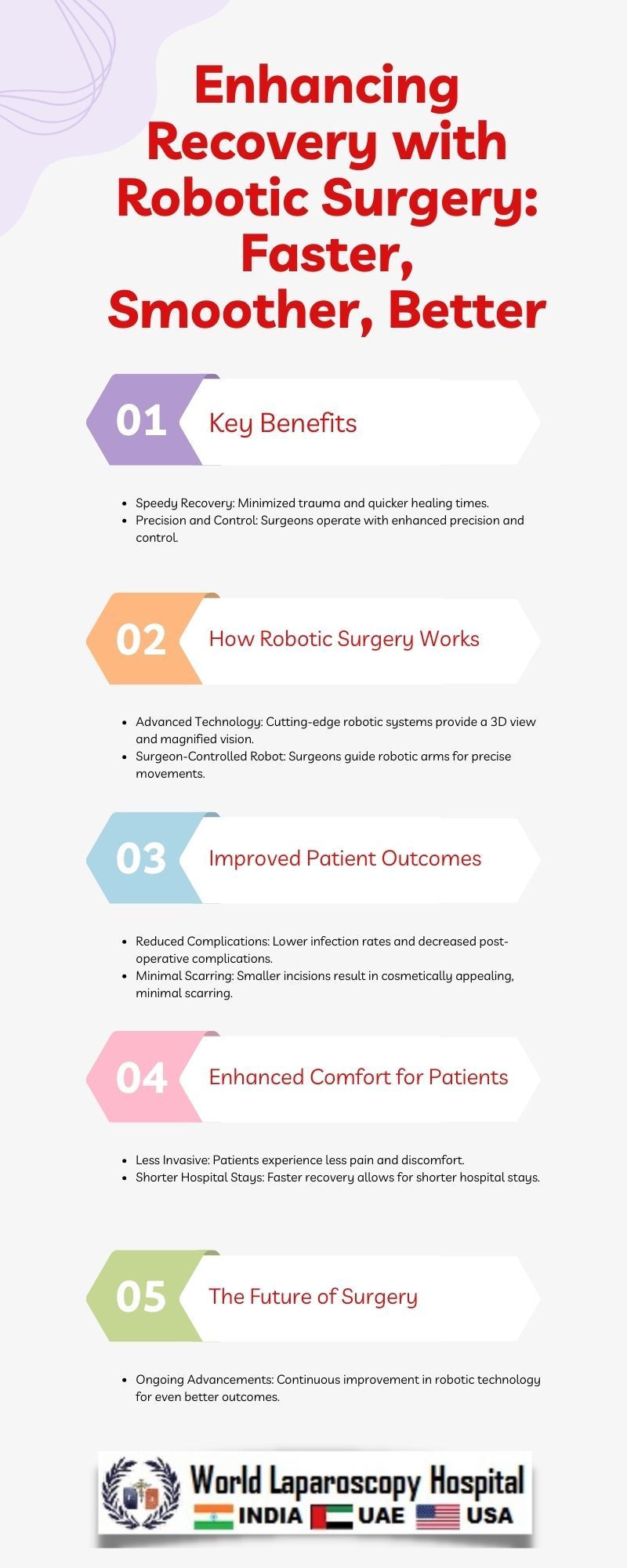
Enhancing Recovery with Robotic Surgery: Faster, Smoother, Better
Introduction
In recent years, the field of surgery has undergone a remarkable transformation with the advent of robotic surgery. This cutting-edge technology has proven to be a game-changer, revolutionizing traditional surgical procedures and significantly impacting patient outcomes. Robotic surgery, characterized by its precision, minimally invasive nature, and improved recovery times, is rapidly becoming the gold standard in various medical specialties. In this article, we will delve into the multifaceted aspects of robotic surgery, exploring how it is making surgeries faster, smoother, and ultimately better for patients.
The Evolution of Robotic Surgery
The concept of robotic surgery traces its roots back to the 1980s, when the first attempts were made to introduce robotic assistance in surgical procedures. However, it wasn't until the early 2000s that the technology matured enough for widespread clinical use. The da Vinci Surgical System, introduced by Intuitive Surgical, became a pioneer in this field. This robotic platform, controlled by a surgeon from a console, allowed for enhanced dexterity, precision, and 3D visualization during surgeries.
Since then, robotic surgery has expanded beyond urology and gynecology, its initial domains, to various other specialties, including general surgery, cardiothoracic surgery, and orthopedics. The integration of robotics into these disciplines has led to significant advancements in surgical techniques and patient care.
The Robotic Advantage: Precision and Miniaturization
One of the key advantages of robotic surgery lies in its precision and the ability to perform highly intricate maneuvers with greater accuracy than traditional methods. The robotic arms, equipped with miniaturized instruments and a high-definition camera, provide surgeons with a magnified, three-dimensional view of the surgical site. This enhanced visualization allows for meticulous dissection and precise suturing, reducing the risk of errors and complications.
Furthermore, the miniaturization of robotic instruments facilitates minimally invasive procedures. Unlike traditional open surgeries that involve large incisions, robotic surgery often requires only a few small incisions, leading to less trauma to surrounding tissues. This minimally invasive approach contributes significantly to faster recovery times, reduced pain, and shorter hospital stays for patients.
Faster Recovery: The Impact on Patient Outcomes
The accelerated recovery associated with robotic surgery is a pivotal factor that distinguishes it from conventional surgical methods. Patients undergoing robotic procedures often experience less postoperative pain, reduced blood loss, and a quicker return to normal activities. The minimally invasive nature of robotic surgery translates into smaller wounds, decreasing the risk of infection and promoting faster healing.
In gynecological surgeries, such as hysterectomies, studies have demonstrated that patients undergoing robotic-assisted procedures experience less pain and require fewer postoperative pain medications compared to those undergoing traditional open surgeries. Similarly, in colorectal surgery, robotic techniques have been associated with shorter hospital stays and a faster return to bowel function.
The speedier recovery offered by robotic surgery not only improves the overall patient experience but also has economic implications by potentially reducing healthcare costs associated with prolonged hospitalization and postoperative care.
Smoother Procedures: Surgeon Ergonomics and Enhanced Maneuverability
Robotic surgery not only benefits patients but also enhances the working conditions for surgeons. The ergonomic design of the robotic console allows surgeons to operate in a comfortable seated position, minimizing fatigue during lengthy procedures. The console provides an immersive experience, with the surgeon viewing a magnified, 3D image of the surgical site, allowing for enhanced depth perception and precision.
The robotic arms replicate the surgeon's hand movements with greater flexibility and a broader range of motion than the human hand. This increased maneuverability is particularly advantageous in complex surgeries where precise movements are crucial. Surgeons can perform intricate tasks with greater ease, whether it involves delicate suturing in cardiac surgery or precise dissection in oncological procedures.
The seamless integration of technology into the surgical workflow enables real-time adjustments and fine-tuning, contributing to smoother procedures and improved overall surgical outcomes. As a result, robotic surgery has become a valuable tool for surgeons seeking to push the boundaries of what is achievable in the operating room.
Better Outcomes: Advancements in Training and Education
The incorporation of robotic surgery into medical training programs has been instrumental in preparing the next generation of surgeons for the evolving landscape of healthcare. Simulation platforms allow trainees to practice and refine their skills in a controlled environment before transitioning to live surgeries. This hands-on training approach ensures that surgeons are proficient in utilizing robotic systems, promoting safety and efficacy in the operating room.
Additionally, the enhanced visualization provided by robotic systems allows for improved training experiences. Trainees can observe surgeries with greater clarity, understanding the intricacies of each procedure in detail. This immersive learning experience contributes to a more knowledgeable and skilled surgical workforce.
Furthermore, the continuous evolution of robotic platforms has led to innovations such as haptic feedback, which provides a sense of touch to surgeons operating the robotic console. This advancement further bridges the gap between traditional open surgery and robotic-assisted procedures, enhancing the surgeon's ability to feel tissue resistance and make nuanced decisions during surgery.
Challenges and Future Directions
While robotic surgery has undeniably transformed the landscape of modern healthcare, it is not without challenges. The high initial costs associated with acquiring and maintaining robotic systems pose financial barriers for some healthcare institutions. Additionally, concerns about the learning curve for surgeons and the need for ongoing specialized training are valid considerations.
As technology advances, addressing these challenges becomes crucial for the continued integration and expansion of robotic surgery. Collaborative efforts between industry stakeholders, regulatory bodies, and healthcare institutions are essential to make robotic surgery more accessible and ensure that its benefits reach a broader patient population.
Looking ahead, the future of robotic surgery holds exciting possibilities. Continued advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotic technologies may lead to further automation of certain aspects of surgery. The development of smaller, more portable robotic systems could extend the reach of robotic surgery to underserved areas, improving access to advanced surgical care.
Conclusion
In conclusion, robotic surgery has emerged as a transformative force in healthcare, offering faster, smoother, and ultimately better outcomes for patients. The precision, miniaturization, and enhanced maneuverability of robotic systems have revolutionized surgical procedures across various specialties. The positive impact on patient recovery, surgeon ergonomics, and the overall quality of healthcare delivery cannot be overstated.
As the field of robotic surgery continues to evolve, addressing challenges and fostering collaboration will be essential. With ongoing advancements, robotic surgery is poised to play an increasingly prominent role in shaping the future of surgery, ushering in an era of enhanced recovery and improved patient outcomes.


