The Role of Robotics in Minimizing Surgical Scars
Introduction:
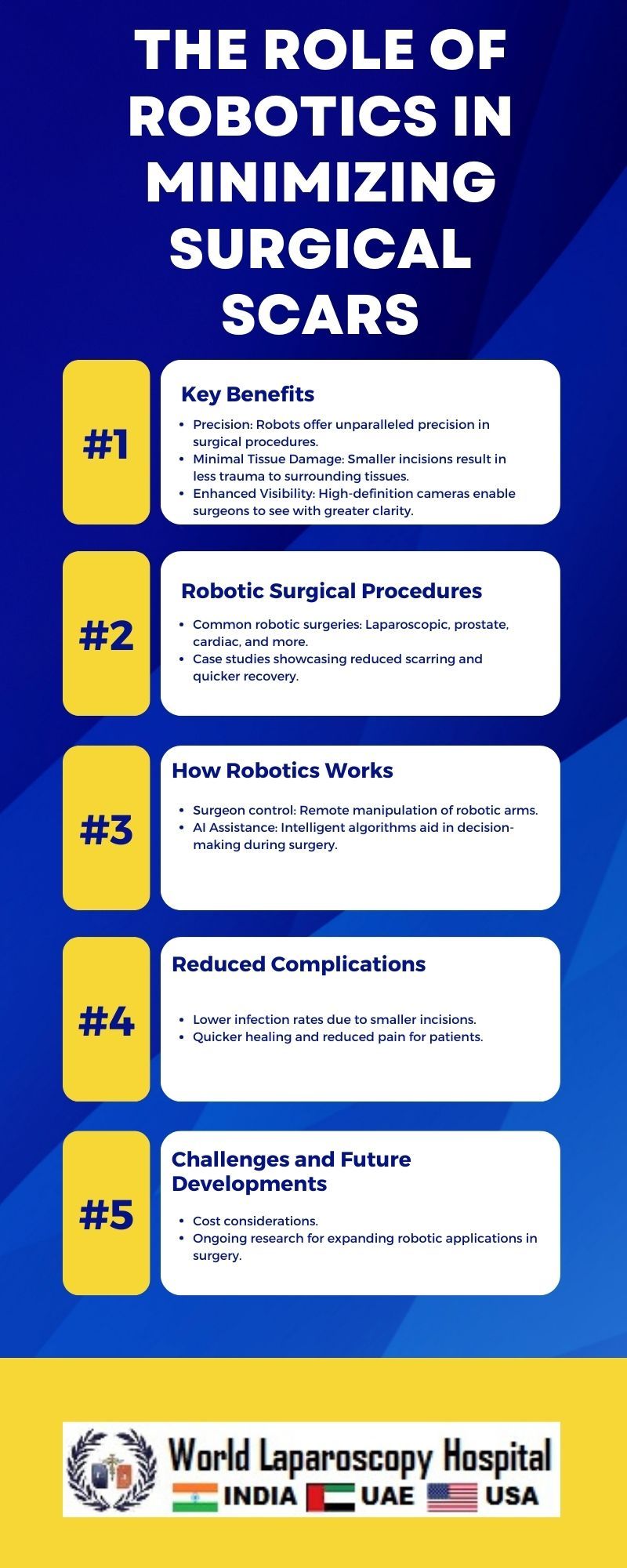
In recent years, the field of surgery has undergone a remarkable transformation with the integration of robotic technology. One of the key advantages of this technological revolution is the significant reduction in surgical scars. As we delve into the intricacies of robotic-assisted surgery, it becomes evident that this innovative approach is not just about precision but also about enhancing patient outcomes and quality of life.
The Evolution of Robotics in Surgery:
The concept of robotic surgery has roots dating back to the 1980s when the Puma 560, a robotic surgical arm, was first used for neurosurgical biopsies. However, it wasn't until the late 1990s that the da Vinci Surgical System, developed by Intuitive Surgical, emerged as a groundbreaking technology. Since then, robotic-assisted surgery has evolved, and its applications have expanded across various medical specialties.
Understanding the Significance of Minimally Invasive Surgery:
The traditional approach to many surgical procedures involved large incisions, leading to extensive scarring, prolonged recovery periods, and increased risk of complications. Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) aimed to address these issues by using smaller incisions and specialized instruments. However, the limitations of MIS, such as reduced dexterity and limited visual field, prompted the exploration of robotic assistance.
The da Vinci Surgical System:
The da Vinci Surgical System, a leader in robotic-assisted surgery, consists of a console, robotic arms, and a high-definition 3D vision system. Surgeons operate the system from the console, manipulating the robotic arms equipped with surgical instruments. The system's advanced technology provides enhanced dexterity, precision, and control, overcoming the limitations of traditional and even minimally invasive procedures.
Precision in Motion: Enhancing Surgical Techniques
Robotic-assisted surgery allows for unparalleled precision in intricate maneuvers. The robotic arms' multi-jointed design mimics the movements of a human hand, providing a range of motion beyond what is achievable with conventional laparoscopic instruments. This level of precision is particularly crucial in delicate procedures, such as cardiac surgery or neurosurgery, where the slightest miscalculation can have profound consequences.
Reducing Incision Size: The Key to Minimal Scarring
One of the primary advantages of robotic-assisted surgery in minimizing surgical scars lies in its ability to work through small incisions. The robotic arms and instruments can navigate through tight spaces with precision, enabling surgeons to perform complex procedures with minimal tissue disruption. Smaller incisions translate to less trauma for the patient, leading to reduced scarring and a quicker recovery.
Enhanced Visualization: A Clear Advantage
The da Vinci system provides surgeons with a three-dimensional, high-definition view of the surgical site. This superior visualization is a game-changer, allowing surgeons to see intricate details with greater clarity. Improved visibility contributes to more accurate decision-making and enhances the overall safety of the procedure. Consequently, surgeons can navigate through tissues more precisely, minimizing unintended damage and further reducing the potential for scarring.
Applications Across Specialties:
The impact of robotics in minimizing surgical scars extends across a spectrum of medical specialties. Let's explore how robotic-assisted surgery has revolutionized scarring outcomes in various fields:
-
General Surgery:
- Robotic technology has transformed common general surgeries like cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal) and appendectomy. The precision of the robotic arms allows for smaller incisions, reducing scarring and postoperative pain.
-
Gynecology:
- In gynecological procedures such as hysterectomy, myomectomy, and endometriosis excision, robotic assistance enables surgeons to navigate intricate anatomical structures with precision. Smaller incisions in these procedures contribute to decreased scarring and faster recovery.
-
Urology:
- Prostatectomy, a common procedure for prostate cancer, has witnessed significant advancements with robotic assistance. The enhanced visualization and dexterity of the robotic arms enable surgeons to spare surrounding tissues, reducing scarring and preserving erectile and urinary function.
-
Cardiac Surgery:
- In cardiac surgery, especially mitral valve repair, the da Vinci system has become instrumental. The precision of robotic instruments allows surgeons to access the heart through small incisions between the ribs, minimizing chest scarring and reducing the recovery period.
-
Neurosurgery:
- The application of robotics in neurosurgery has been transformative. From brain tumor resections to delicate spinal surgeries, robotic assistance ensures precise movements in confined spaces, minimizing damage to surrounding tissues and reducing the potential for visible scars.
Patient Benefits Beyond Aesthetics:
While the aesthetic aspect of minimized scarring is noteworthy, the advantages for patients extend far beyond cosmetic considerations:
-
Quicker Recovery:
- Smaller incisions result in less trauma to the body, allowing patients to recover more swiftly. Reduced postoperative pain and shorter hospital stays contribute to an overall improved recovery experience.
-
Lower Risk of Infection:
- Larger incisions increase the risk of postoperative infections. Robotic-assisted surgery's minimally invasive approach reduces the entry points for bacteria, decreasing the likelihood of infections and complications.
-
Improved Quality of Life:
- Patients undergoing robotic-assisted surgery often experience a faster return to their daily activities. The reduced physical impact of the procedure contributes to an improved quality of life during the recovery phase.
Challenges and Future Directions:
Despite its numerous advantages, robotic-assisted surgery is not without challenges. The high cost of acquiring and maintaining robotic systems, along with the extensive training required for surgeons, presents barriers to widespread adoption. Additionally, some critics argue that the long learning curve for mastering robotic techniques may hinder its broader implementation.
Looking ahead, advancements in robotics, artificial intelligence, and haptic feedback systems are poised to address these challenges. Integration with augmented reality and telesurgery capabilities may further expand the reach of robotic-assisted surgery, bringing its benefits to underserved areas and remote locations.
Conclusion:
The role of robotics in minimizing surgical scars represents a remarkable leap forward in the evolution of medical practices. From its origins as a tool for enhancing precision to its current status as a transformative force in surgery, robotic technology has reshaped the landscape of healthcare. As we continue to witness ongoing advancements, it is clear that the impact of robotics in surgery extends far beyond aesthetics, fundamentally improving patient outcomes and paving the way for a future of safer, more efficient, and less invasive medical interventions.






