Page 10 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 10
Outcome of Laparoscopic Repair of Hiatus Hernia
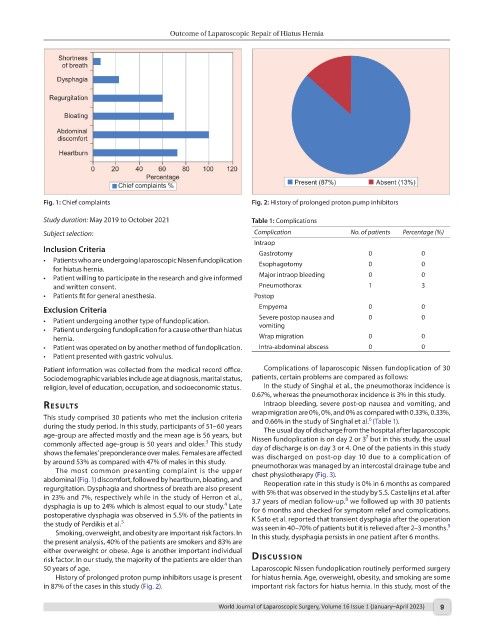
Fig. 1: Chief complaints Fig. 2: History of prolonged proton pump inhibitors
Study duration: May 2019 to October 2021 Table 1: Complications
Subject selection: Complication No. of patients Percentage (%)
Intraop
Inclusion Criteria Gastrotomy 0 0
• Patients who are undergoing laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication Esophagotomy 0 0
for hiatus hernia.
• Patient willing to participate in the research and give informed Major intraop bleeding 0 0
and written consent. Pneumothorax 1 3
• Patients fit for general anesthesia. Postop
Exclusion Criteria Empyema 0 0
• Patient undergoing another type of fundoplication. Severe postop nausea and 0 0
• Patient undergoing fundoplication for a cause other than hiatus vomiting
hernia. Wrap migration 0 0
• Patient was operated on by another method of fundoplication. Intra-abdominal abscess 0 0
• Patient presented with gastric volvulus.
Patient information was collected from the medical record office. Complications of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication of 30
Sociodemographic variables include age at diagnosis, marital status, patients, certain problems are compared as follows:
religion, level of education, occupation, and socioeconomic status. In the study of Singhal et al., the pneumothorax incidence is
0.67%, whereas the pneumothorax incidence is 3% in this study.
results Intraop bleeding, severe post-op nausea and vomiting, and
wrap migration are 0%, 0%, and 0% as compared with 0.33%, 0.33%,
This study comprised 30 patients who met the inclusion criteria and 0.66% in the study of Singhal et al. (Table 1).
6
during the study period. In this study, participants of 51–60 years The usual day of discharge from the hospital after laparoscopic
age-group are affected mostly and the mean age is 56 years, but Nissen fundoplication is on day 2 or 3 but in this study, the usual
7
3
commonly affected age-group is 50 years and older. This study day of discharge is on day 3 or 4. One of the patients in this study
shows the females’ preponderance over males. Females are affected was discharged on post-op day 10 due to a complication of
by around 53% as compared with 47% of males in this study. pneumothorax was managed by an intercostal drainage tube and
The most common presenting complaint is the upper chest physiotherapy (Fig. 3).
abdominal (Fig. 1) discomfort, followed by heartburn, bloating, and Reoperation rate in this study is 0% in 6 months as compared
regurgitation. Dysphagia and shortness of breath are also present with 5% that was observed in the study by S.S. Castelijns et al. after
in 23% and 7%, respectively while in the study of Herron et al., 3.7 years of median follow-up. we followed up with 30 patients
8
4
dysphagia is up to 24% which is almost equal to our study. Late for 6 months and checked for symptom relief and complications.
postoperative dysphagia was observed in 5.5% of the patients in K Sato et al. reported that transient dysphagia after the operation
the study of Perdikis et al. 5 was seen in 40–70% of patients but it is relieved after 2–3 months.
9
Smoking, overweight, and obesity are important risk factors. In In this study, dysphagia persists in one patient after 6 months.
the present analysis, 40% of the patients are smokers and 83% are
either overweight or obese. Age is another important individual
risk factor. In our study, the majority of the patients are older than dIscussIon
50 years of age. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication routinely performed surgery
History of prolonged proton pump inhibitors usage is present for hiatus hernia. Age, overweight, obesity, and smoking are some
in 87% of the cases in this study (Fig. 2). important risk factors for hiatus hernia. In this study, most of the
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 16 Issue 1 (January–April 2023) 9