The Role of Laparoscopic Surgery in Trauma Cases
Introduction:
Trauma cases often present complex challenges that demand swift and effective medical interventions. In recent decades, laparoscopic surgery has emerged as a revolutionary technique, transforming the landscape of trauma care. This minimally invasive approach offers numerous advantages over traditional open surgeries, playing a pivotal role in enhancing patient outcomes and postoperative recovery.
Understanding Laparoscopic Surgery:
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery, involves making small incisions through which a laparoscope, a thin tube with a camera and light, is inserted into the body. This allows surgeons to visualize internal organs on a monitor and perform procedures using specialized instruments. In trauma cases, where rapid intervention is critical, laparoscopy has proven to be a game-changer.
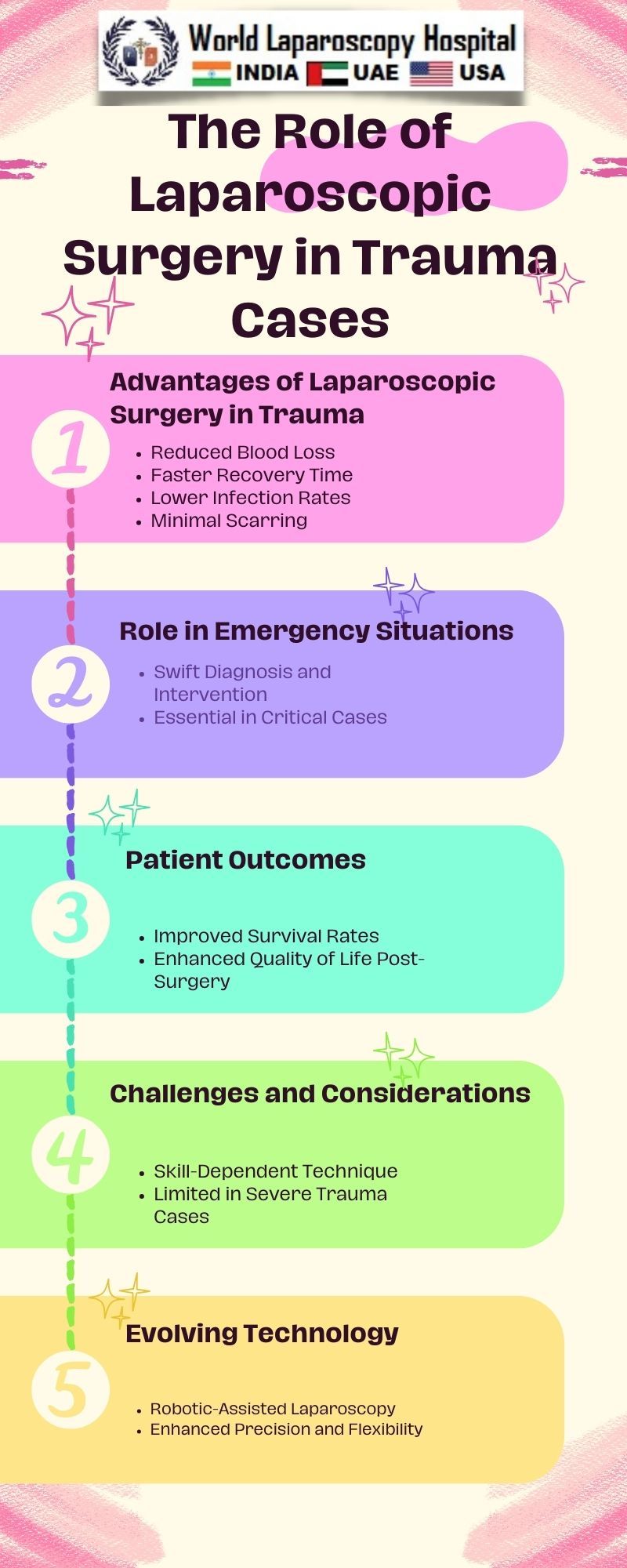
Advantages in Trauma Cases:
Quicker Diagnosis and Intervention:
In trauma situations, time is of the essence. Laparoscopic surgery facilitates rapid diagnosis by providing clear and magnified views of the abdominal cavity. This enables surgeons to identify and assess injuries such as organ damage, internal bleeding, or foreign bodies with greater precision, expediting the decision-making process.
Minimized Blood Loss:
Traditional open surgeries often involve significant blood loss, especially in trauma cases. Laparoscopic procedures, on the other hand, use smaller incisions and specialized tools, resulting in reduced blood loss. This is particularly beneficial in trauma cases where controlling bleeding promptly is crucial for patient survival.
Faster Recovery and Reduced Hospital Stay:
One of the hallmark advantages of laparoscopic surgery is its impact on postoperative recovery. Smaller incisions lead to less tissue damage, reduced pain, and faster healing. Patients undergoing laparoscopic procedures in trauma cases typically experience shorter hospital stays, allowing them to return to normal activities sooner.
Lower Infection Rates:
The risk of postoperative infections is a significant concern in trauma cases. Laparoscopic surgery, with its minimally invasive nature, lowers the risk of infection compared to open surgeries. Smaller incisions mean less exposure of internal organs to external contaminants, contributing to a lower likelihood of surgical site infections.
Cosmetic Benefits:
While the primary focus in trauma cases is on saving lives and ensuring the best possible medical outcomes, the cosmetic benefits of laparoscopic surgery should not be overlooked. Smaller scars result in improved aesthetic outcomes, which can have psychological benefits for the patient, promoting a positive mindset during recovery.
Enhanced Visualization:
The laparoscope provides surgeons with high-resolution, three-dimensional images of the surgical site. This enhanced visualization allows for meticulous exploration of the affected area, aiding in the identification of even subtle injuries. Surgeons can navigate through complex anatomical structures with greater precision, reducing the likelihood of overlooked injuries.
Adaptability to Various Trauma Types:
Laparoscopic surgery is versatile and can be adapted to various trauma scenarios. Whether addressing abdominal injuries, diaphragmatic ruptures, or penetrating wounds, the laparoscopic approach allows for tailored interventions based on the specific nature of the trauma.
Case Studies and Success Stories:
To underscore the effectiveness of laparoscopic surgery in trauma cases, several case studies and success stories can be examined. These real-world examples highlight instances where laparoscopy played a decisive role in saving lives, reducing complications, and improving overall patient outcomes.
Challenges and Considerations:
While laparoscopic surgery offers numerous advantages, it is essential to acknowledge potential challenges and considerations in trauma cases. Factors such as the surgeon's expertise, equipment availability, and patient stability may influence the feasibility of laparoscopic interventions. Additionally, not all trauma cases may be suitable for laparoscopy, and a judicious assessment of each situation is crucial.
Future Trends and Innovations:
The field of laparoscopic surgery continues to evolve, with ongoing research and technological advancements. Future innovations may include the integration of robotics, further enhancing the precision and dexterity of minimally invasive procedures. Additionally, the development of new tools and techniques may expand the applicability of laparoscopy in addressing increasingly complex trauma cases.
Conclusion:
Laparoscopic surgery has revolutionized trauma care by offering a safer, more efficient, and patient-friendly alternative to traditional open surgeries. Its numerous advantages, including quicker diagnosis, minimized blood loss, faster recovery, and enhanced visualization, make it an invaluable tool in the hands of trauma surgeons. As technology continues to advance, the role of laparoscopic surgery in trauma cases is likely to expand, further improving outcomes and redefining standards in emergency medical care.