Page 98 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgeons
P. 98
WJOLS
Meandering Pancreatic Duct as a Cause of Idiopathic Recurrent Pancreatitis
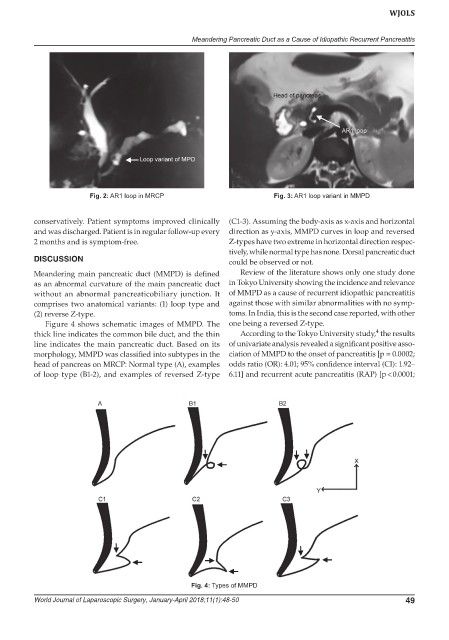
Fig. 2: AR1 loop in MRCP Fig. 3: AR1 loop variant in MMPD
conservatively. Patient symptoms improved clinically (C1-3). Assuming the body-axis as x-axis and horizontal
and was discharged. Patient is in regular follow-up every direction as y-axis, MMPD curves in loop and reversed
2 months and is symptom-free. Z-types have two extreme in horizontal direction respec-
tively, while normal type has none. Dorsal pancreatic duct
DISCUSSION could be observed or not.
Meandering main pancreatic duct (MMPD) is defined Review of the literature shows only one study done
as an abnormal curvature of the main pancreatic duct in Tokyo University showing the incidence and relevance
without an abnormal pancreaticobiliary junction. It of MMPD as a cause of recurrent idiopathic pancreatitis
comprises two anatomical variants: (1) loop type and against those with similar abnormalities with no symp-
(2) reverse Z-type. toms. In India, this is the second case reported, with other
Figure 4 shows schematic images of MMPD. The one being a reversed Z-type.
4
thick line indicates the common bile duct, and the thin According to the Tokyo University study, the results
line indicates the main pancreatic duct. Based on its of univariate analysis revealed a significant positive asso-
morphology, MMPD was classified into subtypes in the ciation of MMPD to the onset of pancreatitis [p = 0.0002;
head of pancreas on MRCP: Normal type (A), examples odds ratio (OR): 4.01; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.92–
of loop type (B1-2), and examples of reversed Z-type 6.11] and recurrent acute pancreatitis (RAP) [p < 0.0001;
Fig. 4: Types of MMPD
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, January-April 2018;11(1):48-50 49