The Economics of Laparoscopic Surgery: Cost-Effectiveness and Value
Introduction:
In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, where advancements in medical technology continuously shape treatment modalities, the economic considerations of medical procedures become paramount. One such innovation that has significantly impacted surgical practices is laparoscopic surgery. This article delves into the intricacies of the economics of laparoscopic surgery, exploring its cost-effectiveness and the inherent value it brings to the modern healthcare system.
Understanding Laparoscopic Surgery:
Laparoscopic surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery, involves performing operations through small incisions with the aid of a camera and specialized instruments. This departure from traditional open surgery has revolutionized various medical fields, from gynecology to gastroenterology, offering patients a host of benefits.
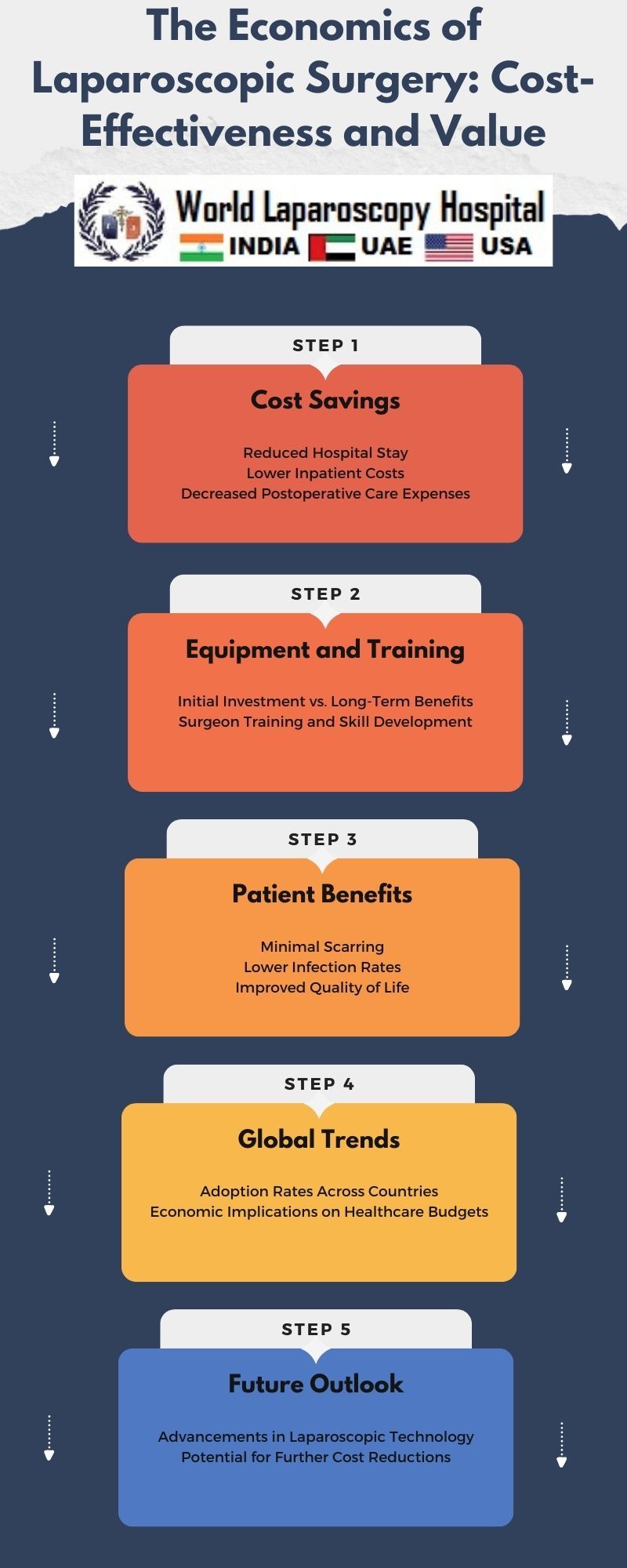
Reduced Hospital Stays:One of the immediate economic advantages of laparoscopic surgery is the reduction in hospital stays. Compared to open surgeries, laparoscopic procedures often allow for quicker recovery and shorter postoperative hospitalization. This not only benefits patients by minimizing disruption to their daily lives but also translates to cost savings for healthcare providers.
Quicker Recovery and Enhanced Productivity:The minimally invasive nature of laparoscopic surgery contributes to faster recovery times. Patients can return to their daily activities sooner, reducing the economic impact of prolonged postoperative rehabilitation. This accelerated recovery is particularly crucial in the context of the working population, as it minimizes the economic burden associated with extended sick leave and disability.
Lower Postoperative Care Costs:Laparoscopic procedures often result in lower postoperative care costs. Reduced pain and complications mean fewer follow-up appointments, less medication, and a decreased need for rehabilitative services. This not only contributes to direct cost savings but also frees up healthcare resources for other patients, optimizing overall system efficiency.
Economic Considerations and Initial Investment:
While the long-term benefits of laparoscopic surgery are evident, it is essential to acknowledge the initial investments required. The acquisition of specialized equipment, training of medical personnel, and infrastructure adjustments all incur costs. However, these upfront expenses must be viewed in the context of the broader economic landscape, where the long-term gains outweigh the initial financial outlay.
Equipment Costs and Return on Investment:The acquisition of laparoscopic equipment, including high-definition cameras and precision instruments, represents a significant initial investment. However, as the volume of laparoscopic procedures increases, the return on investment becomes evident. Hospitals and surgical centers can amortize equipment costs over time, making laparoscopic surgery economically viable in the long run.
Training and Skill Development:
Another aspect of the initial investment lies in training surgeons and medical staff in laparoscopic techniques. While training incurs costs, the improved patient outcomes, reduced complications, and shorter recovery times associated with laparoscopic surgery enhance the overall efficiency of healthcare delivery. Investing in training becomes an investment in the quality of care and, ultimately, the economic sustainability of healthcare systems.
Cost-Effectiveness in Different Specialties:
Laparoscopic surgery has found applications across various medical specialties, each presenting unique economic considerations.
Gynecology:In gynecology, laparoscopic surgery has become the standard for procedures such as hysterectomies and ovarian cyst removal. The reduced recovery time and hospital stays associated with laparoscopic gynecological surgeries translate into cost savings for both patients and healthcare providers. Additionally, the cosmetic benefits of smaller incisions contribute to patient satisfaction.
Gastroenterology:Laparoscopic procedures in gastroenterology, including cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal) and appendectomy, have demonstrated cost-effectiveness. The minimization of postoperative complications and shorter hospital stays reduce the economic burden on healthcare systems. Patients benefit from quicker return to normal activities and lower overall healthcare costs.
Urology:In urology, laparoscopic surgery is employed for procedures such as nephrectomy and prostatectomy. The reduced need for prolonged hospitalization and the quicker return to daily life contribute to cost-effectiveness. Moreover, the precision afforded by laparoscopic instruments in urological surgeries minimizes damage to surrounding tissues, resulting in improved patient outcomes.
Value in Patient Outcomes:
Beyond cost-effectiveness, the value of laparoscopic surgery is underscored by its impact on patient outcomes. The advantages of minimally invasive procedures extend beyond economics, shaping a paradigm where patient well-being is at the forefront.
Reduced Pain and Complications:Compared to open surgery, laparoscopic procedures typically result in reduced postoperative pain. This not only enhances the patient experience but also contributes to a decrease in the need for pain management medications. The diminished pain and discomfort associated with laparoscopic surgery lead to improved patient satisfaction and contribute to a positive overall healthcare experience.
Cosmetic Benefits and Patient Satisfaction:The cosmetic advantages of laparoscopic surgery, characterized by smaller incisions and minimal scarring, are significant contributors to patient satisfaction. In an era where patients are increasingly conscious of aesthetic outcomes, the cosmetic benefits of laparoscopic procedures add a unique dimension to the overall value proposition.
Faster Return to Normal Activities:The quicker recovery times associated with laparoscopic surgery enable patients to resume their normal activities sooner. This is particularly crucial in maintaining the productivity of the workforce, as shorter recovery periods translate to reduced absenteeism. The economic value of patients returning to their daily lives promptly is a testament to the broader societal impact of laparoscopic surgery.
Challenges and Future Directions:
While laparoscopic surgery has become a cornerstone of modern surgical practices, challenges and opportunities for improvement persist.
Access and Affordability:Despite its economic benefits, the accessibility of laparoscopic surgery may be limited in certain regions or healthcare systems. Addressing disparities in access and ensuring affordability for all patients remains a challenge. Policymakers and healthcare stakeholders must work collaboratively to implement measures that promote equitable access to laparoscopic procedures.
Technological Advancements:Ongoing technological advancements continue to shape the landscape of laparoscopic surgery. The integration of robotics, artificial intelligence, and virtual reality into minimally invasive procedures holds the potential to further improve outcomes and efficiency. However, the cost implications of adopting these technologies must be carefully considered in the pursuit of enhancing the economic viability of laparoscopic surgery.
Training and Standardization:The consistent training of surgeons and standardization of laparoscopic techniques are critical factors in ensuring optimal outcomes. Investing in comprehensive training programs and promoting standardized practices across healthcare institutions contribute to the overall success of laparoscopic surgery.
Conclusion:
The economics of laparoscopic surgery are multifaceted, encompassing cost-effectiveness, return on investment, and the inherent value it brings to patient outcomes. As healthcare systems grapple with the challenges of providing high-quality care while managing costs, laparoscopic surgery emerges as a shining example of innovation that aligns economic efficiency with improved patient well-being. By navigating the complexities of initial investments, embracing technological advancements, and prioritizing training and standardization, the economic and societal benefits of laparoscopic surgery can be maximized, ushering in a new era of surgical excellence in modern healthcare.


