Page 39 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 39
Ergonomics
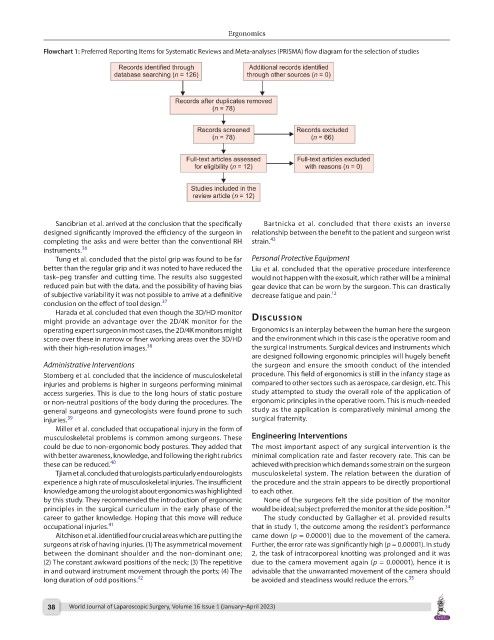
Flowchart 1: Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) flow diagram for the selection of studies
Sancibrian et al. arrived at the conclusion that the specifically Bartnicka et al. concluded that there exists an inverse
designed significantly improved the efficiency of the surgeon in relationship between the benefit to the patient and surgeon wrist
completing the asks and were better than the conventional RH strain. 43
instruments. 36
Tung et al. concluded that the pistol grip was found to be far Personal Protective Equipment
better than the regular grip and it was noted to have reduced the Liu et al. concluded that the operative procedure interference
task–peg transfer and cutting time. The results also suggested would not happen with the exosuit, which rather will be a minimal
reduced pain but with the data, and the possibility of having bias gear device that can be worn by the surgeon. This can drastically
of subjective variability it was not possible to arrive at a definitive decrease fatigue and pain. 12
conclusion on the effect of tool design. 37
Harada et al. concluded that even though the 3D/HD monitor
might provide an advantage over the 2D/4K monitor for the dIscussIon
operating expert surgeon in most cases, the 2D/4K monitors might Ergonomics is an interplay between the human here the surgeon
score over these in narrow or finer working areas over the 3D/HD and the environment which in this case is the operative room and
with their high-resolution images. 38 the surgical instruments. Surgical devices and instruments which
are designed following ergonomic principles will hugely benefit
Administrative Interventions the surgeon and ensure the smooth conduct of the intended
Stomberg et al. concluded that the incidence of musculoskeletal procedure. This field of ergonomics is still in the infancy stage as
injuries and problems is higher in surgeons performing minimal compared to other sectors such as aerospace, car design, etc. This
access surgeries. This is due to the long hours of static posture study attempted to study the overall role of the application of
or non-neutral positions of the body during the procedures. The ergonomic principles in the operative room. This is much-needed
general surgeons and gynecologists were found prone to such study as the application is comparatively minimal among the
injuries. 39 surgical fraternity.
Miller et al. concluded that occupational injury in the form of
musculoskeletal problems is common among surgeons. These Engineering Interventions
could be due to non-ergonomic body postures. They added that The most important aspect of any surgical intervention is the
with better awareness, knowledge, and following the right rubrics minimal complication rate and faster recovery rate. This can be
these can be reduced. 40 achieved with precision which demands some strain on the surgeon
Tjiam et al. concluded that urologists particularly endourologists musculoskeletal system. The relation between the duration of
experience a high rate of musculoskeletal injuries. The insufficient the procedure and the strain appears to be directly proportional
knowledge among the urologist about ergonomics was highlighted to each other.
by this study. They recommended the introduction of ergonomic None of the surgeons felt the side position of the monitor
principles in the surgical curriculum in the early phase of the would be ideal; subject preferred the monitor at the side position. 34
career to gather knowledge. Hoping that this move will reduce The study conducted by Gallagher et al. provided results
occupational injuries. 41 that in study 1, the outcome among the resident’s performance
Aitchison et al. identified four crucial areas which are putting the came down (p = 0.00001) due to the movement of the camera.
surgeons at risk of having injuries. (1) The asymmetrical movement Further, the error rate was significantly high (p = 0.00001). In study
between the dominant shoulder and the non-dominant one; 2, the task of intracorporeal knotting was prolonged and it was
(2) The constant awkward positions of the neck; (3) The repetitive due to the camera movement again (p = 0.00001), hence it is
in and outward instrument movement through the ports; (4) The advisable that the unwarranted movement of the camera should
long duration of odd positions. 42 be avoided and steadiness would reduce the errors. 35
38 World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 16 Issue 1 (January–April 2023)