Page 54 - tmp
P. 54
Perioperative Antidepressant Use in Patients Who Undergo Bariatric Surgery
18
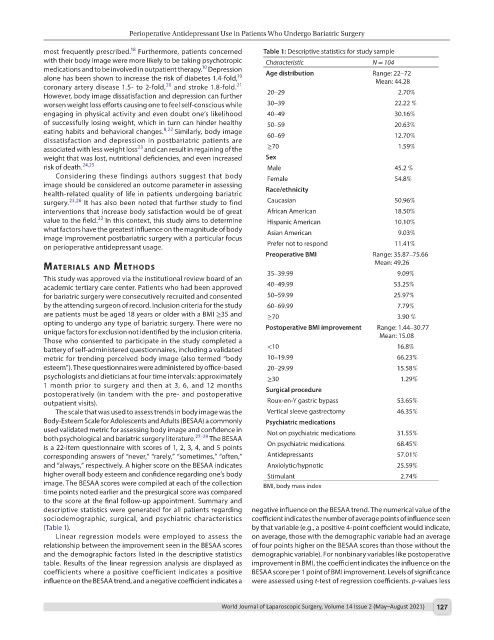
most frequently prescribed. Furthermore, patients concerned Table 1: Descriptive statistics for study sample
with their body image were more likely to be taking psychotropic Characteristic N = 104
10
medications and to be involved in outpatient therapy. Depression Age distribution Range: 22–72
19
alone has been shown to increase the risk of diabetes 1.4-fold, Mean: 44.28
20
coronary artery disease 1.5- to 2-fold, and stroke 1.8-fold. 21
However, body image dissatisfaction and depression can further 20–29 2.70%
worsen weight loss efforts causing one to feel self-conscious while 30–39 22.22 %
engaging in physical activity and even doubt one’s likelihood 40–49 30.16%
of successfully losing weight, which in turn can hinder healthy 50–59 20.63%
eating habits and behavioral changes. 8,22 Similarly, body image 60–69
dissatisfaction and depression in postbariatric patients are 12.70%
23
associated with less weight loss and can result in regaining of the ≥70 1.59%
weight that was lost, nutritional deficiencies, and even increased Sex
risk of death. 24,25 Male 45.2 %
Considering these findings authors suggest that body Female 54.8%
image should be considered an outcome parameter in assessing
health-related quality of life in patients undergoing bariatric Race/ethnicity
surgery. 23,26 It has also been noted that further study to find Caucasian 50.96%
interventions that increase body satisfaction would be of great African American 18.50%
23
value to the field. In this context, this study aims to determine Hispanic American 10.10%
what factors have the greatest influence on the magnitude of body Asian American
image improvement postbariatric surgery with a particular focus 9.03%
on perioperative antidepressant usage. Prefer not to respond 11.41%
Preoperative BMI Range: 35.87–75.66
Mean: 49.26
MAterIAls And Methods
This study was approved via the institutional review board of an 35–39.99 9.09%
academic tertiary care center. Patients who had been approved 40–49.99 53.25%
for bariatric surgery were consecutively recruited and consented 50–59.99 25.97%
by the attending surgeon of record. Inclusion criteria for the study 60–69.99 7.79%
are patients must be aged 18 years or older with a BMI ≥35 and ≥70 3.90 %
opting to undergo any type of bariatric surgery. There were no
Range: 1.44–30.77
unique factors for exclusion not identified by the inclusion criteria. Postoperative BMI improvement Mean: 15.08
Those who consented to participate in the study completed a
battery of self-administered questionnaires, including a validated <10 16.8%
metric for trending perceived body image (also termed “body 10–19.99 66.23%
esteem”). These questionnaires were administered by office-based 20–29.99 15.58%
psychologists and dieticians at four time intervals: approximately ≥30 1.29%
1 month prior to surgery and then at 3, 6, and 12 months
postoperatively (in tandem with the pre- and postoperative Surgical procedure
outpatient visits). Roux-en-Y gastric bypass 53.65%
The scale that was used to assess trends in body image was the Vertical sleeve gastrectomy 46.35%
Body-Esteem Scale for Adolescents and Adults (BESAA) a commonly Psychiatric medications
used validated metric for assessing body image and confidence in Not on psychiatric medications
both psychological and bariatric surgery literature. 27–29 The BESAA 31.55%
is a 22-item questionnaire with scores of 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 points On psychiatric medications 68.45%
corresponding answers of “never,” “rarely,” “sometimes,” “often,” Antidepressants 57.01%
and “always,” respectively. A higher score on the BESAA indicates Anxiolytic/hypnotic 25.59%
higher overall body esteem and confidence regarding one’s body Stimulant 2.74%
image. The BESAA scores were compiled at each of the collection BMI, body mass index
time points noted earlier and the presurgical score was compared
to the score at the final follow-up appointment. Summary and
descriptive statistics were generated for all patients regarding negative influence on the BESAA trend. The numerical value of the
sociodemographic, surgical, and psychiatric characteristics coefficient indicates the number of average points of influence seen
(Table 1). by that variable (e.g., a positive 4-point coefficient would indicate,
Linear regression models were employed to assess the on average, those with the demographic variable had an average
relationship between the improvement seen in the BESAA scores of four points higher on the BESAA scores than those without the
and the demographic factors listed in the descriptive statistics demographic variable). For nonbinary variables like postoperative
table. Results of the linear regression analysis are displayed as improvement in BMI, the coefficient indicates the influence on the
coefficients where a positive coefficient indicates a positive BESAA score per 1 point of BMI improvement. Levels of significance
influence on the BESAA trend, and a negative coefficient indicates a were assessed using t-test of regression coefficients. p-values less
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 14 Issue 2 (May–August 2021) 127