Page 64 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 64
Validation of CLOC Score
Table 3: Logistic regression model
95% CI
Coefficient df OR Lower Upper p
6th step Diameter (1) 2.396 1 10.974 1.721 69.952 0.011
Constant −4.241 1 0.014 0.000
(55.20 ± 17.2 vs 50.93 ± 13.3; p = 0.483). According to the age-group,
the largest difference of proportion is among the age-group 30–39
years, who had an 8.7% higher risk for conversion compared with
subjects in the age-group <30 years. Other risk factors not found to
be significantly associated with the rate of conversion in this study
are sex, indication for surgery, gallbladder wall thickness, and ASA
classification. Dilation of the common biliary duct above the normal
diameter was found to be significantly associated with the risk of
conversion. The group with dilation of the common biliary duct had
a 12.2% higher risk for conversion to open procedure compared with
those with normal diameter with a p-value of 0.018.
The most common surgical indication associated with
conversion was mostly colicky pain (symptomatic gallstones), which
was found in four subjects (2.8%). This finding was different with
4
the study by Sutcliffe et al., which reported that the most common
indication of conversion to open surgery was CBD calculi (9.1%), in
stark contrast with colicky pain (1.2%).
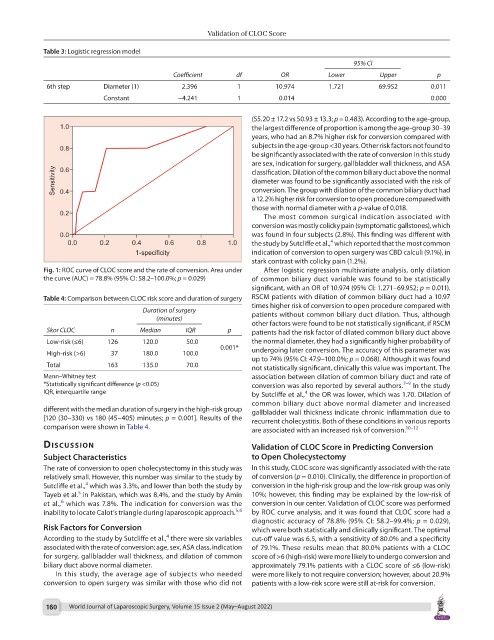
Fig. 1: ROC curve of CLOC score and the rate of conversion. Area under After logistic regression multivariate analysis, only dilation
the curve (AUC) = 78.8% (95% CI: 58.2–100.0%; p = 0.029) of common biliary duct variable was found to be statistically
significant, with an OR of 10.974 (95% CI: 1.271–69.952; p = 0.011).
Table 4: Comparison between CLOC risk score and duration of surgery RSCM patients with dilation of common biliary duct had a 10.97
times higher risk of conversion to open procedure compared with
Duration of surgery patients without common biliary duct dilation. Thus, although
(minutes)
other factors were found to be not statistically significant, if RSCM
Skor CLOC n Median IQR p patients had the risk factor of dilated common biliary duct above
Low-risk (≤6) 126 120.0 50.0 the normal diameter, they had a significantly higher probability of
0.001* undergoing later conversion. The accuracy of this parameter was
High-risk (>6) 37 180.0 100.0
up to 74% (95% CI: 47.9–100.0%; p = 0.068). Although it was found
Total 163 135.0 70.0 not statistically significant, clinically this value was important. The
Mann–Whitney test association between dilation of common biliary duct and rate of
*Statistically significant difference (p <0.05) conversion was also reported by several authors. 7–9 In the study
IQR, interquartile range by Sutcliffe et al., the OR was lower, which was 1.70. Dilation of
4
common biliary duct above normal diameter and increased
different with the median duration of surgery in the high-risk group gallbladder wall thickness indicate chronic inflammation due to
[120 (30–330) vs 180 (45–405) minutes; p = 0.001]. Results of the recurrent cholecystitis. Both of these conditions in various reports
comparison were shown in Table 4. are associated with an increased risk of conversion. 10–12
dIscussIon Validation of CLOC Score in Predicting Conversion
Subject Characteristics to Open Cholecystectomy
The rate of conversion to open cholecystectomy in this study was In this study, CLOC score was significantly associated with the rate
relatively small. However, this number was similar to the study by of conversion (p = 0.010). Clinically, the difference in proportion of
4
Sutcliffe et al., which was 3.3%, and lower than both the study by conversion in the high-risk group and the low-risk group was only
5
Tayeb et al. in Pakistan, which was 8.4%, and the study by Amin 10%; however, this finding may be explained by the low-risk of
6
et al., which was 7.8%. The indication for conversion was the conversion in our center. Validation of CLOC score was performed
inability to locate Calot’s triangle during laparoscopic approach. 5,6 by ROC curve analysis, and it was found that CLOC score had a
diagnostic accuracy of 78.8% (95% CI: 58.2–99.4%; p = 0.029),
Risk Factors for Conversion which were both statistically and clinically significant. The optimal
4
According to the study by Sutcliffe et al., there were six variables cut-off value was 6.5, with a sensitivity of 80.0% and a specificity
associated with the rate of conversion: age, sex, ASA class, indication of 79.1%. These results mean that 80.0% patients with a CLOC
for surgery, gallbladder wall thickness, and dilation of common score of >6 (high-risk) were more likely to undergo conversion and
biliary duct above normal diameter. approximately 79.1% patients with a CLOC score of ≤6 (low-risk)
In this study, the average age of subjects who needed were more likely to not require conversion; however, about 20.9%
conversion to open surgery was similar with those who did not patients with a low-risk score were still at-risk for conversion.
160 World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 15 Issue 2 (May–August 2022)