Page 18 - tmp
P. 18
Diagnostic Lap in NCPA
Table 4: Laparoscopic findings compared with final diagnosis
Final diagnosis
Positive Negative
Laparoscopic findings Frequency Percentage (%) Frequency Percentage (%) p value
Positive 54 98.2 0 0.0
Negative 1 1.8 7 100.0 <0.001
Total 55 100 7 100
Sensitivity Specificity PPV NPV Accuracy
98.2% 100.0% 100.0% 87.5% 98.4%
Table 5: Radiological findings compared with laparoscopic findings
Laparoscopic findings
Positive Negative
Radiological findings Frequency Percentage (%) Frequency Percentage (%) p value
Positive 9 16.7 3 37.5
Negative 45 83.3 5 62.5 0.177
Total 54 100 8 100
Sensitivity Specificity PPV NPV Accuracy
16.7% 62.5% 75.0% 10.0% 22.6%
Table 6: Effect of diagnostic laparoscopy on diagnosis Table 7: Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of laparoscopy in
various study
Diagnosis status Frequency Percentage (%)
Confirmed diagnosis 45 72.58 Study Diagnostic accuracy (%)
Failed in diagnosing 7 11.29 Mehta’s et al. 88
Diagnosed after laparoscopy 6 9.67 Al-Akeely et al. 94
Changed diagnosis 4 6.45 El-Labban et al. 83.3
Total 62 100 Ahmad et al. 85.2
Present study 88.7
lymphadenopathy. Twenty-four subjects out of 88 cases (24.2%)
had altogether new findings, while 64 (72.4%) cases had findings
like the radiological means. Twenty-five out of 64 had new
finding along with previous finding. Therefore, DL enables the
surgeon to visualize surface anatomy of intra-abdominal organs
with greater details better than any other imaging modality.
DL has been used as a diagnostic tool in patients in nonspecific
pain abdomen in numerous studies. However, it is still not a
standard of care for this subset of patients. In our series, 62 (100%)
patients of NCPA were subjected to DL and reached to final
definitive diagnosis in 55 (88.7%) patients, and in 7 (11.3%) patients,
we could not reach to any diagnosis (i.e., normal study). DL could
15
establish diagnosis in 88% cases in Mehta’s series, whereas in the
16
series of Al-Akeely et al., it was 94%. Our series had a diagnostic
14
accuracy of 88.7%. Ahmad et al. could reach to final diagnosis
in 75 of 88 cases of NCPA after DL. This is like the study carried
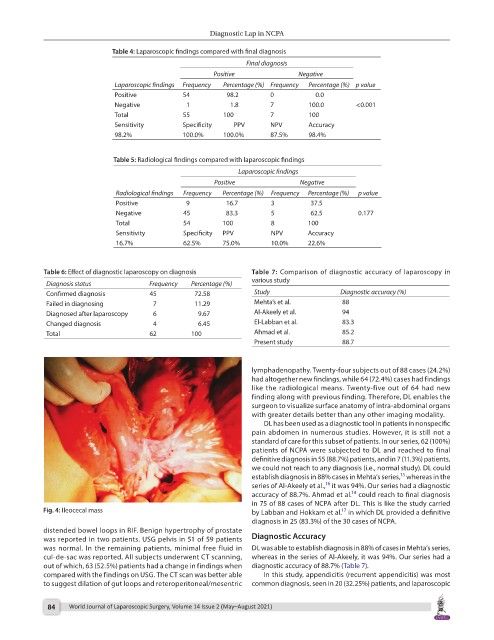
Fig. 4: Ileocecal mass by Labban and Hokkam et al. in which DL provided a definitive
17
diagnosis in 25 (83.3%) of the 30 cases of NCPA.
distended bowel loops in RIF. Benign hypertrophy of prostate
was reported in two patients. USG pelvis in 51 of 59 patients Diagnostic Accuracy
was normal. In the remaining patients, minimal free fluid in DL was able to establish diagnosis in 88% of cases in Mehta’s series,
cul-de-sac was reported. All subjects underwent CT scanning, whereas in the series of Al-Akeely, it was 94%. Our series had a
out of which, 63 (52.5%) patients had a change in findings when diagnostic accuracy of 88.7% (Table 7).
compared with the findings on USG. The CT scan was better able In this study, appendicitis (recurrent appendicitis) was most
to suggest dilation of gut loops and reteroperitoneal/mesentric common diagnosis, seen in 20 (32.25%) patients, and laparoscopic
84 World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 14 Issue 2 (May–August 2021)