Page 72 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 72
Rare Case of Ovarian Preserving Surgery in Unmarried Woman
Fig. 4: Post-detorsion, there is reduction in the congestion and regaining
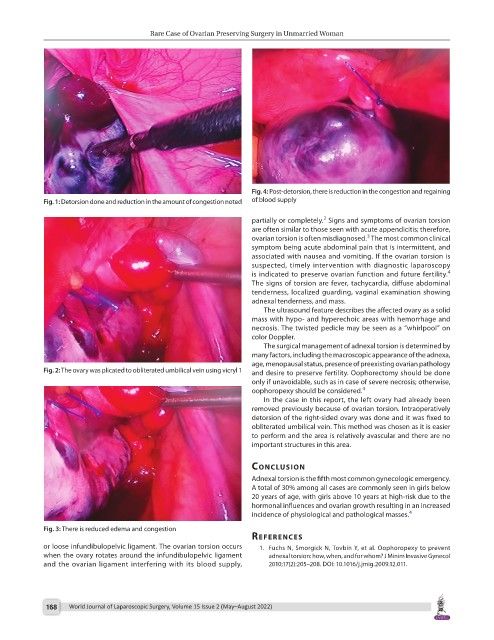
Fig. 1: Detorsion done and reduction in the amount of congestion noted of blood supply
2
partially or completely. Signs and symptoms of ovarian torsion
are often similar to those seen with acute appendicitis; therefore,
3
ovarian torsion is often misdiagnosed. The most common clinical
symptom being acute abdominal pain that is intermittent, and
associated with nausea and vomiting. If the ovarian torsion is
suspected, timely intervention with diagnostic laparoscopy
4
is indicated to preserve ovarian function and future fertility.
The signs of torsion are fever, tachycardia, diffuse abdominal
tenderness, localized guarding, vaginal examination showing
adnexal tenderness, and mass.
The ultrasound feature describes the affected ovary as a solid
mass with hypo- and hyperechoic areas with hemorrhage and
necrosis. The twisted pedicle may be seen as a “whirlpool” on
color Doppler.
The surgical management of adnexal torsion is determined by
many factors, including the macroscopic appearance of the adnexa,
age, menopausal status, presence of preexisting ovarian pathology
Fig. 2: The ovary was plicated to obliterated umbilical vein using vicryl 1 and desire to preserve fertility. Oophorectomy should be done
only if unavoidable, such as in case of severe necrosis; otherwise,
oophoropexy should be considered. 4
In the case in this report, the left ovary had already been
removed previously because of ovarian torsion. Intraoperatively
detorsion of the right-sided ovary was done and it was fixed to
obliterated umbilical vein. This method was chosen as it is easier
to perform and the area is relatively avascular and there are no
important structures in this area.
conclusIon
Adnexal torsion is the fifth most common gynecologic emergency.
A total of 30% among all cases are commonly seen in girls below
20 years of age, with girls above 10 years at high-risk due to the
hormonal influences and ovarian growth resulting in an increased
incidence of physiological and pathological masses. 4
Fig. 3: There is reduced edema and congestion
references
or loose infundibulopelvic ligament. The ovarian torsion occurs 1. Fuchs N, Smorgick N, Tovbin Y, et al. Oophoropexy to prevent
when the ovary rotates around the infundibulopelvic ligament adnexal torsion: how, when, and for whom? J Minim Invasive Gynecol
and the ovarian ligament interfering with its blood supply, 2010;17(2):205–208. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmig.2009.12.011.
168 World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 15 Issue 2 (May–August 2022)