The Role of Laparoscopy in Trauma Surgery
Introduction
Trauma surgery has witnessed significant advancements over the years, with laparoscopy emerging as a revolutionary tool in the armamentarium of surgeons. Traditionally, trauma cases necessitated exploratory laparotomies, involving large incisions for abdominal exploration. However, the advent of laparoscopy has transformed this landscape, offering a minimally invasive approach that is reshaping the field of trauma surgery.
Understanding Trauma and its Impact
Trauma, resulting from accidents, falls, or violent incidents, often leads to abdominal injuries that require immediate medical attention. The abdomen, housing vital organs such as the liver, spleen, and intestines, is particularly vulnerable in trauma cases. Prompt and accurate diagnosis, followed by timely intervention, is crucial in optimizing patient outcomes.
Challenges in Traditional Trauma Surgery
Historically, trauma surgeries involved exploratory laparotomies, a procedure where a large incision is made to visually inspect the abdominal cavity. While effective, this approach has inherent drawbacks, including increased postoperative pain, longer recovery times, and a higher risk of complications such as infections and hernias. Additionally, the extensive nature of laparotomies can result in significant blood loss.
Enter Laparoscopy: A Minimally Invasive Game-Changer
Laparoscopy, also known as minimally invasive surgery or keyhole surgery, has revolutionized the field of trauma surgery. This technique involves making small incisions through which a camera and specialized instruments are inserted into the abdominal cavity. The camera provides high-resolution images of the internal organs, allowing surgeons to visualize and address injuries with precision.
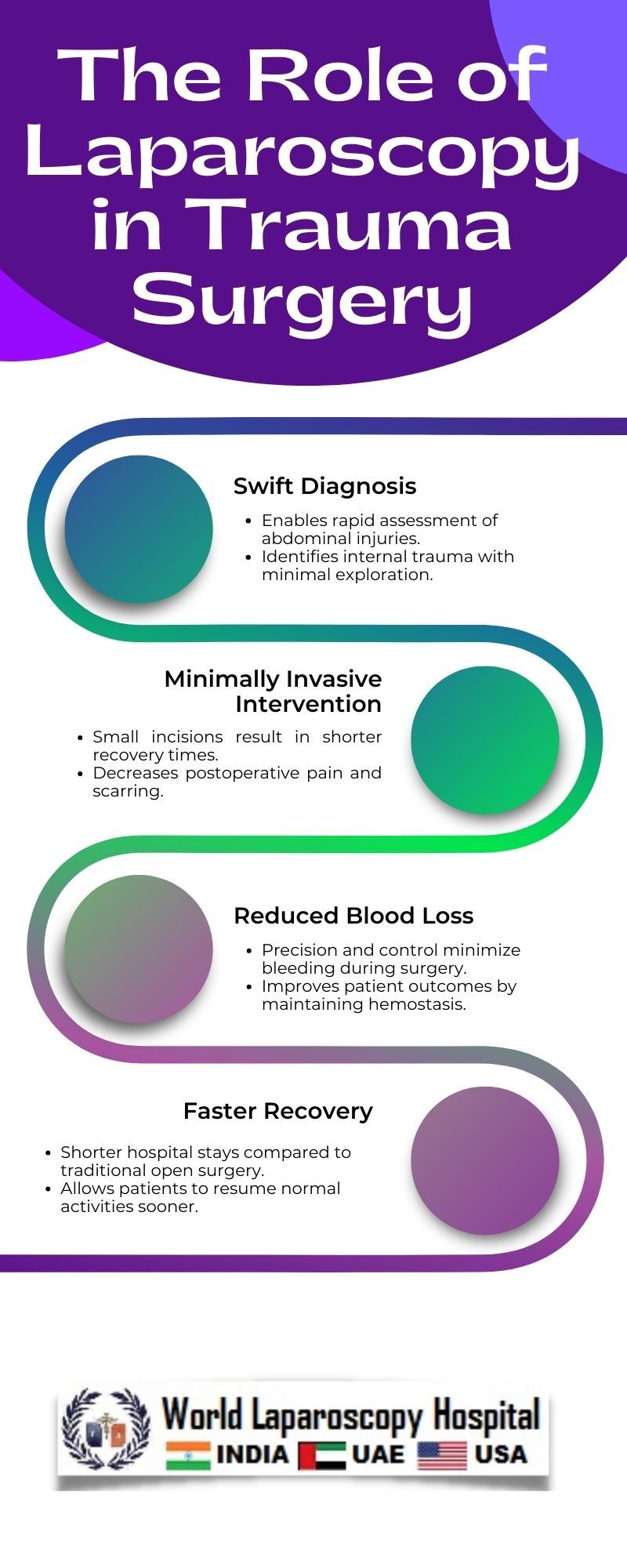
Key Advantages of Laparoscopy in Trauma Surgery
Faster Recovery and Reduced Pain:
Unlike traditional laparotomies, laparoscopic procedures are associated with smaller incisions, resulting in less postoperative pain. Patients often experience quicker recovery times and shorter hospital stays, allowing them to resume normal activities sooner.
Minimized Blood Loss:
The minimally invasive nature of laparoscopy reduces the risk of significant blood loss during surgery. This is especially critical in trauma cases where preserving blood volume is paramount to patient recovery.
Improved Cosmesis:
The smaller incisions used in laparoscopy result in minimal scarring, contributing to improved cosmetic outcomes. This aspect is not only aesthetically advantageous for patients but also reduces the likelihood of complications related to wound healing.
Enhanced Diagnostic Precision:
Laparoscopy enables high-resolution visualization of internal structures, facilitating accurate diagnosis of abdominal injuries. Surgeons can identify and assess the extent of damage with greater precision, guiding appropriate therapeutic interventions.
Reduced Complication Rates:
Studies have shown that laparoscopic trauma surgery is associated with lower rates of postoperative complications, such as infections and adhesions, compared to traditional open procedures. This contributes to overall better patient outcomes.
Applications of Laparoscopy in Trauma Surgery
Diagnostic Laparoscopy:
In cases where the extent of abdominal injury is uncertain, diagnostic laparoscopy allows surgeons to explore the abdominal cavity, identify injuries, and determine the need for further intervention. This targeted approach aids in avoiding unnecessary laparotomies.
Hemostasis and Organ Repair:
Laparoscopy facilitates precise hemostasis, enabling surgeons to control bleeding more effectively. Additionally, damaged organs can be repaired using specialized instruments inserted through small incisions, minimizing the need for extensive open surgery.
Exploration in Stab Wounds and Gunshot Injuries:
Penetrating trauma, such as stab wounds or gunshot injuries, often requires exploration to assess internal damage. Laparoscopy provides a minimally invasive means of investigating these injuries, reducing the morbidity associated with exploratory laparotomies.
Abdominal Compartment Syndrome Management:
In cases of abdominal compartment syndrome—a condition characterized by increased pressure within the abdominal cavity—laparoscopy can be employed to release intra-abdominal pressure and prevent further organ damage.
Solid Organ Injuries:
Laparoscopy is particularly beneficial in managing injuries to solid organs like the liver and spleen. It allows for meticulous inspection, hemostasis, and repair while minimizing the trauma to surrounding tissues.
Challenges and Considerations
While laparoscopy has brought about significant improvements in trauma surgery, certain challenges and considerations exist:
Skill and Training:
Performing laparoscopic trauma surgery requires specialized skills and training. Surgeons must be proficient in manipulating instruments in a confined space while interpreting images from the laparoscope.
Equipment Availability:
Laparoscopic trauma surgery necessitates specialized equipment, including high-quality cameras and instruments. Availability of such resources may be limited in certain healthcare settings, impacting the widespread adoption of this technique.
Patient Selection:
Not all trauma cases are suitable for laparoscopic intervention. Patient stability, the nature of injuries, and the surgeon's expertise play crucial roles in determining the appropriateness of laparoscopy in a given scenario.
Cost Implications:
While laparoscopy can lead to reduced hospital stays and faster recovery, the initial costs associated with acquiring and maintaining laparoscopic equipment may be a barrier for some healthcare facilities.
Future Directions and Innovations
As technology continues to advance, the future of laparoscopy in trauma surgery looks promising. Innovations such as robotic-assisted laparoscopy, improved imaging modalities, and augmented reality integration hold the potential to further enhance the precision and outcomes of minimally invasive trauma interventions.
Conclusion
Laparoscopy has undeniably transformed the landscape of trauma surgery, offering a paradigm shift from traditional open procedures to minimally invasive interventions. Its benefits, including faster recovery, reduced pain, and improved diagnostic precision, position it as a cornerstone in the evolving field of trauma surgery. As ongoing research and technological advancements continue, laparoscopy is poised to play an even more integral role in optimizing outcomes for patients facing abdominal trauma. Surgeons, healthcare providers, and policymakers must collaborate to ensure that this transformative approach becomes more widely accessible, ultimately raising the standard of care for trauma patients worldwide.