Page 49 - WJOLS - Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 49
Shalmali Alva (Cont’d…)
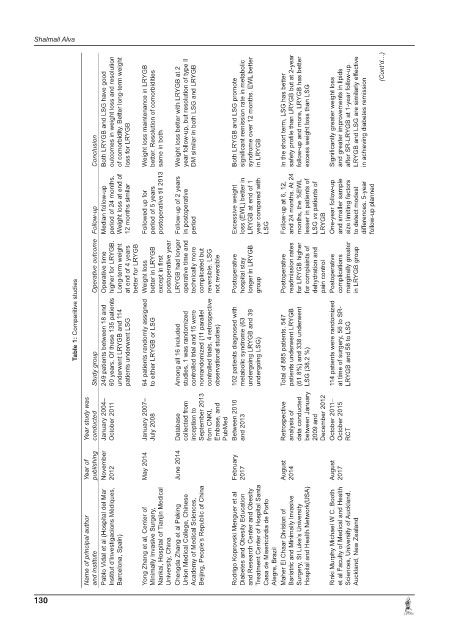
Both LRYGB and LSG have good outcomes in weight loss and resolution of comorbidity. Better long-term weight Weight loss maintenance in LRYGB better. Resolution of comorbidities Weight loss better with LRYGB at 2 year follow-up, but resolution of type II DM similar in both LSG and LRYGB Both LRYGB and LSG promote significant remission rate in metabolic syndrome over 12 months. EWL better In the short term, LSG has better safe
Conclusion loss for LRYGB same in both in LRYGB
Follow-up Median follow-up period of 24 months. Weight loss at end of 12 months similar Followed up for period of 5 years postoperative till 2013 Follow-up of 2 years in postoperative period Excessive weight loss (EWL) better in LRYGB at end of 1 year compared with LSG Follow-up at 6, 12, and 24 months. At 24 months, the %EWL lesser in patients of LSG vs patients of LRYGB One-year follow-up and smaller
Operative outcome Operative time higher for LRYGB. Long-term weight at end of 4 years better for LRYGB Weight loss better in LRYGB except in first postoperative year LRYGB had longer operative time and technically more complicated but reversible. LSG not reversible Postoperative hospital stay longer in LRYGB group Postoperative readmission rates for LRYGB higher for complaints of dehydration and p
Table 1: Comparitive studies 249 patients between 18 and 60 years. Of these 135 patients 64 patients randomly assigned controlled trials, 4 retrospective 114 patients were randomized
Study group underwent LRYGB and 114 patients underwent LSG to either LRYGB or LSG Among all 16 included studies, 1 was randomized controlled trial and 15 were nonrandomized (11 parallel observational studies) 102 patients diagnosed with metabolic syndrome (63 undergoing LRYGB and 39 undergoing LSG) Total of 885 patients. 547 patients underwent LRYGB (61.8%) and 338 underwent LSG (38.2 %) at time of surgery, 56 to SR- L
Year study was conducted January 2004– October 2011 January 2007– July 2008 Database collected from inception to September 2013 from CNKI, Embase, and PubMed Between 2010 and 2013 Retrospective analysis of data conducted between January 2009 and December 2012 October 2011– October 2015 RCT
Year of publishing November 2012 May 2014 June 2014 February 2017 August 2014 August 2017
Name of principal author and institute Pablo Vidal et al (Hospital del Mar Institut d’Investigacions Mèdiques, Barcelona, Spain) Yong Zhang et al, Center of Minimally Invasive Surgery, Nankai, Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, China Chengda Zhang et al Peking Union Medical College, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, People’s Republic of China Rodrigo Koprovski Menguer et al Diabetes and Obesity Education and Re
130