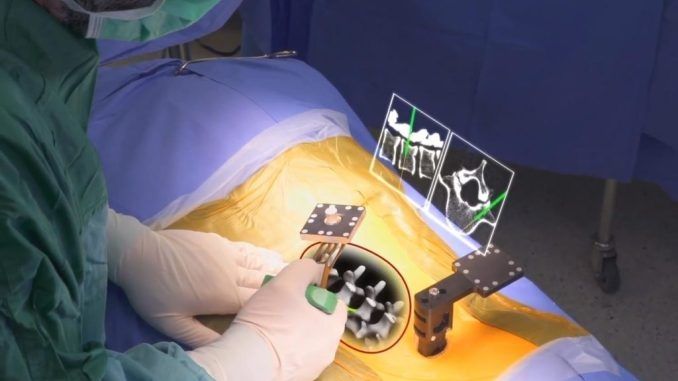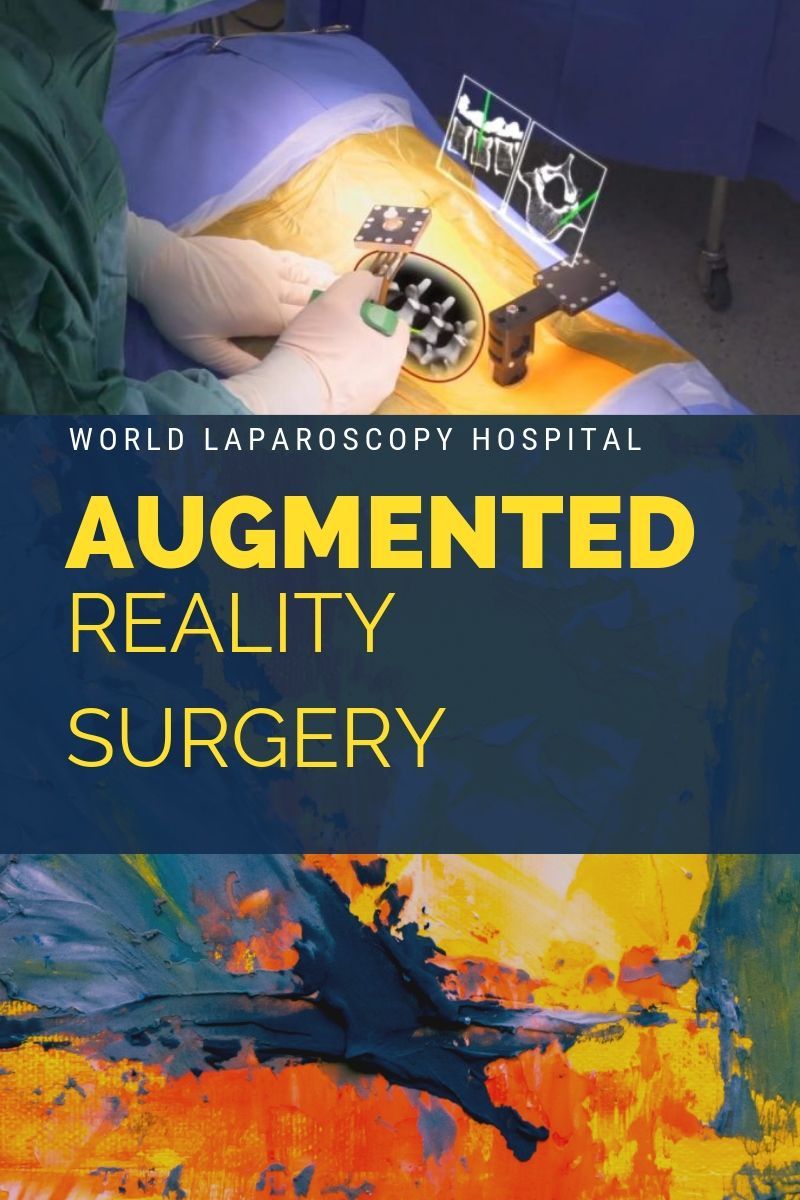
Augmented reality-assisted surgery is a surgical tool utilizing technology that superimposes a computer-generated image on a surgeon’s view of the operative field, thus providing a composite view for the surgeon of the patient with a computer-generated overlay enhancing the operative experience.
The technology includes a motion-tracking system using infrared cameras and markers on the patient's body, as well as a projector to display the laparoscopic videos taken by the laparoscopic camera. But the really difficult part is having the image track properly on the patient's body even as they shift and move. The solution is customized software written that gets all of the components working together.
One way augmented reality could participate in surgeries would be through head-mounted displays (HMD). These are similar to current VR glasses, or smartglasses. Without obstructing a doctor's view of the patient, HMD could show the patients vital signs, steps in the surgery, medical images, and so on. This would allow doctors to have all the necessary information right in front of them. At the same time, they could focus on the procedure without having to look away or having their vision obstructed.
Surgery is a critical medical procedure that requires a high level of precision and accuracy. Over the years, advancements in technology have led to the development of new surgical techniques that are less invasive and result in fewer scars and incisions. One such technique is Augmented Reality Laparoscopic Surgery (ARLS), which uses augmented reality to display video directly on the patient's body. In this essay, we will explore how ARLS works and its benefits over traditional laparoscopic surgery.
Augmented Reality Laparoscopic Surgery:
Augmented Reality Laparoscopic Surgery is a minimally invasive surgical technique that uses augmented reality to display video directly on the patient's body. The procedure involves placing a small camera inside the patient's body to provide a view of the surgical site. The camera captures images and transmits them to a computer, which uses augmented reality to display the video directly on the patient's body.
The augmented reality display is created using special glasses that are worn by the surgeon. The glasses use sensors to track the position of the surgeon's head and adjust the display accordingly. The display provides the surgeon with a real-time view of the surgical site and allows them to manipulate surgical instruments with a high degree of precision.
Benefits of Augmented Reality Laparoscopic Surgery:
Augmented Reality Laparoscopic Surgery has several benefits over traditional laparoscopic surgery. One of the primary benefits is that it allows for more precise surgery. The augmented reality display provides the surgeon with a real-time view of the surgical site and allows them to manipulate surgical instruments with a high degree of precision. This can be especially beneficial for surgeries that require a high level of precision, such as surgeries on delicate organs.
ARLS also reduces the risk of complications associated with surgery. Traditional laparoscopic surgery requires the surgeon to make several incisions, which increases the risk of infection, bleeding, and other complications. ARLS only requires one small incision for the camera, which reduces the risk of complications.
Another benefit of ARLS is that it allows for more efficient surgery. The augmented reality display provides the surgeon with a real-time view of the surgical site, which allows them to work more efficiently. This can result in shorter surgery times and reduce the risk of complications associated with longer surgeries.
ARLS also has the potential to reduce the need for open surgery. Open surgery is a surgical procedure that involves making a large incision in the patient's body. The procedure is more invasive and results in more significant scarring and longer recovery times than laparoscopic surgery. ARLS can be used in surgeries that would otherwise require open surgery, reducing the need for more invasive procedures.
ARLS also has potential applications in training and education. The augmented reality display can be used to train surgeons and medical students in surgical techniques, allowing them to practice surgeries in a safe and controlled environment.
One of the challenges associated with ARLS is the need for specialized equipment and trained personnel. Not all medical facilities have the necessary equipment and personnel to perform ARLS, which can limit its availability. However, as the technology continues to advance, it is expected that more medical facilities will adopt ARLS and make it more widely available.
In addition to reducing the number of incisions and scars, ARLS also has the potential to reduce the risk of complications associated with surgery. The use of augmented reality to display video directly on the patient's body reduces the need for the surgeon to manipulate organs or tissues, which can reduce the risk of damage to surrounding structures. This can be especially beneficial in surgeries that involve delicate organs or tissues, such as the pancreas or liver.
Another potential benefit of ARLS is its use in robotic surgery. Robotic surgery is a minimally invasive surgical technique that uses robots to perform surgery. The use of ARLS in robotic surgery can improve the precision and accuracy of the surgical instruments, making robotic surgery even more effective.
ARLS has also been used in pediatric surgery. Children are particularly vulnerable to the risks associated with surgery, such as infection, bleeding, and damage to surrounding structures. The use of ARLS in pediatric surgery can reduce these risks and improve outcomes for children. The technique is especially beneficial in surgeries that require a high level of precision, such as surgeries on the liver or pancreas.
One of the potential limitations of ARLS is the need for specialized training. Surgeons who perform ARLS require specialized training to use the augmented reality display to guide surgical instruments through the body. This can be a challenge for medical facilities that do not have the necessary equipment or personnel to provide this training.
Another potential limitation of ARLS is its cost. The equipment required to perform ARLS can be expensive, which can limit its availability in some medical facilities. However, as the technology continues to advance and become more widely adopted, it is expected that the cost of ARLS will decrease, making it more accessible to patients.
Conclusion:
Augmented Reality Laparoscopic Surgery is a minimally invasive surgical technique that uses augmented reality to display video directly on the patient's body. The technique allows for more precise surgery, reduces the risk of complications associated with surgery, and allows for more efficient surgery. ARLS also has the potential to reduce the need for open surgery and has applications in training and education. As the technology continues to advance, it is expected that ARLS will become more widely adopted and be used in an increasing number of surgical procedures.