Page 56 - Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 56
Nidhi Mehta et al.
Fig. 3: Identification of fistulous tract Fig. 4: Fistulous tract
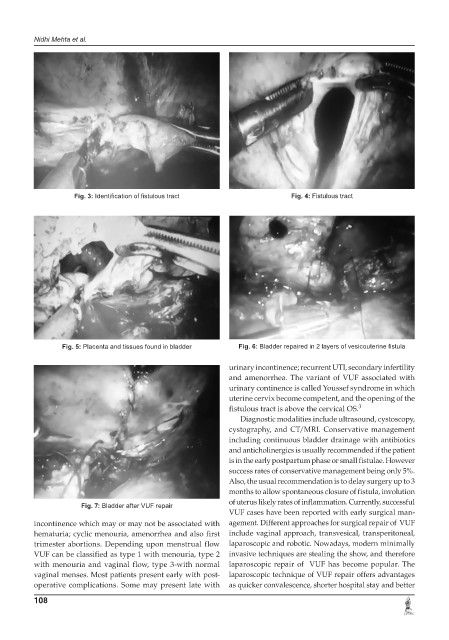
Fig. 5: Placenta and tissues found in bladder Fig. 6: Bladder repaired in 2 layers of vesicouterine fistula
urinary incontinence; recurrent UTI, secondary infertility
and amenorrhea. The variant of VUF associated with
urinary continence is called Youssef syndrome in which
uterine cervix become competent, and the opening of the
fistulous tract is above the cervical OS. 3
Diagnostic modalities include ultrasound, cystoscopy,
cystography, and CT/MRI. Conservative management
including continuous bladder drainage with antibiotics
and anticholinergics is usually recommended if the patient
is in the early postpartum phase or small fistulae. However
success rates of conservative management being only 5%.
Also, the usual recommendation is to delay surgery up to 3
months to allow spontaneous closure of fistula, involution
of uterus likely rates of inflammation. Currently, successful
Fig. 7: Bladder after VUF repair
VUF cases have been reported with early surgical man-
incontinence which may or may not be associated with agement. Different approaches for surgical repair of VUF
hematuria; cyclic menouria, amenorrhea and also first include vaginal approach, transvesical, transperitoneal,
trimester abortions. Depending upon menstrual flow laparoscopic and robotic. Nowadays, modern minimally
VUF can be classified as type 1 with menouria, type 2 invasive techniques are stealing the show, and therefore
with menouria and vaginal flow, type 3-with normal laparoscopic repair of VUF has become popular. The
vaginal menses. Most patients present early with post- laparoscopic technique of VUF repair offers advantages
operative complications. Some may present late with as quicker convalescence, shorter hospital stay and better
108