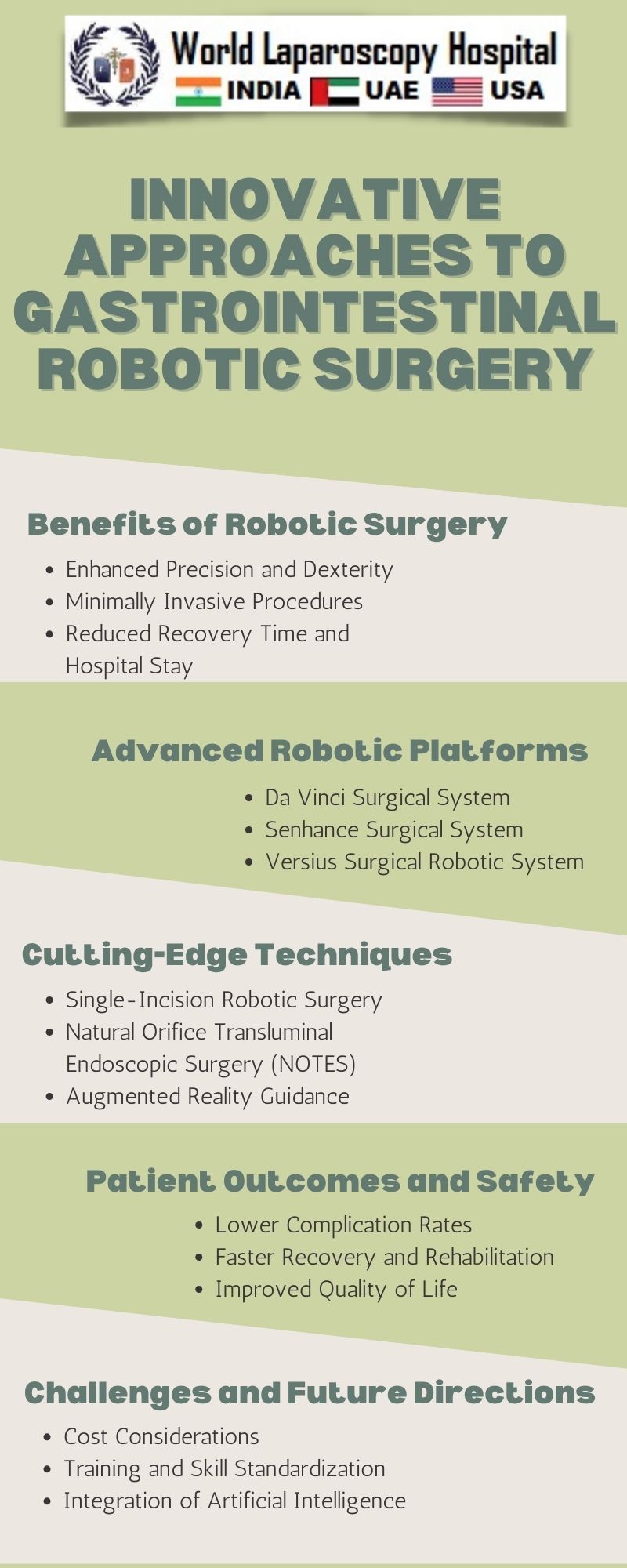
In recent years, the field of surgery has witnessed a paradigm shift with the advent of robotic technologies. Gastrointestinal robotic surgery, in particular, has seen remarkable advancements, redefining the landscape of surgical interventions. This article delves into the innovative approaches that are reshaping the way we approach gastrointestinal surgeries, offering enhanced precision, reduced invasiveness, and improved patient outcomes.
The Evolution of Robotic Surgery in Gastrointestinal Procedures
Historical Perspective
Robotic surgery in gastrointestinal procedures has its roots in the early 21st century when the first robotic-assisted surgical system was approved by the FDA. Initially employed in simple procedures, such as cholecystectomy and appendectomy, the technology has rapidly evolved to encompass complex gastrointestinal surgeries.
Rise of Robotic Systems
The introduction of da Vinci Surgical System in the early 2000s marked a significant milestone in robotic surgery. With its advanced features, including 3D visualization and wristed instruments, surgeons gained improved control and precision. This laid the foundation for innovative approaches in gastrointestinal surgeries.
Enhanced Visualization and Instrumentation
3D Visualization
Traditional laparoscopic surgeries often faced limitations in depth perception due to the two-dimensional view provided by the camera. Innovative robotic systems now offer three-dimensional visualization, providing surgeons with a more immersive and accurate view of the surgical field. This enhanced depth perception contributes to improved precision in gastrointestinal procedures.
Wristed Instruments
One of the critical limitations of traditional laparoscopic instruments is their restricted range of motion. Robotic systems address this challenge by incorporating wristed instruments that mimic the natural movements of the human hand. This increased dexterity enables surgeons to perform intricate maneuvers with greater ease, especially in the confined spaces of the gastrointestinal tract.
Minimally Invasive Approaches
Reduced Incision Size
Robotic surgery has paved the way for minimally invasive approaches in gastrointestinal procedures. Unlike traditional open surgeries that require large incisions, robotic-assisted surgeries often involve smaller, strategically placed incisions. This results in reduced trauma to surrounding tissues, faster recovery times, and minimized postoperative pain for patients.
Single-Incision Robotic Surgery
Taking minimally invasive approaches to the next level, single-incision robotic surgery has emerged as a groundbreaking technique. This approach involves performing the entire surgery through a single incision, often hidden in the umbilicus. The cosmetic benefits are evident, but more importantly, this approach further reduces the trauma to the patient's body.
Telesurgery and Remote Interventions
Telepresence in Gastrointestinal Surgery
Advancements in connectivity and robotics have enabled the concept of telesurgery, allowing surgeons to operate on patients located miles away. This is particularly valuable in cases where a specialist's expertise is required but not geographically accessible. Telesurgery has the potential to bridge the gap in healthcare, ensuring that patients receive the best possible care regardless of their location.
Remote Robotic Interventions
In addition to telesurgery, remote robotic interventions have been explored, where a surgeon controls the robotic system from a remote console. This approach holds promise for providing surgical expertise in regions with limited access to highly specialized surgeons. However, challenges such as latency and ensuring patient safety are critical considerations in the implementation of remote robotic interventions.
Artificial Intelligence in Gastrointestinal Robotic Surgery
Surgical Planning and Navigation
Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly being integrated into robotic surgical systems to enhance preoperative planning and intraoperative navigation. AI algorithms analyze patient data, aiding surgeons in identifying optimal incision sites, predicting potential complications, and providing real-time guidance during surgery. This synergy between AI and robotic surgery contributes to more personalized and precise interventions.
Machine Learning for Skill Enhancement
Machine learning algorithms are being developed to analyze and learn from the vast amounts of data generated during robotic surgeries. These algorithms have the potential to assess a surgeon's skill level, offer real-time feedback, and contribute to ongoing professional development. This integration of machine learning aims to standardize and elevate the proficiency of surgeons in robotic procedures.
Challenges and Future Directions
Cost and Accessibility
Despite the evident benefits of robotic surgery, cost remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption. The initial investment in robotic systems and the ongoing expenses associated with maintenance and training contribute to the high overall cost. Addressing these financial challenges is crucial to ensuring equitable access to the benefits of innovative gastrointestinal robotic surgery.
Surgeon Training and Learning Curve
While robotic systems offer increased precision, mastering the technology requires a learning curve for surgeons. Training programs are essential to ensure that surgeons can harness the full potential of robotic platforms. The development of comprehensive training curricula and simulation technologies is key to overcoming this challenge and promoting the widespread adoption of robotic surgery.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
As telesurgery and remote interventions become more prevalent, ethical and legal considerations come to the forefront. Ensuring patient privacy, consent, and the ability to respond promptly to unforeseen complications are critical aspects that must be carefully addressed. Establishing clear guidelines and regulations is essential to navigating the ethical landscape of innovative approaches in gastrointestinal robotic surgery.
Continued Technological Advancements
The field of robotic surgery is dynamic, with ongoing advancements in technology. Continued research and development are essential to refine existing robotic platforms, introduce new features, and address current limitations. Collaborations between engineers, surgeons, and healthcare providers will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of gastrointestinal robotic surgery.
Conclusion
Innovative approaches to gastrointestinal robotic surgery are reshaping the landscape of surgical interventions. Enhanced visualization, wristed instruments, and minimally invasive techniques contribute to improved precision and reduced patient trauma. Telesurgery, remote interventions, and the integration of artificial intelligence herald a new era of possibilities. Addressing challenges related to cost, training, and ethical considerations will be crucial for ensuring the widespread adoption and ethical implementation of these transformative technologies. As the field continues to evolve, the synergy between human expertise and robotic capabilities holds immense promise for advancing patient care in gastrointestinal surgery.