Page 17 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 17
Anatomical Variations of Rouviere’s Sulcus in Egyptian Patients
In cirrhotic patients, the incidence of gallstones is higher than
in general population. In cirrhotic patients, symptomatic gallstones
are associated with higher morbidity compared to the rest of the
population. The risk for developing complicated gallstone disease
must be strictly weighed against the risk of surgery. 7,8
AIm of the Work
The aim of this study is to determine the frequency and types of
RS as seen during LC and to assess the benefits of identifying RS
as an anatomical landmark in avoidance of bile ducts injury during
LC in Egyptian patients.
mAterIAls And methods
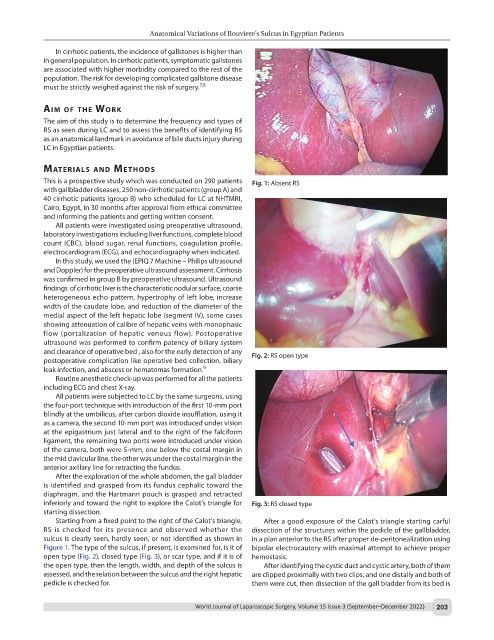
This is a prospective study which was conducted on 290 patients Fig. 1: Absent RS
with gallbladder diseases, 250 non-cirrhotic patients (group A) and
40 cirrhotic patients (group B) who scheduled for LC at NHTMRI,
Cairo, Egypt, in 30 months after approval from ethical committee
and informing the patients and getting written consent.
All patients were investigated using preoperative ultrasound,
laboratory investigations including liver functions, complete blood
count (CBC), blood sugar, renal functions, coagulation profile,
electrocardiogram (ECG), and echocardiography when indicated.
In this study, we used the (EPIQ 7 Machine – Philips ultrasound
and Doppler) for the preoperative ultrasound assessment. Cirrhosis
was confirmed in group B by preoperative ultrasound. Ultrasound
findings of cirrhotic liver is the characteristic nodular surface, coarse
heterogeneous echo-pattern, hypertrophy of left lobe, increase
width of the caudate lobe, and reduction of the diameter of the
medial aspect of the left hepatic lobe (segment IV), some cases
showing attenuation of calibre of hepatic veins with monophasic
flow (portalization of hepatic venous flow). Postoperative
ultrasound was performed to confirm patency of biliary system
and clearance of operative bed , also for the early detection of any Fig. 2: RS open type
postoperative complication like operative bed collection, biliary
leak infection, and abscess or hematomas formation. 9
Routine anesthetic check-up was performed for all the patients
including ECG and chest X-ray.
All patients were subjected to LC by the same surgeons, using
the four-port technique with introduction of the first 10-mm port
blindly at the umbilicus, after carbon dioxide insufflation, using it
as a camera, the second 10-mm port was introduced under vision
at the epigastrium just lateral and to the right of the falciform
ligament, the remaining two ports were introduced under vision
of the camera, both were 5-mm, one below the costal margin in
the mid clavicular line, the other was under the costal margin in the
anterior axillary line for retracting the fundus.
After the exploration of the whole abdomen, the gall bladder
is identified and grasped from its fundus cephalic toward the
diaphragm, and the Hartmann pouch is grasped and retracted
inferiorly and toward the right to explore the Calot’s triangle for Fig. 3: RS closed type
starting dissection.
Starting from a fixed point to the right of the Calot’s triangle, After a good exposure of the Calot’s triangle starting carful
RS is checked for its presence and observed whether the dissection of the structures within the pedicle of the gallbladder,
sulcus is clearly seen, hardly seen, or not identified as shown in in a plan anterior to the RS after proper de-peritonealization using
Figure 1. The type of the sulcus, if present, is examined for, is it of bipolar electrocautery with maximal attempt to achieve proper
open type (Fig. 2), closed type (Fig. 3), or scar type, and if it is of hemostasis.
the open type, then the length, width, and depth of the sulcus is After identifying the cystic duct and cystic artery, both of them
assessed, and the relation between the sulcus and the right hepatic are clipped proximally with two clips, and one distally and both of
pedicle is checked for. them were cut, then dissection of the gall bladder from its bed is
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 15 Issue 3 (September–December 2022) 203