Page 4 - tmp
P. 4
Role of Laparoscopy in Abdominal Tuberculosis Diagnosis
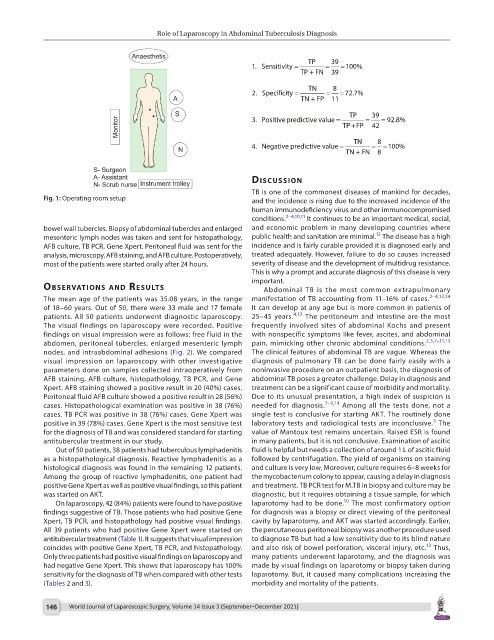
TP 39
1. Sensitivity = = = 100%
TP + FN 39
TN 8
2. Specificity = = = 72.7%
TN + FP 11
TP 39
3. Positive predictive value = = = 92.8%
TP+FP 42
TN 8
4. Negative predictive value = = = 100%
TN + FN 8
dIscussIon
TB is one of the commonest diseases of mankind for decades,
Fig. 1: Operating room setup and the incidence is rising due to the increased incidence of the
human immunodeficiency virus and other immunocompromised
conditions. 2–4,10,11 It continues to be an important medical, social,
bowel wall tubercles. Biopsy of abdominal tubercles and enlarged and economic problem in many developing countries where
12
mesenteric lymph nodes was taken and sent for histopathology, public health and sanitation are minimal. The disease has a high
AFB culture, TB PCR, Gene Xpert. Peritoneal fluid was sent for the incidence and is fairly curable provided it is diagnosed early and
analysis, microscopy, AFB staining, and AFB culture. Postoperatively, treated adequately. However, failure to do so causes increased
most of the patients were started orally after 24 hours. severity of disease and the development of multidrug resistance.
This is why a prompt and accurate diagnosis of this disease is very
important.
observAtIons And results Abdominal TB is the most common extrapulmonary
The mean age of the patients was 35.08 years, in the range manifestation of TB accounting from 11–16% of cases. 2–4,13,14
of 18–60 years. Out of 50, there were 33 male and 17 female It can develop at any age but is more common in patients of
patients. All 50 patients underwent diagnostic laparoscopy. 25–45 years. 4,12 The peritoneum and intestine are the most
The visual findings on laparoscopy were recorded. Positive frequently involved sites of abdominal Kochs and present
findings on visual impression were as follows: free fluid in the with nonspecific symptoms like fever, ascites, and abdominal
abdomen, peritoneal tubercles, enlarged mesenteric lymph pain, mimicking other chronic abdominal conditions. 2,3,7–11,13
nodes, and intraabdominal adhesions (Fig. 2). We compared The clinical features of abdominal TB are vague. Whereas the
visual impression on laparoscopy with other investigative diagnosis of pulmonary TB can be done fairly easily with a
parameters done on samples collected intraoperatively from noninvasive procedure on an outpatient basis, the diagnosis of
AFB staining, AFB culture, histopathology, TB PCR, and Gene abdominal TB poses a greater challenge. Delay in diagnosis and
Xpert. AFB staining showed a positive result in 20 (40%) cases. treatment can be a significant cause of morbidity and mortality.
Peritoneal fluid AFB culture showed a positive result in 28 (56%) Due to its unusual presentation, a high index of suspicion is
cases. Histopathological examination was positive in 38 (76%) needed for diagnosis. 7–9,14 Among all the tests done, not a
cases. TB PCR was positive in 38 (76%) cases. Gene Xpert was single test is conclusive for starting AKT. The routinely done
3
positive in 39 (78%) cases. Gene Xpert is the most sensitive test laboratory tests and radiological tests are inconclusive. The
for the diagnosis of TB and was considered standard for starting value of Mantoux test remains uncertain. Raised ESR is found
antitubercular treatment in our study. in many patients, but it is not conclusive. Examination of ascitic
Out of 50 patients, 38 patients had tuberculous lymphadenitis fluid is helpful but needs a collection of around 1 L of ascitic fluid
as a histopathological diagnosis. Reactive lymphadenitis as a followed by centrifugation. The yield of organisms on staining
histological diagnosis was found in the remaining 12 patients. and culture is very low. Moreover, culture requires 6–8 weeks for
Among the group of reactive lymphadenitis, one patient had the mycobacterium colony to appear, causing a delay in diagnosis
positive Gene Xpert as well as positive visual findings, so this patient and treatment. TB PCR test for M.TB in biopsy and culture may be
was started on AKT. diagnostic, but it requires obtaining a tissue sample, for which
10
On laparoscopy, 42 (84%) patients were found to have positive laparotomy had to be done. The most confirmatory option
findings suggestive of TB. Those patients who had positive Gene for diagnosis was a biopsy or direct viewing of the peritoneal
Xpert, TB PCR, and histopathology had positive visual findings. cavity by laparotomy, and AKT was started accordingly. Earlier,
All 39 patients who had positive Gene Xpert were started on the percutaneous peritoneal biopsy was another procedure used
antitubercular treatment (Table 1). It suggests that visual impression to diagnose TB but had a low sensitivity due to its blind nature
13
coincides with positive Gene Xpert, TB PCR, and histopathology. and also risk of bowel perforation, visceral injury, etc. Thus,
Only three patients had positive visual findings on laparoscopy and many patients underwent laparotomy, and the diagnosis was
had negative Gene Xpert. This shows that laparoscopy has 100% made by visual findings on laparotomy or biopsy taken during
sensitivity for the diagnosis of TB when compared with other tests laparotomy. But, it caused many complications increasing the
(Tables 2 and 3). morbidity and mortality of the patients.
146 World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 14 Issue 3 (September–December 2021)